多线程编程
一、基本概念
线程与进程:
进程是程序一次完整的从代码加载、执行到执行完毕的完整过程。
线程是比进程更小的执行单位,是在进程的基础上进行进一步划分。多线程是指一个进程在执行过程中可以产生多个更小的程序单元(即线程),这些线程可以同时存在、同时运行。一个进程可能包含多个同时执行的线程。
我们需要一个多任务操作系统,可以同时支持多个进程的执行。 进程比线程开销更大,因此在同类多任务计算时, 采用多线程 。由于速度差以及多处理器问题,使多线程比单线程执行效率更高
二、线程的创建
(一)实现Runable接口
实现 Runnable 接口的类。该类然后实现 run 方法。然后可以分配该类的实例,在创建 Thread 时作为一个参数来传递并启动。

public class SimpleThread1 implements Runnable{
private int countDown = 5;
private int threadNumber;
private static int threadCount = 0;
public SimpleThread1(){
threadNumber = ++threadCount;
System.out.println("Making " + threadNumber);
}
public void run(){ //线程体:每个线程执行countdown的递减
while(true){
System.out.println("Thread " +
threadNumber + "(" + countDown + ")");
if(--countDown == 0) return;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
Thread thr = new Thread(new SimpleThread1());//创建线程 注意!!仍需包装在Thread线程类里
thr.start();//启动线程
}
System.out.println("All Threads Started");
}
}
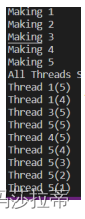
可以看到各个线程之间的竞争关系,处于无序状态
(二)继承类Thread

Thread是Runnable的子类,Thread类的run方法是调用的Runnable的方法
public class mythread extends Thread
public class SimpleThread extends Thread {
private int countDown = 5;
private int threadNumber;
private static int threadCount = 0;
public SimpleThread(){
threadNumber = ++threadCount;
System.out.println("Making " + threadNumber);
}
public void run(){
while(true){
System.out.println("Thread " +
threadNumber + "(" + countDown + ")");
if(--countDown == 0) return;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
new SimpleThread().start();//这里直接调用Thread的继承类
System.out.println("All Threads Started");
}
}
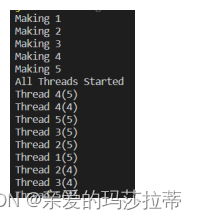
创建并启动线程 ,上面两种方式创建线程时会略有不同 ,启动线程均用start() 方法
每个线程都有一个标识名,多个线程可以同名。如果线程创建时没有指定标识名,就会为其生成一个新名称
– run方法是运行线程的主体,启动线程时,会直接被调用
联系与区别 :

Thread是Runnable的子类,Thread类的run方法是调用的Runnable的方法
继承Thread类不适合资源共享,实现Runnab接口,适合资源共享
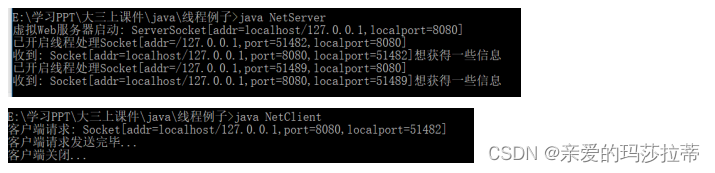
网络多线程(TCP):
(一个人守门,然后安排多个人接待,把Socket作为入口参数传给新的线程)
/*服务器端*/
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class NetServer
{
public static final int PORT =8080;
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception
{
ServerSocket s = null;
try{
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
s =new ServerSocket(PORT,10,addr);
System.out.println("虚拟Web服务器启动: "+s);
while(true){
Socket socket =s.accept();
SocketHandler sh = new SocketHandler(socket);
sh.start();
System.out.println("已开启线程处理"+socket);
}
}catch(Exception e){
System.out.println(e);
s.close();
}
}
}
/*客户端*/
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
public class NetClient
{
public static final int PORT =8080;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException
{
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
Socket socket =new Socket(addr,PORT);
try{
System.out.println("客户端请求: "+socket);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream())) ;
PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
socket.getOutputStream())),true);
out.println(socket+"想获得一些信息");
//byte[] input = new byte[20];
//System.in.read(input);
out.println("END");
String str;
System.out.println("客户端请求发送完毕...");
//while((str = in.readLine()).length()!=0){
//System.out.println("接收: "+in.readLine());
//}
}finally{
System.out.println("客户端关闭...");
socket.close();
}
}
}
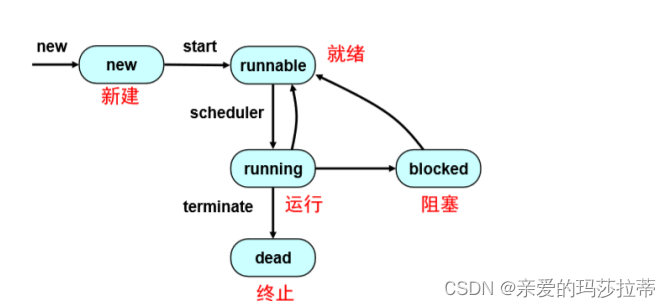
三、线程状态
四、控制线程的几种方式
• 线程睡眠 – sleep()方法,是静态方法,Thread.sleep()是让当前线程睡眠(异常爆发可以唤醒,大程序多使用sleep节能)

