介绍:
Session,又被称为会话。是指有始有终的一系列动作/消息。
用户请求访问某个网站域名时,如果该用户还没有会话,则 Web 服务器将自动创建一个 Session 对象,存放在服务端,此对象的唯一标识放入cookie中。这样,当用户在应用程序的 Web 页之间跳转时,存储在 Session 对象中的变量将不会丢失,而是在整个用户会话中一直存在下去。但是session对象是有生命周期的,当会话过期或被放弃后,服务器将终止该会话。
Session 对象存储特定用户会话所需的属性及配置信息。最常见的一个用法就是存储用户的首选项。例如,用户登录之后的登录信息,就可以将该信息存储在 Session 对象中。
在开发工程中,常用到的是javax.servlet.http.HttpSession。
cookie与session:
我们都知道,HTTP协议本身是无状态的,客户端只需要简单的向服务器发送请求,无论是客户端还是服务器都没有必要纪录彼此过去的行为,每一次请求之间都是独立的。
但是在后来发展应用中,需要客户端和服务端保持状态。这样cookie就产生了,其中cookie的作用就是为了解决HTTP协议无状态的缺陷所作出的努力。至于后来出现的session机制则是又一种在客户端与服务器之间保持状态的解决方案。cookie就是在客户端保持状态,session是在服务端保持状态,但是又是借助客户端的,所以在使用过程中,session的唯一标识常保持在cookie中的。一般取名JSESSIONID=唯一标识(可以动过UUID方式产生)。考虑到实际情况中,cookie在客户端被禁用了,这时候可以直接通过请求参数方式传入。
因为session的唯一标识在cookie当中,跟随着cookie的生命周期。一般cookie的默认生命周期是浏览器关闭结束,所以session在浏览器关闭时也当做结束。但是,只要服务端session还在,通过相同的session唯一标示依然可以保持状态。
前面说过,session保持在服务端,当大量请求时,session就会占用大量内存,所以在会给session设置个过期时间,释放空间。
httpsession:
httpSession是java提供的一个接口。提供了一些对session的操作方法:
- public String getId(); //获取session的唯一标识
- public long getLastAccessedTime(); //获取最后的请求过来的时间(毫秒)
- public ServletContext getServletContext();//获取session所属的上下文
- public void setMaxInactiveInterval(int interval);//设置有效期(秒)
- public Object getAttribute(String name); //获取session中存放的对象
- public Enumeration getAttributeNames(); //获取所有存放对象
- public void setAttribute(String name, Object value); //存放对象到session中。如果放入的对象为null,效果跟removeAttribute()一致。
- public void removeAttribute(String name);//移出session中的对象
- public void invalidate(); //无效session
public boolean isNew(); //判断客户端是不是支持session的。如果客户端不支持cookie,每次请求都会创建个新的session。
一般情况下,session都是存储在内存里,当服务器进程被停止或者重启的时候,内存里的session也会被清空,如果设置了session的持久化特性,服务器就会把session保存到硬盘上,当服务器进程重新启动或这些信息将能够被再次使用。
文章开头,当请求过来时,没有就创建。其实严格的来说,并非这样的,实际上是调用了HttpServletRequest中的public HttpSession getSession(boolean create);实现时才获取出来session。
我们先来看下源码中这个方法的说明:
*返回此请求的关联当前httpSession,如果没有,当create设置为true时,就会创建个新的session;
如果create为false,同时请求request没有有效的httpSession,则就会返回null;*
我们可以这样测试:创建两个页面,一个是jsp,一个是html。jsp本质上就是一个servlet,参与服务交互,SP文件在编译成Servlet时将会自动加上这样一条语句HttpSession session = HttpServletRequest.getSession(true);这也是JSP中隐含的session对象的来历。html是个静态页面,与服务器没有啥交互。
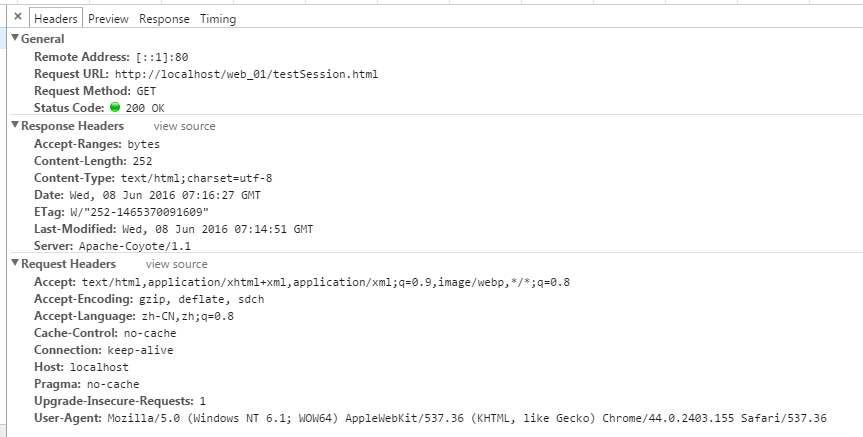
http://localhost/web_01/testSession.html 请求后,可以看出返回response中没有session。
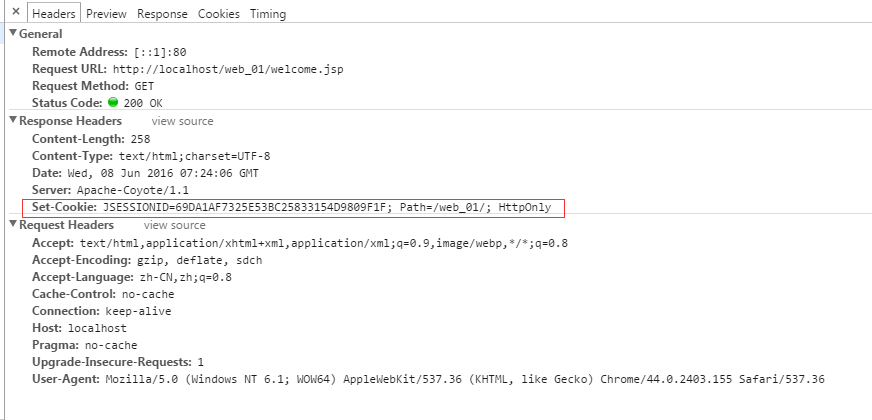
http://localhost/web_01/welcome.jsp 请求后,可以看出有session了。
我们也是可以控制不创建session。在webcome.jsp页面上添加:
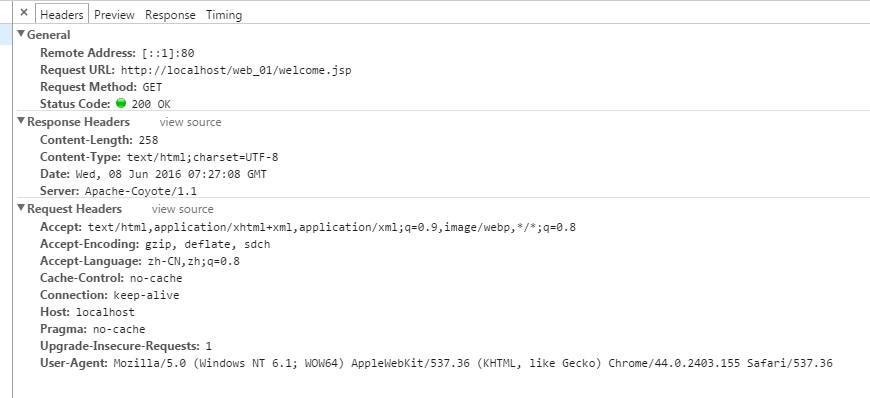
<%@ page session="false" %> 设置session为false时,关闭session。再次请求可以看到,没有看到session了。
我们可以深入源码中探查:
新创建个jsp页面error.jsp,这个session默认是打开的。请求welcome.jsp和error.jsp页面后,在tomcat中查看所生成的对应servlet文件。生成的servlet文件在tomcat下面的 work\Catalina\localhost\web_01\org\apache\jsp文件夹中。
首先看到error.jsp生成的servlet文件error_jsp.java:
package org.apache.jsp;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
import javax.servlet.jsp.*;
public final class error_jsp extends org.apache.jasper.runtime.HttpJspBase
implements org.apache.jasper.runtime.JspSourceDependent {
private static final javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory _jspxFactory =
javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
//其他代码省略
