数据结构与算法
栈
什么是栈数据结构
栈是一种遵从后进先出(LIFO)last-in-first-out原则的有序集合。新添加的或待删除的元素都保存在栈的 末尾,称作栈顶,另一端就叫栈底。在栈里,新元素都靠近栈顶,旧元素都接近栈底。
实现一个栈
// 栈的创建
class Stack {
constructor() {
// 用数组来存储
this.items = []
}
// 添加一个(或几个)新元素到栈顶
push(val) {
this.items.push(val)
}
// 移除栈顶的元素,同时返回被移除的元素
pop() {
return this.items.pop()
}
//返回栈顶的元素,不对栈做任何修改(这个方法不会移除栈顶的元素,仅仅返 回它)
peek() {
return this.items[this.items.length - 1]
}
// 如果栈里没有任何元素就返回true,否则返回false
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0
}
// 移除栈里的所有元素
clear() {
this.items = []
}
// 返回栈里的元素个数。这个方法和数组的length属性很类似。
size() {
return this.items.length
}
// 辅助方法,它会把栈里的元素都输出到控制台
print() {
console.log(this.items.toString());
}
}
Stack类的使用
在深入了解栈的应用前,我们先来学习如何使用Stack类。
let stack = new Stack();
console.log(stack.isEmpty());
stack.push(1)
stack.push(2)
console.log(stack.peek());
stack.push(11);
console.log(stack.size());
console.log(stack.isEmpty());
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
console.log(stack.size());
stack.print();
打印结果依次如下:
true
2
3
false
1
1
栈数据结构使用场景
十进制转换成任何进制
function divideBy2(decNumber, base) {
let remStack = new Stack(), rem, binaryString = '', digits = '0123456789ABCDEF';
while (decNumber > 0) {
rem = Math.floor(decNumber % base);
remStack.push(rem);
decNumber = Math.floor(decNumber / base);
}
while (!remStack.isEmpty()) {
binaryString += digits[remStack.pop()];
}
return binaryString;
}
console.log(divideBy2(100, 2));
console.log(divideBy2(100, 8));
console.log(divideBy2(100, 16));
队列
什么是队列
队列是遵循FIFO(First In First Out,先进先出,也称为先来先服务)原则的一组有序的项。 队列在尾部添加新元素,并从顶部移除元素。最新添加的元素必须排在队列的末尾
实现一个队列
// 创建Queue类
class Queue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
// 向队列尾部添加一个(或多个)新的项
enqueue(val) {
this.items.push(val);
}
// 移除队列的第一(即排在队列最前面的)项,并返回被移除的元素
dequeue() {
return this.items.shift();
}
// front():返回队列中第一个元素——最先被添加,也将是最先被移除的元素。队列不 做任何变动(不移除元素,只返回元素信息——与Stack类的peek方法非常类似)。
front() {
return this.items[0];
}
// 如果队列中不包含任何元素,返回true,否则返回false
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
// 返回队列包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似。
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 辅助方法
print() {
console.log(this.items.toString());
}
}
Queue的使用
let queue = new Queue();
console.log(queue.isEmpty());
queue.enqueue('John');
queue.enqueue('Jack');
queue.enqueue('Camila');
queue.print();
console.log(queue.size());
console.log(queue.isEmpty());
queue.dequeue();
queue.dequeue();
queue.print();
打印结果如下:
true
John,Jack,Camila
3
false
Camila
优先队列
为啥会有这种队列出现,想下医院的急诊科就会明白。实现一个优先队列,有两种选项:设置优先级,然后在正确的位置添加元素;或者用入列操 作添加元素,然后按照优先级移除它们。在这个示例中,我们将会在正确的位置添加元素,因此 可以对它们使用默认的出列操作:
// 优先队列类
class PriorityQueue {
constructor() {
this.items = [];
}
/**
* 向队列尾部添加一个(或多个)新的项
* @param val 要插入的元素
* @param priority 权重 一般为number数字,
*/
enqueue(val, priority = 0) {
