1.使用pytorch复现课上例题

源代码:
import torch
x1, x2 = torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor([0.3])
y1, y2 = torch.Tensor([0.23]), torch.Tensor([-0.07])
print("=====输入值:x1, x2;真实输出值:y1, y2=====")
print(x1, x2, y1, y2)
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = torch.Tensor([0.2]), torch.Tensor([-0.4]), torch.Tensor([0.5]), torch.Tensor(
[0.6]), torch.Tensor([0.1]), torch.Tensor([-0.5]), torch.Tensor([-0.3]), torch.Tensor([0.8]) # 权重初始值
w1.requires_grad = True
w2.requires_grad = True
w3.requires_grad = True
w4.requires_grad = True
w5.requires_grad = True
w6.requires_grad = True
w7.requires_grad = True
w8.requires_grad = True
def sigmoid(z):
a = 1 / (1 + torch.exp(-z))
return a
def forward_propagate(x1, x2):
in_h1 = w1 * x1 + w3 * x2
out_h1 = sigmoid(in_h1) # out_h1 = torch.sigmoid(in_h1)
in_h2 = w2 * x1 + w4 * x2
out_h2 = sigmoid(in_h2) # out_h2 = torch.sigmoid(in_h2)
in_o1 = w5 * out_h1 + w7 * out_h2
out_o1 = sigmoid(in_o1) # out_o1 = torch.sigmoid(in_o1)
in_o2 = w6 * out_h1 + w8 * out_h2
out_o2 = sigmoid(in_o2) # out_o2 = torch.sigmoid(in_o2)
print("正向计算:o1 ,o2")
print(out_o1.data, out_o2.data)
return out_o1, out_o2
def loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2): # 损失函数
y1_pred, y2_pred = forward_propagate(x1, x2) # 前向传播
loss = (1 / 2) * (y1_pred - y1) ** 2 + (1 / 2) * (y2_pred - y2) ** 2 # 考虑 : t.nn.MSELoss()
print("损失函数(均方误差):", loss.item())
return loss
def update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8):
# 步长
step = 1
w1.data = w1.data - step * w1.grad.data
w2.data = w2.data - step * w2.grad.data
w3.data = w3.data - step * w3.grad.data
w4.data = w4.data - step * w4.grad.data
w5.data = w5.data - step * w5.grad.data
w6.data = w6.data - step * w6.grad.data
w7.data = w7.data - step * w7.grad.data
w8.data = w8.data - step * w8.grad.data
w1.grad.data.zero_() # 注意:将w中所有梯度清零
w2.grad.data.zero_()
w3.grad.data.zero_()
w4.grad.data.zero_()
w5.grad.data.zero_()
w6.grad.data.zero_()
w7.grad.data.zero_()
w8.grad.data.zero_()
return w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("=====更新前的权值=====")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
for i in range(1):
print("=====第" + str(i) + "轮=====")
L = loss_fuction(x1, x2, y1, y2) # 前向传播,求 Loss,构建计算图
L.backward() # 自动求梯度,不需要人工编程实现。反向传播,求出计算图中所有梯度存入w中
print("\tgrad W: ", round(w1.grad.item(), 2), round(w2.grad.item(), 2), round(w3.grad.item(), 2),
round(w4.grad.item(), 2), round(w5.grad.item(), 2), round(w6.grad.item(), 2), round(w7.grad.item(), 2),
round(w8.grad.item(), 2))
w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8 = update_w(w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6, w7, w8)
print("更新后的权值")
print(w1.data, w2.data, w3.data, w4.data, w5.data, w6.data, w7.data, w8.data)
运行结果:

2.对比作业三和作业二的程序,观察两种方法结果是否相同?如果不同,哪个正确?
不相同,PyTorch算出来的正确。
3.作业2 程序更新:
人工智能作业2
更改后STEP = 999时的梯度与权值:

可以看出y1’ = 0.22994,y2’ = 0.00199 与所期待的0.23,-0.07相比以及较为接近。
4.对比【作业2】与【作业3】的反向传播的实现方法。总结并陈述。
作业二为手动计算反向传播过程中的各参数最后得到参数梯度
作业三使用了tensor数据结构,最后在张量节点的loss中使用backword()方法自动计算梯度值。
5.激活函数Sigmoid用PyTorch自带函数torch.sigmoid(),观察、总结并陈述。
原本写的:

使用pytorch自带:

自带函数效率更高。
6.激活函数Sigmoid改变为Relu,观察、总结并陈述。

速度相较于前两个更快,效率更高。
7.损失函数MSE用PyTorch自带函数 t.nn.MSELoss()替代,观察、总结并陈述。
 通过预测值和实际值y_pred和y计算函数的损失值loss。
通过预测值和实际值y_pred和y计算函数的损失值loss。
8.损失函数MSE改变为交叉熵,观察、总结并陈述。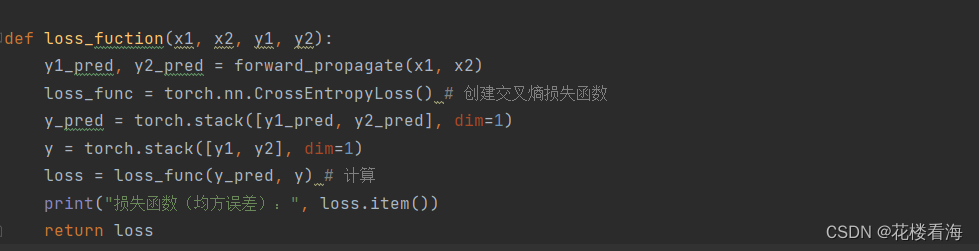
误差相对与前几个较大
九、改变步长,训练次数,观察、总结并陈述
step = 5
step = 20

step =100

收敛速度随着step增加而变快
10.权值w1-w8初始值换为随机数,对比【作业2】指定权值结果,观察、总结并陈述。

随机初始化8个权值为(-1, 1)之间的数,
结果:

随着迭代次数增加逐渐准确,初始值基本不影响最后收敛
11.全面总结反向传播原理和编码实现,认真写心得体会。
反向传播可以解决偏导数计算过多的情况,有点像连坐,就是数学中的迭代算法就是根据上一层的输出,计算下一层的更新量,与结果。






















 3179
3179

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