**********
public void _jspService(final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest request, final javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse response)
throws java.io.IOException, javax.servlet.ServletException {
final javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext pageContext;
//注意:这里是HttpSession
javax.servlet.http.HttpSession session = null;
final javax.servlet.ServletContext application;
final javax.servlet.ServletConfig config;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter out = null;
final java.lang.Object page = this;
javax.servlet.jsp.JspWriter _jspx_out = null;
javax.servlet.jsp.PageContext _jspx_page_context = null;
try {
response.setContentType("text/html; charset=UTF-8");
pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response,
null, true, 8192, true);
_jspx_page_context = pageContext;
application = pageContext.getServletContext();
config = pageContext.getServletConfig();
//从页面上下文中获取session
session = pageContext.getSession();
out = pageContext.getOut();
_jspx_out = out;
//省略页面渲染代码
} catch (java.lang.Throwable t) {
//省略异常处理代码
} finally {
_jspxFactory.releasePageContext(_jspx_page_context);
}
}
}代码中可以看到HttpSession是从PageContext中获取。注意,这里的pageContext所属package为javax.servlet.jsp下面,此所属jar在tomcat本身的lib文件jsp-api.jar中。
这个pageContext是个抽象类,代码中pageContext = _jspxFactory.getPageContext(this, request, response, null, true, 8192, true);是个抽象类赋上具体的实现,再通过代码:
private static final javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory _jspxFactory = 定位到JspFactory类。进入看下源代码:
javax.servlet.jsp.JspFactory.getDefaultFactory();
//***********
先省略,后续补上。
//*********
当session关闭时,web.jsp的servlet文件中就没有看到HttpSession的相关内容。
当session被调用invalidate()方法时,或过期时就会终止。
分布式环境下的session:
因为session是存在服务器上,当应用集群时就成为一个问题。请求同一个网站,前一个请求到A服务器上,获取session,保持在A服务器上,但是下一个请求可能会分配到B服务器上,此时就识别不了session了。
一般来说有几种解决方法:
1:服务器直接同步session:集群中的服务器相互同步session,但是问题不少。首先实时性不好保证,其次同步的次数随着服务器的数量二指数级别增加,所以在实际中很少用到。
2:对请求进行筛选处理:判断请求的IP,给分配到固定的服务器上,达到同一个IP请求始终访问同一个服务器。但是依然问题不少:请求IP解析匹配的开销不少;如果某个服务器挂掉了,会导致访问这个请求失败;削弱了负载均衡的能力,会导致某些服务器负载很高,而某些却空闲;动态增减服务器需要修改ip的分配,这回增减很多难度。
3:使用缓存:让集群的session都放入同一个缓存中,与服务器脱离依赖。现实中常用这样的方式。不过这样缓存就会成为一个瓶颈,不过可以考虑对缓存进行集群来解决。
缓存session实例:
首先配置redis相关:
mvn包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>1.7.1.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>2.8.1</version>
</dependency>xml配置(使用的是spring-context-4.2.xsd):
<context:property-placeholder location="config/redis.properties"/>
<bean id="jedisPoolConfig" class="redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig">
<!-- 池中可借的最大数 -->
<property name="maxTotal" value="50" />
<!-- 允许池中空闲的最大连接数 -->
<property name="maxIdle" value="10" />
<!-- 允许池中空闲的最小连接数 -->
<property name="minIdle" value="2" />
<!-- 获取连接最大等待时间(毫秒) -->
<property name="maxWaitMillis" value="12000" />
<!-- 当maxActive到达最大数,获取连接时的操作 是否阻塞等待 -->
<property name="blockWhenExhausted" value="true" />
<!-- 在获取连接时,是否验证有效性 -->
<property name="testOnBorrow" value="true" />
<!-- 在归还连接时,是否验证有效性 -->
<property name="testOnReturn" value="true" />
<!-- 当连接空闲时,是否验证有效性 -->
<property name="testWhileIdle" value="true" />
<!-- 设定间隔没过多少毫秒进行一次后台连接清理的行动 -->