// 如果队列中没有元素,则不管权重,直接插入
if (this.isEmpty) {
this.items.push({ val, priority });
} else {
let added = false;
for (let i = 0; i < this.items.length; i++) {
let items = this.items[i]
if (priority < items[i].priority) {
this.items.splice(i, 0, { val, priority });
added = true;
break
}
}
// 添加元素的priority值大于任何已有的元素,把它添加到队列的末尾就行了
if (!added) {
this.items.push({ val, priority });
}
}
}
// 移除队列的第一(即排在队列最前面的)项,并返回被移除的元素
dequeue() {
return this.items.shift();
}
// front():返回队列中第一个元素——最先被添加,也将是最先被移除的元素。队列不 做任何变动(不移除元素,只返回元素信息——与Stack类的peek方法非常类似)。
front() {
return this.items[0];
}
// 如果队列中不包含任何元素,返回true,否则返回false
isEmpty() {
return this.items.length === 0;
}
// 返回队列包含的元素个数,与数组的length属性类似。
size() {
return this.items.length;
}
// 辅助方法
print() {
console.log(this.items.toString());
}
}
默认的Queue类和PriorityQueue类实现上的区别是,要向PriorityQueue添加元素,需 要创建一个特殊的元素。这个元素包含了要添加到队列的元素(它可以是任意类型) 及其在队列中的优先。我们在这里实现的优先队列称为最小优先队列,因为优先级的值较小的元素被放置在队列最 前面,最大优先队列则与之相反,把优先级的值较大的元素放置在队列最前面,可以根据实际业务场景来实现队列。
循环队列-击鼓传花
function hotPotato(nameList, num) {
let queue = new Queue();
for (let i = 0; i < nameList.length; i++) {
queue.enqueue(nameList[i]);
}
let eliminated = '';
while (queue.size() > 1) {
for (let i = 0; i < num; i++) {
queue.enqueue(queue.dequeue());
}
eliminated = queue.dequeue();
console.log(eliminated + '在击鼓传花游戏中被淘汰。');
}
return queue.dequeue();
}
let names = ['John', 'Jack', 'Camila', 'Ingrid', 'Carl'];
let winner = hotPotato(names, 7);
console.log('胜利者:' + winner)
链表
什么是链表
链表存储有序的元素集合,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的。每个 元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(也称指针或链接)组成。下图展 示了一个链表的结构:
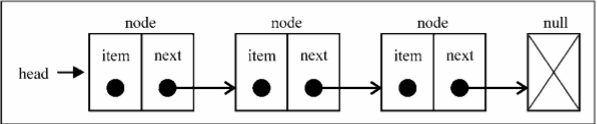
相对于传统的数组,链表的一个好处在于,添加或移除元素的时候不需要移动其他元素。然 而,链表需要使用指针,因此实现链表时需要额外注意。数组的另一个细节是可以直接访问任何 位置的任何元素,而要想访问链表中间的一个元素,需要从起点(表头)开始迭代列表直到找到 所需的元素。
单向链表
单向链表只有一个指针域,在整个节点中数据域用来存储数据元素,指针域用于指向下一个具有相同结构的节点。
实现单向链表类
// 创建链表类
class LinkedList {
constructor() {
this.length = 0; // 存储列表项的数量的length属性
this.head = null; // 存储第一个节点的引用
}
// 向列表尾部添加一个新的项。
append(element) {}
// 向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项。
insert(position, element) {}
// 从列表中移除一项
remove(element) {}
// 返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
indexOf(element) {}
//从列表的特定位置移除一项。
removeAt(position) {}
// 如果链表不包含元素的个数返回true,反之false
isEmpty() {}
// 返回链表包含元素的个数
size() {}
// 重写继承自JavaScript对象默认的 toString方法,让其只输出元素的值
toString() {}
}
向链表尾部追加元素
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null
}
}
借助一个Node类来辅助,表示要加入项,它包含一个element属性,即要添加到列表的元素,以及一个next属性,即指向列表中下一个节点的指针。
append(element) {
// 是把element作为值传入,创建Node项
let node = new Node(element);
// 说明当前列表为空,添加的是第一个元素,直接让head元素指向node元素,下一个node将会自动成为null(Node类的next为null)
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node
}
console.log(this.head);
}
