STL和Boost中的算法和函数大量使用了函数对象作为判断式或谓词参数,而这些参数都是传值语义,算法或函数在内部保修函数对象的拷贝并使用,例如:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
#include "vector"
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
struct square
{
typedef void result_type;
void operator()(int& x)
{
x = x * x;
cout << x << endl;
}
};
vector<int> v = (boost::assign::list_of(1), 2, 3, 4, 5);
for_each (v.begin(), v.end(), square());
return 0;
}
一般情况下传值语义都是可行的,但也有很多特殊情况,作为参数的函数对象拷贝代价过高(具有复杂的内部状态),或者不希望拷贝对象(内部状态不应该被改变),甚至拷贝是不可行的(noncopyable、单件)。
boost.ref应用代理模式,引入对象引用的包装器概念解决了这个问题。
a、类介绍
ref库定义了一个很小很简单的引用类型的包装器,名字叫reference_wrapper,它的类摘要如下:
template<class T> class reference_wrapper
{
public:
typedef T type;
#if defined( BOOST_MSVC ) && BOOST_WORKAROUND( BOOST_MSVC, < 1300 )
explicit reference_wrapper(T& t): t_(&t) {}
#else
explicit reference_wrapper(T& t): t_(boost::addressof(t)) {}
#endif
operator T& () const { return *t_; }
T& get() const { return *t_; }
T* get_pointer() const { return t_; }
private:
T* t_;
};
注意,reference_wrapper的构造函数被声明为explicit,因此必须在创建reference_wrapper对象时就赋值初始化,就像是使用一个引用类型的变量。
reference_wrapper还支持隐式类型转换,可以在需要的语境下返回存储的引用,因此它很像引用类型,能够在任何需要T出现的地方使用reference_wrapper。
b、基本用法
看一个例子:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "boost/ref.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
int x = 10;
reference_wrapper<int> rw(x);
assert(x == rw);
(int &)rw = 100;
assert(x == 100);
reference_wrapper<int> rw2(rw);
assert(rw.get() == 100);
string str;
boost::reference_wrapper<string> rws(str);
*rws.get_pointer() = "zengraoli";
cout << rws.get().size() << endl;
return 0;
}
reference_wrapper<int>rw(x);在这里包装int类型的引用,assert(x==rw);隐式转换为int类型,assert(x==100);显式转换为int&类型,用于左值;boost::reference_wrapper<string>rws(str);包装字符串的引用
c、工厂函数
reference_wrapper的名字过长,声明引用包装对象很不方便,因而ref库提供了两个便捷的工厂函数ref()和cref(),可以通过参数类型推导很容易地构造reference_wrapper对象。
ref()和cref()会根据参数类型自动地推导生成正确的reference_wrapper<T>对象,ref()产生的类型是T,而cref()产生的类型是Tconst,例如:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "boost/ref.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
double x = 1.9999l;
BOOST_AUTO(rw, cref(x));
cout << typeid(rw).name() << endl;
BOOST_AUTO(rw2, ref(x));
cout << typeid(rw2).name() << endl;
return 0;
}
第一个输出的是double const---cref
第二个输出的是double const--- ref
因为reference_wrapper支持拷贝,因此ref()和cref()可以直接用在需要拷贝的语义的函数参数中,而不必专门使用一个reference_wrapper来暂存,例如:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "boost/ref.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
double x = 5.0;
cout << sqrt(boost::ref(x)) << endl;
return 0;
}
d、操作包装
ref库运用模板元编程技术提供两个特征类is_reference_wrapper和unwrap_reference,用于检测reference_wrapper对象:
is_reference_wrapper<T>的bool成员变量value可以判断T是否为一个reference_wrapper;
unwrap_reference<T>的内部类型定义type表明了T的真实类型,无论它是否经过reference_wrapper包装;
下面是代码:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "boost/ref.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
vector<int> v(10, 2);
BOOST_AUTO(rw, cref(v));
// assert(boost::is_reference_wrapper<BOOST_TYPEOF(rw)>::value);
assert(!boost::is_reference_wrapper<BOOST_TYPEOF(v)>::value);
string str;
BOOST_AUTO(rws, ref(str));
cout << typeid(boost::unwrap_reference<BOOST_TYPEOF(rws)>::type).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(boost::unwrap_reference<BOOST_TYPEOF(str)>::type).name() << endl;