<property name="timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis" value="1800000" />
<!-- 每次检查的连接数 -->
<property name="numTestsPerEvictionRun" value="5" />
</bean>
<bean id="redisFactory" class="org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory">
<property name="poolConfig" ref="jedisPoolConfig"></property>
<property name="hostName" value="${redis.host}"></property>
<property name="port" value="${redis.port}"></property>
<property name="timeout" value="${redis.timeout}"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="redisTemplate" class="org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate">
<property name="connectionFactory" ref="redisFactory" />
<property name="keySerializer">
<bean class="org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer" />
</property>
</bean>自定义session类:
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import com.zcl.session.util.SessionManager;
/**
* 自定义Session类
*
*/
public class SystemSession implements Serializable {
/**
*
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 3596476624020390228L;
/**
* session数据存储map
*/
private Map<String,Object> sessionData = new HashMap<String,Object>();
/**
* sessionId session标识
*/
private String sessionId = null;
public String getSessionId() {
return sessionId;
}
public void setSessionId(String sessionId) {
this.sessionId = sessionId;
}
public Object getAttribute(String name){
Object value = sessionData.get(name);
return value;
}
public void setAttribute(String name,Object value){
sessionData.put(name, value);
SessionManager.updateSession(this.sessionId, this);
}
public void removeAttribute(String name){
sessionData.remove(name);
SessionManager.updateSession(this.sessionId, this);
}
public void removeAllAttribute(){
sessionData.clear();
SessionManager.updateSession(this.sessionId, this);
}
public void disable(){
SessionManager.deleteSession(this.sessionId);
}
public boolean hasAttributeName(String name){
return sessionData.containsKey(name);
}
public Set<String> getAttributeNames(){
return sessionData.keySet();
}
public Map<String, Object> getSessionData() {
return sessionData;
}
public void setSessionData(Map<String, Object> sessionData) {
this.sessionData = sessionData;
}
}
session管理类:
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import com.zcl.constants.Constants;
import com.zcl.session.bean.SystemSession;
import com.zcl.util.CookieUtil;
import com.zcl.util.SpringUtils;
import com.zcl.util.UUIDUtils;
/**
* 自定义Session的工具类
*
*
*/
public class SessionManager {
private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(SessionManager.class);
/**
* 从request中获取sessionKey的值
*
* @Title: getSessionIdFromRequest
* @Description: TODO
* @param request
* @param sessionKey
* @return
*/
public static String getSessionIdFromRequest(HttpServletRequest request, String sessionKey) {
String sessionId = null;
// 请求参数 中获取session_id
if (StringUtils.isBlank(sessionId)) {
sessionId = request.getParameter(sessionKey);
}
// 请求头 中获取session_id
if (StringUtils.isBlank(sessionId)) {
sessionId = request.getHeader(sessionKey);
}
// 从cookie中获取session_id
Cookie cookie = CookieUtil.getCookieByName(request, sessionKey);
if (cookie != null && StringUtils.isBlank(sessionId)) {