这里实现的是向为空的列表添加一个元素。接下来实现向一个不为空的列表的尾部添加元素。要向列表的尾部添加一个元素,首先需要找到最后一个元素。记住,我们只有第一个元素的 引用,因此需要循环访问列表,直到找到最后一项。为此,我们需要一个指向列表中 current项的变量。循环访问列表时,当current.next元素为null时,我们就知道 已经到达列表尾部了。然后要做的就是让当前(也就是最后一个)元素的next指针指向想要添 加到列表的节点。
// 向列表尾部添加一个新的项。
append(element) {
// 是把element作为值传入,创建Node项
let node = new Node(element);
let current; // 列表中的当前项
// 说明当前列表为空,添加的是第一个元素,直接让head元素指向node元素,下一个node将会自动成为null(Node类的next为null)
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node
// 列表不为空
} else {
current = this.head; // 先让当前项指向第一个元素
// 循环列表,直到找到最后一项
while (current.next) {
current = current.next
}
// 找到最后一项,将其next赋为node,建立链接
current.next = node
}
this.length++; //更新列表的长度
}
从链表中给定位置移除元素
//从列表的特定位置移除一项,返回移除的项
removeAt(position) {
// 校验位置的合法性
if (position > -1 && position < this.length) {
let current = this.head;
let previous; // 前一个元素引用
let index = 0;
// 移除列表中的第一项,head指向列表的第二个元素
if (position == 0) {
this.head = current.next
// 移除不是列表中第一项的
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next
}
// 要从列表中移除当前元素,要做的就是将previous.next和current.next链接起来。这样,当前元素就会被丢弃在计算机内存中,等着被垃圾回收器清除。
// 对于最后一个元素,跳出循环时,current变量将是对列表中最后一个元素 的引用(要移除的元素)。current.next的值将是null(因为它是最后一个元素)
previous.next = current.next
}
this.length--;
return current
} else {
return null
}
}
在任意位置插入一个元素
// 向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项。
insert(position, element) {
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
let previous;
let index = 0;
// 在第一个位置添加
if (position == 0) {
node.next = current;
this.head = node;
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next
}
node.next = current
previous.next = node;
}
this.length++;
return true;
} else {
return false
}
}
实现其他方法
// 返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head;
let index = -1;
while (current) {
index++;
if (element === current.element) {
return index
}
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
// 如果链表不包含元素的个数返回true,反之false
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
// 返回链表包含元素的个数
size() {
return this.length
}
getHead() {
return this.head
}
// 重写继承自JavaScript对象默认的 toString方法,让其只输出元素的值
toString() {
let current = this.head;
let string = '';
while (current) {
string = current.element;
current = current.next;
}
return string
}
双向链表
要在单向链表中找到某个节点的前驱节点,必须从链表的头节点出发依次向后寻找,但是需要Ο(n)时间。为此我们可以扩展单向链表的节点结构,使得通过一个节点的引用,不但能够访问其后续节点,也可以方便的访问其前驱节点。扩展单向链表节点结构的方法是,在单链表节点结构中新增加一个域,该域用于指向节点的直接前驱节点。该链表称为双向链表。单向链表只能从一个方向遍历,双向链表可以从两个方向遍历。
class Node {
constructor(element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null
this.prev = null
}
}
// 创建链表类
class DoublyLinkedList {
constructor() {
this.length = 0; // 存储列表项的数量的length属性
this.head = null; // 存储第一个节点的引用
this.tail = null; // 存储第一个节点的引用
}
// 向列表尾部添加一个新的项。
append(element) {
// 是把element作为值传入,创建Node项
let node = new Node(element);