return 0;
}
自由函数unwrap_ref()为解开包装提供了简便的方法,他利用unwrap_reference<T>直接解开reference_wrapper的包装(如果有的话),返回被包装对象的引用,例如:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "boost/ref.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
set<int> s;
BOOST_AUTO(rw, boost::ref(s)); // 获得一个包装对象
boost::unwrap_ref(rw).insert(12); // 直接解开包装
string str("zengraoli");
BOOST_AUTO(rws, boost::cref(str)); // 获得一个常对象的包装
cout << typeid(boost::unwrap_ref(rws)).name() << endl; // 解包装
return 0;
}
直接对一个未包装的对象使用unwrap_ref()也是允许的,他将直接返回对象自身的引用:
cout << unwrap_ref(str)<< endl; // 对未包装对象解包装
e、综合使用
假设有一个类BigClass,他具有复杂的内部状态,构造、拷贝都具有很高的代价:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "boost/ref.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
class BigClass
{
public:
BigClass() : x(0)
{
}
~BigClass()
{
}
void Print()
{
cout << "big class x value : " << ++x << endl;
}
private:
int x;
};
template<typename T>
void Print(T a)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 2; ++i)
{
boost::unwrap_ref(a).Print();
}
}
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
BigClass bigclass;
BOOST_AUTO(rw, boost::ref(bigclass));
bigclass.Print();
Print(bigclass);
Print(rw);
Print(bigclass);
bigclass.Print();
return 0;
}
这段代码演示了拷贝传参和引用传参的不同。当调用Print(bigclass)时是拷贝传参,因此bigclass在函数中被复制,它内部状态的变化不影响原对象,在函数调用完成后bigclass的内部值仍然为1。
但调用Print(rw);时由于使用了reference_wrapper的包装,函数拷贝的是reference_wrapper对象,在函数内部被解包装为原对象的引用,因此改变了原对象的内部状态。
f、为ref增加函数调用功能
ref将对象包装为引用语义,降低了复制的代价,使引用的行为更像对象(因为对象更有用更强大),可以让容器安全地持有被包装的引用对象,可以被称为是“智能引用”。
但很遗憾的是ref库没有提供韩式调用操作operator(),这使得我们无法包装一个函数对象的引用并传递给标准库算法,而实际上这并不是一件困难的事情(下面开始改造一下ref库),先看看如下代码:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include "boost/utility/result_of.hpp"
#include "boost/typeof/typeof.hpp"
#include "boost/assign.hpp"
#include "boost/ref.hpp"
#include "iostream"
using namespace std;
struct square
{
typedef void result_type;
void operator()(int& x)
{
x = x * x;
cout << x << endl;
}
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
typedef double (*pFunc)(double);
pFunc pf = sqrt;
cout << boost::ref(pf)(5.0) << endl;
square sq;
int x = 5;
boost::ref(sq)(x);
cout << x << endl;
vector<int> v = (boost::assign::list_of(1), 2, 3, 4, 5);
for_each (v.begin(), v.end(), boost::ref(sq));
return 0;
}
这是不正确的,因为ref库并没有函数调用功能。
下面我们来改造ref库。打开ref.hpp,找到reference_wrapper类,加上如下部分:
typename result_of<T()>::type operator()() const
{
return (*t_)();
}
template<typename T0>
typename result_of<T(T0)>::type operator()(T0 t0) const
{
return (*t_)(t0);
}
template<typename T0, typename T1>
typename result_of<T(T0, T1)>::type operator()(T0 t0, T1 t1) const
{
return (*t_)(t0, t1);
}
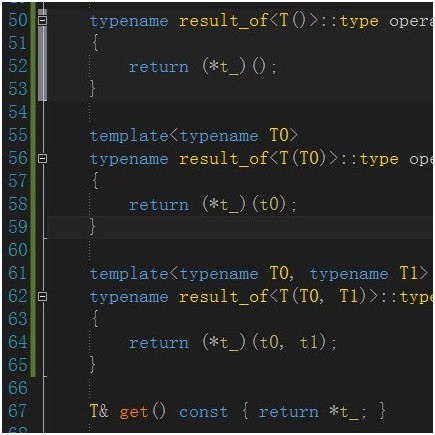
这里用result_of<T()>::type确定了一个无参函数调用的返回类型,还需要在前面加上关键字typename,让编译器知道type是一个类型而不是成员变量。另外operator()必须是const的,因为他不变动referen_wrapper类的状态。参看代码,还有另外的部分是使用成员模板函数重载,同样地我们可以实现带N个参数的函数调用。
这样我们就完成了ref增加函数调用的功能。但需要注意,函数调用依赖的是result_of的功能,因此referen_wrapper包装的对象类型可以是函数指针、函数引用、成员函数指针或函数对象。
对函数对象有特别的要求,简单来说,其内部必须有typedefresult_type,用来定义返回值类型,否则无法推导。
























 1740
1740

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