sessionId = cookie.getValue();
}
// 从request参数中获取
if (StringUtils.isBlank(sessionId))
sessionId = (String) request.getAttribute(sessionKey + "_attr");
return sessionId;
}
/**
* 获取一个session
*
* @param request
* @param response
* @return
*/
public static SystemSession createSession(String sessionKey, String sessionId, HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response) {
if (StringUtils.isBlank(sessionKey))
return null;
if (StringUtils.isBlank(sessionId))
sessionId = UUIDUtils.generateSessionKey();
/*
* sessionId保持入cookie中
*/
response.setHeader("P3P","CP='CP=CAO PSA OUR'");
CookieUtil.addCookie(request, response, sessionKey, sessionId, null);
//现实中考虑到这里创建session后,后续就要立即使用,之后放在request的attribute中的。
request.setAttribute(sessionKey+"_attr", sessionId);
/*
* 新建session.保存入redis
*/
SystemSession session = new SystemSession();
session.setSessionId(sessionId);
RedisTemplate<String, SystemSession> redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(sessionId, session);
redisTemplate.expire(sessionId, Constants.APP_SESSION_TIMEOUT, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return session;
}
/**
* 根据sessionId从redis中获取对应session信息
*
* @Title: getSession
* @Description: TODO
* @param sessionId
* @return
*/
public static SystemSession getSessionFromRedis(String sessionId) {
SystemSession session = null;
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(sessionId)) {
RedisTemplate<String, SystemSession> redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
session = (SystemSession) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(sessionId);
}
return session;
}
/**
* 通过uuid生成sessionID
*
* @return
*/
public static String generateSessionKey() {
String sessionKey = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
return sessionKey.replace("-", "");
}
/**
* 更新session数据内容
*
* @param sessionKey
* @param session
*/
public static void updateSession(String sessionKey, SystemSession session) {
setSessionTimeout(sessionKey, session);
}
/**
* 删除session,使其失效
*
* @param sessionKey
*/
public static void deleteSession(String sessionKey) {
RedisTemplate<String, SystemSession> redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.delete(sessionKey);
}
public static RedisTemplate<String, SystemSession> getRedisTemplate() {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
RedisTemplate<String, SystemSession> redisTemplate = (RedisTemplate<String, SystemSession>) SpringUtils
.getBeanByName("redisTemplate");
return redisTemplate;
}
/**
* 设置Session超时时间
*
* @return
*/
private static void setSessionTimeout(String sessionKey, SystemSession session) {
long sessionTimeout = Constants.APP_SESSION_TIMEOUT;
RedisTemplate<String, SystemSession> redisTemplate = getRedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(sessionKey, session);
redisTemplate.expire(sessionKey, sessionTimeout, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
}在管理方法中获取redisTemplate对象是通过SpringUtils的公共方法
SpringUtils方法:
import org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
public class SpringUtils {
private static WebApplicationContext webAppContext = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