let current; // 列表中的当前项
// 说明当前列表为空,添加的是第一个元素,直接让head和tail指向node元素
if (this.head === null) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
// 列表不为空
} else {
current = this.tail;
// 找到最后一项,将其next赋为node,建立链接
current.next = node
node.prev = current
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++; //更新列表的长度
}
// 向列表的特定位置插入一个新的项。
insert(position, element) {
if (position >= 0 && position <= this.length) {
let node = new Node(element);
let current = this.head;
let previous;
let index = 0;
// 在第一个位置添加
if (position == 0) {
if (!this.head) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next
}
node.next = current
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous
}
this.length++;
return true;
} else {
return false
}
}
remove(element) {
let index = this.indexOf(element);
return this.removeAt(index);
}
// 返回元素在列表中的索引。如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1
indexOf(element) {
let current = this.head;
let index = -1;
while (current) {
index++;
if (element === current.element) {
return index
}
current = current.next
}
return -1
}
//从列表的特定位置移除一项,返回移除的项
removeAt(position) {
// 校验位置的合法性
if (position > -1 && position < this.length) {
let current = this.head;
let previous; // 前一个元素引用
let index = 0;
// 移除列表中的第一项,head指向列表的第二个元素
if (position == 0) {
this.head = current.next;
if (this.length === 1) {
this.tail = null;
} else {
this.head.prev = null
}
} else if (position === this.length - 1) {// 移除的是最后一项
current = this.tail;
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null
} else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next
}
// 要从列表中移除当前元素,要做的就是将previous.next和current.next链接起来。这样,当前元素就会被丢弃在计算机内存中,等着被垃圾回收器清除。
// 对于最后一个元素,跳出循环时,current变量将是对列表中最后一个元素 的引用(要移除的元素)。current.next的值将是null(因为它是最后一个元素)。
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous
}
this.length--;
return current
} else {
return null
}
}
// 如果链表不包含元素的个数返回true,反之false
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
// 返回链表包含元素的个数
size() {
return this.length
}
}
循环链表
循环链表可以像链表一样只有单向引用,也可以像双向链表一样有双向引用。循环链表和链 表之间唯一的区别在于,最后一个元素指向下一个元素的指针(tail.next)不是引用null, 而是指向第一个元素(head)。
树
什么是树
一个树结构包含一系列存在父子关系的节点。每个节点都有一个父节点(除了顶部的第一个 节点)以及零个或多个子节点
- 位于树顶部的节点叫作根节点
- 树中的每个元素都叫作节点,节点分 为内部节点和外部节点。至少有一个子节点的节点称为内部节点,没有子元素的节点称为外部节点或叶节点
- 一个节点可以有祖先和后代
- 子树由节点和它的后代构成
- 节点的一个属性是深度,节点的深度取决于它的祖先节点的数量
- 树的高度取决于所有节点深度的最大值
二叉树
二叉树中的节点最多只能有两个子节点:一个是左侧子节点,另一个是右侧子节点。这些定 义有助于我们写出更高效的向/从树中插入、查找和删除节点的算法。二叉树在计算机科学中的 应用非常广泛。
二叉搜索树
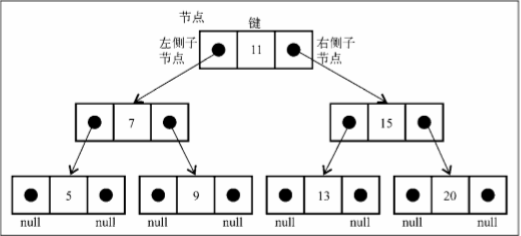
二叉搜索树(BST)是二叉树的一种,但是它只允许你在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值, 在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大(或者等于)的值。
实现BinarySearchTree类
下图展现了二叉搜索树数据结构的组织方式:
树的遍历
树的所有节点有三种方 式:中序、先序和后序。 这里前,中,后都是针对根结点来说的.同时遍历顺序是对访问到的当前结点来判断,这个很重要,理解了就不会再出错了.