• 中断线程 – interrupt()方法,当线程被阻塞(sleep, wait)时,也有可 能被通知处理一些内容,通过InterruptedException 异 常来实现,注意:中断≠终止
import java.util.*;
public class TestInterrupt {
public static void main(String[] args){
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
try{
Thread.sleep(10000);//当前线程main线程睡眠10秒
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {}
thread.interrupt();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread { //线程体
boolean flag = true;
public void run(){
while(flag){
System.out.println("==="+new Date()+"===");
try {
sleep(1000);//线程内部,MyThread线程睡眠1秒
}catch (InterruptedException e){
System.out.println(e);
return;
}
}
}
}
10秒后主程序线程的醒来会打断类里面的线程(上面的日期一秒出来一个说明类线程在一秒睡次觉)
• 停止线程 – stop()方法,该方法已被弃用,因为会导致无法预测的 情况
替代停止方法是使用boolean 标志位
public class TestThread {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Runner4 r = new Runner4();
Thread t = new Thread(r);
t.start();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
if (i % 10000 == 0 & i > 0)
System.out.println("in thread main i=" + i);
}
System.out.println("Thread main is over");
r.shutDown();
// t.stop();
}
}
class Runner4 implements Runnable {
private boolean flag = true;
public void run() {
int i = 0;
while (flag == true) {
System.out.print(" " + i++);
}
}
public void shutDown() {
flag = false;
}
}

主线程执行飞快,子线程一次次循环比较慢
**• 主动让出 ** – yield()方法,主动放弃执行的时间片

public class TestYield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread3 t1 = new MyThread3("t1");
MyThread3 t2 = new MyThread3("t2");
t1.start(); t2.start();
}
}
class MyThread3 extends Thread {
MyThread3(String s){super(s);}
public void run(){
for(int i =1;i<=100;i++){
System.out.println(getName()+": "+i);
if(i%10==0){
yield();
}
}
}
}

本来是在抢,然后到10的倍数就让给对方
(操作线程的主要方法在Thread类里)
五、线程优先级
每个线程都有优先级,调度器根据优先级 决定调度顺序 • 优先级从1-10,缺省值为5,通过 setPriority (int priority)来设定 Thread类

| 定义 | 描述 | 常量 |
|---|---|---|
| public static final int MIN_PRIORITY | 最低优先级 | 1 |
| public static final int NORM_PRIORITY | 中等优先级(默认) | 5 |
| public static final int MAX_PRIORITY | 最高优先级 | 10 |
public class TestPriority {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new T1());
Thread t2 = new Thread(new T2());
t1.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY + 3);//可以直接设数字
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
class T1 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println("T1: " + i);
}
}
}
class T2 implements Runnable {
public void run() {
for(int i=0; i<10; i++) {
System.out.println("------T2: " + i);
}
}
}

优先运行T1,再运行T2
六、互斥与锁
存在多个线程同时访问一个对象的情况, 如果不进行有效互斥,则会出现混乱
中关键的代码段需要加锁,防止 顺序执行过程中被其它线程“插入”
synchronized :关键字,不属于包和类

public class TestSync implements Runnable {
Timer timer = new Timer();
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestSync test = new TestSync();
Thread t1 = new Thread(test);
Thread t2 = new Thread(test);
t1.setName("t1");
t2.setName("t2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
public void run(){
timer.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());//取当前进程的名字
}
}
class Timer{
private static int num = 0;
public void add(String name){ //给方法加锁
//synchronized (this) {
num ++;
try {Thread.sleep(100);}
catch (InterruptedException e) {}
System.out.println(name+", 你是第"+num+"个使用timer的线程");
//}
}
}

不加锁时:T1的顺序执行流程会被T2插入,导致T2也会使得NUM’加一,最后t1显示的结果也会是第二次调用

加锁后:T1能够完整地执行完代码,可以显示第一个调用(T1,T2谁先跑,要看谁抢得赢)






















 630
630











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