public static Object getBeanByName(String beanName) {
return webAppContext.getBean(beanName);
}
public static Object getBeanByClass(Class<?> className) {
return webAppContext.getBean(className);
}
}以上基本上搭建好了一个自定义的session。然后在模拟session的生产和使用情况。通过Filter或者Interceptor的方式:
SessionFilter方法:
import java.io.IOException;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import com.zcl.constants.Constants;
import com.zcl.session.bean.SystemSession;
import com.zcl.session.util.SessionManager;
public class SessionFilter implements Filter {
private boolean openFlag = false;
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
String openFlagStr = filterConfig.getInitParameter("openFlag");
openFlag = StringUtils.equals(openFlagStr, "true");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(openFlag) {
SystemSession session = null;
//从请求从获取sessionId
String sessionId = SessionManager.getSessionIdFromRequest((HttpServletRequest)request, Constants.SESSION_KEY);
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(sessionId)) {
//判断此sessionId在redis中是否还存在
session = SessionManager.getSessionFromRedis(sessionId);
}
//不存在,则创建新的
if(session == null) {
session = SessionManager.createSession(Constants.SESSION_KEY, sessionId,
(HttpServletRequest)request, (HttpServletResponse)response);
}
request.setAttribute(Constants.SESSION_KEY, session);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}然后在web.xml中配置:
<filter>
<filter-name>sessionFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.zcl.filter.SessionFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>openFlag</param-name>
<param-value>true</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>sessionFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>*.htm</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>此个filter应放在最先的位置。
在使用的地方,直接从httpServletRequest中获取即可
public SystemSession getSystemSession(HttpServletRequest request) {
return (SystemSession)request.getAttribute(Constants.SESSION_KEY_USER);
}上门是使用的filter过滤器方式,下面修改成拦截器Interceptor方式,同时加上登录之后才能访问的地址过滤处理:
SecurityInterceptor
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
import com.zcl.constants.Constants;
import com.zcl.session.bean.SystemSession;
import com.zcl.session.util.SessionManager;
import com.zcl.util.CookieUtil;
import com.zcl.util.JSEscape;
import com.zcl.util.PropertyUtils;
/**
* 判断用户权限,未登录用户跳转到登录页面
*
* @ClassName: SecurityInterceptor
* @Description: TODO
* @date May 5, 2016 2:53:34 PM
*
*
*/
public class SecurityInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
// 需要安全验证的 URL
private List<String> includedUrls;
// 不需要安全过滤的 URL
private List<String> excludedUrls;
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler,
ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView);
}
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
request.setAttribute("mid", PropertyUtils.getProperty("MLTrackerz_MID"));
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI();
//获取session信息
SystemSession session = null;
String sessionId = SessionManager.getSessionIdFromRequest(request, Constants.SESSION_KEY);
if(sessionId != null){
session = SessionManager.getSessionFromRedis(sessionId);
}
if (session == null) {
