本文主要阐述HDFSRPCserver端一个socket连接接收字节流的构成,帮助读者理解HDFSRPC协议。注意hadoop版本为3.1.1。
写在前面
-
关于proto写入和读取,使用writeDelimitedTo和read,应该是通用的方式,不作过多的介绍。
-
处理rpc各种情况以后server都会使用统一的应答格式(包含错误与正确),即
RpcResponseHeaderProto+Message(rpc调用结果,错误时为NULL)
message RpcResponseHeaderProto {
/**
* RpcStastus - success or failure
* The reponseHeader's errDetail, exceptionClassName and errMsg contains
* further details on the error
**/
required uint32 callId = 1; // callId used in Request
required RpcStatusProto status = 2;
optional uint32 serverIpcVersionNum = 3; // Sent if success or fail
optional string exceptionClassName = 4; // if request fails
optional string errorMsg = 5; // if request fails, often contains strack trace
optional RpcErrorCodeProto errorDetail = 6; // in case of error
optional bytes clientId = 7; // Globally unique client ID
optional sint32 retryCount = 8 [default = -1];
}
RpcStatus的枚举类,注意当使用FATAL时,connection会关闭
enum RpcStatusProto {
SUCCESS = 0; // RPC succeeded
ERROR = 1; // RPC or error - connection left open for future calls
FATAL = 2; // Fatal error - connection closed
}
RPC错误的枚举类
enum RpcErrorCodeProto {
// Non-fatal Rpc error - connection left open for future rpc calls
ERROR_APPLICATION = 1; // RPC Failed - rpc app threw exception
ERROR_NO_SUCH_METHOD = 2; // Rpc error - no such method
ERROR_NO_SUCH_PROTOCOL = 3; // Rpc error - no such protocol
ERROR_RPC_SERVER = 4; // Rpc error on server side
ERROR_SERIALIZING_RESPONSE = 5; // error serializign response
ERROR_RPC_VERSION_MISMATCH = 6; // Rpc protocol version mismatch
// Fatal Server side Rpc error - connection closed
FATAL_UNKNOWN = 10; // unknown Fatal error
FATAL_UNSUPPORTED_SERIALIZATION = 11; // IPC layer serilization type invalid
FATAL_INVALID_RPC_HEADER = 12; // fields of RpcHeader are invalid
FATAL_DESERIALIZING_REQUEST = 13; // could not deserilize rpc request
FATAL_VERSION_MISMATCH = 14; // Ipc Layer version mismatch
FATAL_UNAUTHORIZED = 15; // Auth failed
}
RPC如果成功,会在head写完后,紧接着写入rpc调用结果proto。
Rpc连接数据流说明
连接中接收的数据结构图
| 7byte | 4byte(int len)+RpcrequestconnectionContext | 4byte(int len)+Rpcrequest | … |
|---|---|---|---|
| connectionHeader | RpcrequestconnectionContext | Rpcrequest |
connectionHeader
/**
* The Rpc-connection header is as follows
* +----------------------------------+
* | "hrpc" 4 bytes |
* +----------------------------------+
* | Version (1 byte) |
* +----------------------------------+
* | Service Class (1 byte) |
* +----------------------------------+
* | AuthProtocol (1 byte) |
* +----------------------------------+
*/
任何一个连接都会有connectionHeader,connectionHeader由7个字节组成,内容如上。
关于header的check:第一是check前4个字节是否为hrpc,第二是check version。Check version由于要兼顾老版本,处理起来会比较复杂。
当前正确的Version为9:
// 1 : Introduce ping and server does not throw away RPCs
// 3 : Introduce the protocol into the RPC connection header
// 4 : Introduced SASL security layer
// 5 : Introduced use of {@link ArrayPrimitiveWritable$Internal} in ObjectWritable to efficiently transmit arrays of primitives
// 6 : Made RPC Request header explicit
// 7 : Changed Ipc Connection Header to use Protocol buffers
// 8 : SASL server always sends a final response
// 9 : Changes to protocol for HADOOP-8990
public static final byte CURRENT_VERSION = 9;
Version的错误处理:
String errMsg = "Server IPC version " + CURRENT_VERSION + " cannot communicate with client version " + clientVersion;
String errClassName = "org.apache.hadoop.ipc.VersionMismatch";
Version=1 不处理
Version=2
| 4byte(int = 0) | 1byte(boolean=true) | Int+bytes(int为String长度)(String=errClassName) | Int+bytes(String=errMsg) |
|---|
Version=3~8
| 4byte(int = callId) | 4byte(int=-1) | Int+bytes(int为String长度)(String=errClassName) | Int+bytes(String=errMsg) |
|---|
Version>9(如果前4个字节不为hrpc,也是此错误)
RpcStatusProto.FATAL
RpcErrorCodeProto.FATAL_VERSION_MISMATCH
errMsg
errClassName
AuthProtocol:
现有两个值:NONE(0),SASL(-33),现在只使用0,sasl在后续文章中会有解析。
processOneRpc
任何一个rpcRequest都是由head和body组成
Head的结构
message RpcRequestHeaderProto { // the header for the RpcRequest
enum OperationProto {
RPC_FINAL_PACKET = 0; // The final RPC Packet
RPC_CONTINUATION_PACKET = 1; // not implemented yet
RPC_CLOSE_CONNECTION = 2; // close the rpc connection
}
optional RpcKindProto rpcKind = 1;
optional OperationProto rpcOp = 2;
required sint32 callId = 3; // a sequence number that is sent back in response
required bytes clientId = 4; // Globally unique client ID
// clientId + callId uniquely identifies a request
// retry count, 1 means this is the first retry
optional sint32 retryCount = 5 [default = -1];
optional RPCTraceInfoProto traceInfo = 6; // tracing info
optional RPCCallerContextProto callerContext = 7; // call context
}
关于Head的check
必须有rpcOP;rpcOP必须为RPC_FINAL_PACKET;必须有rpcKind