前序遍历: 对访问到的每个结点,先访问根结点,然后是左结点,然后是右结点
中序遍历: 对访问到的每个结点,先访问左结点,然后是根结点,然后是右结点
后序遍历: 对访问到的每个结点,先访问左结点,然后是右结点,然后是根结点
中序遍历
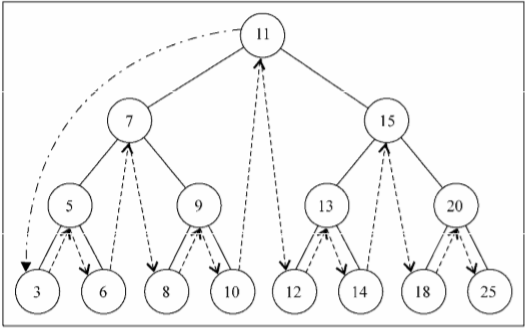
中序遍历是一种以上行顺序访问BST所有节点的遍历方式,也就是以从最小到最大的顺序访 问所有节点。中序遍历的一种应用就是对树进行排序操作。我们来看它的实现
inOrderTraverse(callback) {
function inOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node !== null) {
inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback)
callback(node.key)
inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback)
}
}
inOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback)
}
下面的图描绘了inOrderTraverse方法的访问路径:
inOrderTraverse方法接收一个回调函数作为参数。回调函数用来定义我们对遍历到的每 个节点进行的操作(这也叫作访问者模式)。由于我们在BST中最常实现的算法是递归,这里使用了一个 私有的辅助函数,来接收一个节点和对应的回调函数作为参数。
先序遍历
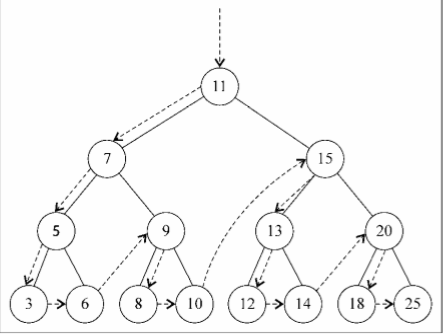
先序遍历是以优先于后代节点的顺序访问每个节点的。先序遍历的一种应用是打印一个结构 化的文档。
preOrderTraverse(callback) {
function preOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node !== null) {
callback(node.key)
preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback)
preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback)
}
}
preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback)
}
下面的图描绘了preOrderTraverse方法的访问路径:
后序遍历
后序遍历则是先访问节点的后代节点,再访问节点本身。后序遍历的一种应用是计算一个目 录和它的子目录中所有文件所占空间的大小。
// 后序遍历 先访问左节点,再访问右节点,最后访问根节点
postOrderTraverse(callback) {
function postOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node !== null) {
postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback)
postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback)
callback(node.key)
}
}
postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback)
}
下面的图描绘了postOrderTraverse方法的访问路径:
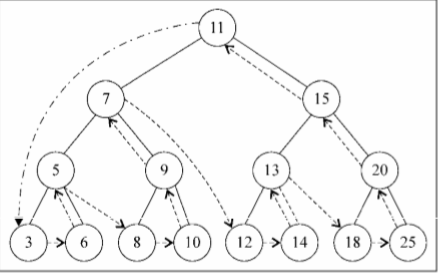
搜索树中的值
在树中,有三种经常执行的搜索类型: 最大值,最小值,特定值。
树最后一层最左侧的节点,这是这棵树中最小的键。树最右端的节点(同样是树的最后一层),这是这棵树中最大的 键。这条信息在我们实现搜索树节点的最小值和最大值的方法时能给予我们很大的帮助。
最小值
// 获取树的最小键
min() {
function minNode(node) {
if (node) {
while (node && node.left !== null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node.key
}
return null
}
return minNode(this.root);
}
最大值
同理,可以实现max方法:
// 获取树的最大键
max() {
function maxNode(node) {
if (node) {
while (node && node.right !== null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node.key
}
return null
}
return maxNode(this.root);
}
搜索一个特定的值
// 搜索特定的值
search(key) {
function searchNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (key < node.key) {
return searchNode(node.left, key)
} else if (key > node.key) {
return searchNode(node.right, key)
} else {
return true
}
}
return searchNode(this.root, key);
}
移除一个节点
- 在树中找到要移除的节点。
- 要找的键比当前节点小,就沿着树的左边找到下一个节点。
- 要找的键比当前节点大,就沿着树的右边找到下一个节点。
- 找到需要移除的节点之后需要处理三种情况。
- 移除一个叶节点
- 移除一个有左侧或者右侧的节点
- 移除有两个子节点的节点
- 移除有两个节点的需要以下4部操作
- 找到需要移除的节点之后,要找到它右边子树中最小的节点
- 用右侧子树最小节点的节点更新这个节点的值
- 继续把右侧子树中总的最小节点移除
- 向它的父节点返回更新后节点的引用
// 删除某一个节点
remove(key) {
function findMinNode(node) {
if (node) {
while (node && node.left !== null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node
}
return null
}
function removeNode(node, key) {
// 检验传入的节点
if (node == null) return null;
if (key < node.key) { // 如果要找的键比当前节点的值小,就沿着树的左边找到下一个节点
node.left = removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
} else if (key > node.key) { // 如果要找的键比当前节点的值大,那么就沿着树的右边找到下一个节点
node.right = removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
} else { // 键等于node.key
// 第一种情况——一个叶节点
if (node.left == null && node.left == null) {
node = null;
return node
}
// 第二种情况——一个只有一个子节点的节点
if (node.left == null) {
node = node.right;
return node;
} else if (node.right == null) {
node = node.left;
return node;