session = SessionManager.createSession(Constants.SESSION_KEY, sessionId, request, response);
}
request.setAttribute(Constants.SESSION_KEY, session);
/*
* 需要登录才能访问url地址过滤
*/
boolean mustLogin = false;
if (includedUrls != null && includedUrls.size() > 0) {
for (String url : includedUrls) {
// 请求地址匹配到 includedUrls里面的任何一个地址,就要求登录
if (requestUri.matches(url)) {
mustLogin = true;
break;
}
}
// 请求地址没有匹配到 includedUrls里面的任何一个地址
if (!mustLogin) {
return true;
}
} else if (excludedUrls != null && excludedUrls.size() > 0) {
for (String url : excludedUrls) {
// 请求地址匹配到 excludedUrls里面地址,可以通过拦截器,不需要登录
if (requestUri.matches(url)) {
return true;
}
}
}
//未登录时,跳到登录界面
if (session == null
|| session.getAttribute(Constants.LOGIN_USER_KEY) == null) {
// 记录登录前页面
StringBuffer beforeLoginPage = request.getRequestURL();
//参数
if(StringUtils.isNotBlank(request.getQueryString())){
beforeLoginPage.append("?").append(request.getQueryString());
}
// 只记录get请求
if (request.getMethod().equalsIgnoreCase(
RequestMethod.GET.toString())
&& beforeLoginPage.toString().indexOf("logout") == -1) {
CookieUtil.addCookie(request, response,
Constants.BEFORE_PAGE, JSEscape.escape(beforeLoginPage.toString()), null);
}
response.sendRedirect(request.getContextPath() + "/tologin");
return false;
}
return super.preHandle(request, response, handler);
}
public void setExcludedUrls(List<String> excludedUrls) {
this.excludedUrls = excludedUrls;
}
public void setIncludedUrls(List<String> includedUrls) {
this.includedUrls = includedUrls;
}
}这时候context.xml中的配置要变成interceptor的方式了:
<bean id="securityInterceptor" class="com.zcl.interceptor.SecurityInterceptor">
<property name="excludedUrls">
<list>
<value>/tologin.htm</value>
<value>/loginout.htm</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="includedUrls">
<list>
<value>/myaddress.htm</value>
<value>/mycredit.htm</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<mvc:interceptors>
<!-- session/登录访问地址过滤处理 -->
<mvc:interceptor>
<mvc:mapping path="/*"/>
<mvc:exclude-mapping path="/resource/**"/>
<ref bean="securityInterceptor"/>
</mvc:interceptor>
</mvc:interceptors>然后我们在controller中使用:
@RequestMapping(value={"/","index.htm"})
public ModelAndView index(HttpServletRequest request, ModelAndView mav) {
SystemSession session = (SystemSession)request.getAttribute(Constants.SESSION_KEY);
String userName = (String) session.getAttribute("userName");
if(StringUtils.isBlank(userName)) {
System.out.println("setUserName");
session.setAttribute("userName", "zcl");
}
System.out.println("getUserName:" + userName);
mav.setViewName("index");
return mav;
}结果符合预期:
第一次请求时userName为NULL;第二次时为”zcl”。表示session唯一,同时放入session中的值也是跟随着用户的。
以上是我们单独构建的session处理,其实spring也提供了相关的封装,spring-session中已经封装了类似的处理。
springSession
观察上面我们的session处理过程,可以看出有两部分重点:
一是session怎样定义?session是个怎样的结果。
二是session怎样存放?因为在分布式环境下,session要采取啥方式存放;
三是session怎样与Request关联?因为每次请求中,都涉及到session的。
在上面的session构建中,通过redis方式存放session;通过cookie/header/参数方式与request/response关联。
知道了原理后,我们查看sping-session的源码,可以看出,实现的原理是一致的,只不过它提供了更好更多的扩展。
具体分析可以查看后面关于springSession学习的文章。
























 1108
1108











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