Head中比较重要的是callId属性,callId<0为特殊包,callId>=0为正常请求包。
callId<0

callId=PING_CALL_ID 不处理只打印日志
callId=CONNECTION_CONTEXT_CALL_ID
一般接收完connectionHeader,第一个RPC就为connectionContext。
connectionContext的结构
message IpcConnectionContextProto {
// UserInfo beyond what is determined as part of security handshake
// at connection time (kerberos, tokens etc).
optional UserInformationProto userInfo = 2;
// Protocol name for next rpc layer.
// The client created a proxy with this protocol name
optional string protocol = 3;
}
message UserInformationProto {
optional string effectiveUser = 1;
optional string realUser = 2;
}
主要是注意用户,hdfs server会把用户名作为connection Map的key。
还要注意connectionContext每个连接一直有一个,并且接收完此rpc以后立刻会接收下个rpc。
callId=AuthProtocol.SASL.callId(-33)
后续安全文章介绍。
callId>=0
需要注意的是如果没有接收connectionContext,将不会接收callId>=0的rpcRequest,否则则报错。
Hdfs server会根据rpcRequest head中的rpcKind,把rpcRequest body变成对应的对象。
enum RpcKindProto {
RPC_BUILTIN = 0; // Used for built in calls by tests
RPC_WRITABLE = 1; // Use WritableRpcEngine
RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER = 2; // Use ProtobufRpcEngine
}
例如当rpcKind=RPC_PROTOCOL_BUFFER
Body=RpcProtobufRequest
RpcProtobufRequest又由RequestHeaderProto和Message(body)组成
RequestHeaderProto的结构
message RequestHeaderProto {
required string methodName = 1;
required string declaringClassProtocolName = 2;
required uint64 clientProtocolVersion = 3;
}
Message(body)一般就是方法的入参。
Server在启动的时候会注册需要用的ProtocolName列表和实现类。例如
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB

ClientNamenodeProtocolPB继承与ClientNamenodeProtocol.BlockingInterface,实际就是ClientNamenodeProtocol.proto中的service定义
service ClientNamenodeProtocol {
rpc getBlockLocations(GetBlockLocationsRequestProto)
returns(GetBlockLocationsResponseProto);
rpc getServerDefaults(GetServerDefaultsRequestProto)
returns(GetServerDefaultsResponseProto);
...
}
ClientNamenodeProtocolPB会有自己的
ProtocolName(org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.protocol.ClientProtocol)和ProtocolVersion(1)。
RequestHeaderProto中包含了declaringClassProtocolName 和clientProtocolVersion 可以找到对应的协议已经实现类,并根据methodName 去调用对应的方法。例如getBlockLocations方法,如下图。
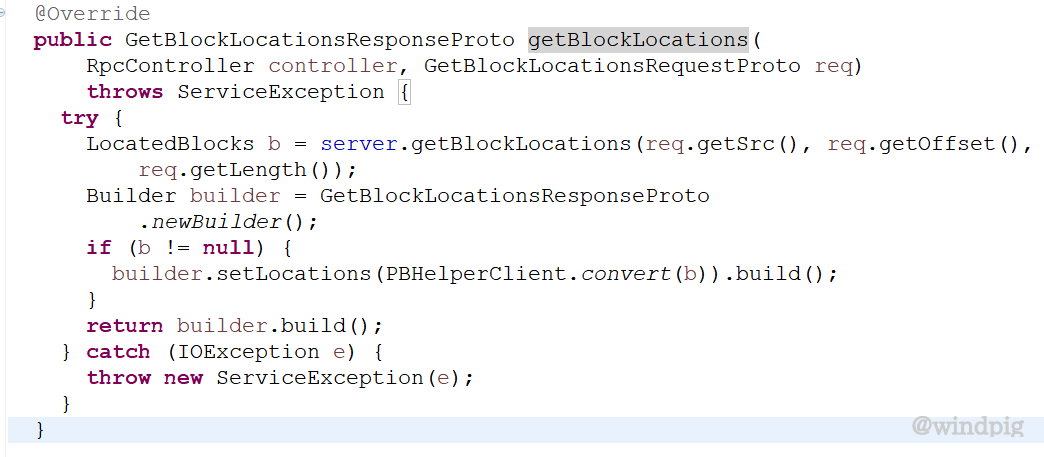
在此方法中最终的RpcProtobufRequest中的Message(body)会format成
GetBlockLocationsRequestProto对象,调用完成后会返回GetBlockLocationsResponseProto。返回格式具体参考统一返回。
rotocolVersion 可以找到对应的协议已经实现类,并根据methodName 去调用对应的方法。例如getBlockLocations方法,如下图。
[外链图片转存中…(img-PY9haIcM-1710299505785)]
在此方法中最终的RpcProtobufRequest中的Message(body)会format成
GetBlockLocationsRequestProto对象,调用完成后会返回GetBlockLocationsResponseProto。返回格式具体参考统一返回。























 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