}
//第三种情况——一个有两个子节点的节点
let aux = findMinNode(node.right);
node.key = aux.key;
node.right = removeNode(node.right, aux.key);
return node
}
}
this.root = removeNode(this.root, key)
}
完整的代码
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// 创建BinarySearchTree类
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null; // 根节点
}
// 向树中插入一个键
insert(key) {
// 创建用来表示新节点的Node类实例,它的左指针和右指针的值会由构造函数自动设置为null
let node = new Node(key);
// 说明插入的是根节点
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = node;
} else {
insertNode(this.root, node)
}
function insertNode(node, newNode) {
// 如果新节点的键小于当前节点的键
if (newNode.key < node.key) {
if (node.left === null) {
node.left = newNode
} else {
insertNode(node.left, newNode)
}
} else {
if (node.right === null) {
node.right = newNode
} else {
insertNode(node.right, newNode)
}
}
}
}
// 中序遍历 先访问左节点,再访问根节点,最后访问右节点
inOrderTraverse(callback) {
function inOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node !== null) {
inOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback)
callback(node.key)
inOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback)
}
}
inOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback)
}
// 先序遍历 先访问根节点,再访问左节点,最后访问右节点
preOrderTraverse(callback) {
function preOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node !== null) {
callback(node.key)
preOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback)
preOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback)
}
}
preOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback)
}
// 后序遍历 先访问左节点,再访问右节点,最后访问根节点
postOrderTraverse(callback) {
function postOrderTraverseNode(node, callback) {
if (node !== null) {
postOrderTraverseNode(node.left, callback)
postOrderTraverseNode(node.right, callback)
callback(node.key)
}
}
postOrderTraverseNode(this.root, callback)
}
// 获取树的最小键
min() {
function minNode(node) {
if (node) {
while (node && node.left !== null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node.key
}
return null
}
return minNode(this.root);
}
// 获取树的最大键
max() {
function maxNode(node) {
if (node) {
while (node && node.right !== null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node.key
}
return null
}
return maxNode(this.root);
}
// 搜索特定的值
search(key) {
function searchNode(node, key) {
if (node == null) return false;
if (key < node.key) {
return searchNode(node.left, key)
} else if (key > node.key) {
return searchNode(node.right, key)
} else {
return true
}
}
return searchNode(this.root, key);
}
// 删除某一个节点
remove(key) {
function findMinNode(node) {
if (node) {
while (node && node.left !== null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node
}
return null
}
function removeNode(node, key) {
// 检验传入的节点
if (node == null) return null;
if (key < node.key) { // 如果要找的键比当前节点的值小,就沿着树的左边找到下一个节点
node.left = removeNode(node.left, key);
return node;
} else if (key > node.key) { // 如果要找的键比当前节点的值大,那么就沿着树的右边找到下一个节点
node.right = removeNode(node.right, key);
return node;
} else { // 键等于node.key
// 第一种情况——一个叶节点
if (node.left == null && node.left == null) {
node = null;
return node
}
// 第二种情况——一个只有一个子节点的节点
if (node.left == null) {
node = node.right;
return node;
} else if (node.right == null) {
node = node.left;
return node;
}
//第三种情况——一个有两个子节点的节点
let aux = findMinNode(node.right);
node.key = aux.key;
node.right = removeNode(node.right, aux.key);
return node
}
}
this.root = removeNode(this.root, key)
}
}






















 825
825











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








