目录
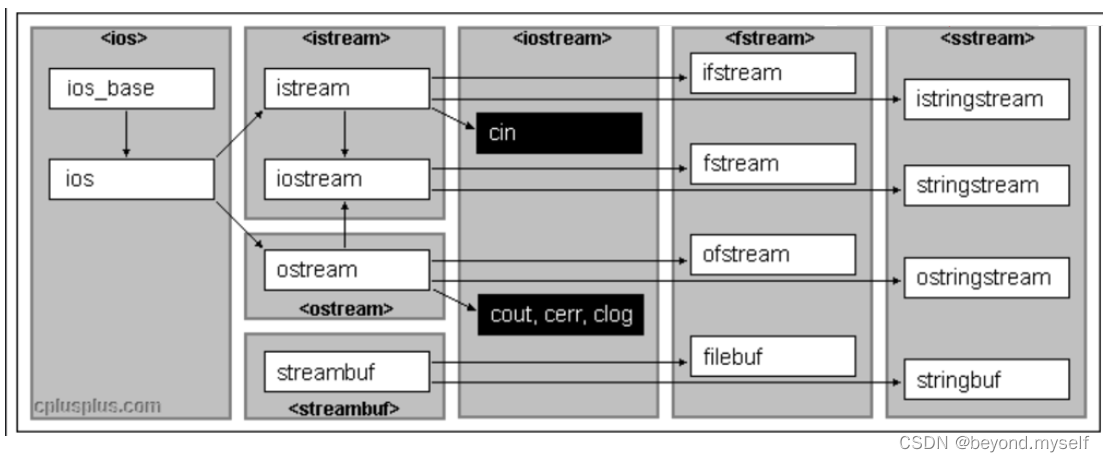
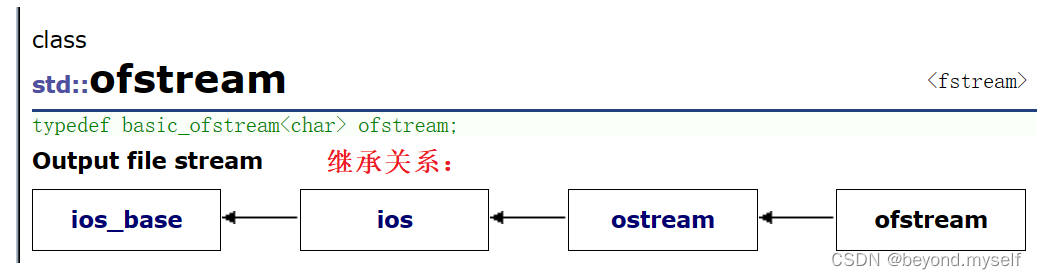
箭头是子类继承,例如istream和ostream都继承ios,stream和ostream都是ios 子类;文件读写的ifstream继承istream,ofstream继承ostream。
注意:他们用法相同,只是去向不同:istream去向是控制台;fstream去向是文件;sstringstream去向是string对象
一.C++标准IO流
while (scanf("%s", buff) != EOF)如何终止?
答:ctrl z+换行 是规定,ctrl c 是发送信号杀死进程(一般不建议ctrl c)。
int main()
{
string str;
while (cin >> str) // operator>>(cin, str)
{
cout << str << endl;
}
char buff[128];
while (scanf("%s", buff) != EOF)
{
printf("%s\n", buff);
}
return 0;
}
cin >> str 和 scanf("%s", buff) 自定义类型无法做真假逻辑判断,那他们在while循环中是如何判断返回值的?——用operator bool
1.operator bool

operator bool:本质是为了支持自定义类型对象转换成bool类型,转换逻辑是自己设置的。(operator int 就是把自定义类型对象转换成int类型)
解释下面:operator bool() 这里是把Date对象转换成bool,返回值就是bool类型
operator bool()
{
// 这里是随意写的,假设输入_year为0,则结束
if (_year < 1)
return false;
else
return true;
}
Date d2 = { 2022, 10, 11 };
bool ret2 = d2; 支持自定义类型对象转换成bool类型
cout << ret2 << endl; 打印结果:1(true)#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
// 支持Date对象转换成bool
operator bool()
{
// 这里是随意写的,假设输入_year为0,则结束
if (_year < 1)
return false;
else
return true;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
int main()
{
Date d1 = -1;
Date d2 = { 2022, 10, 11 };
bool ret1 = d1; 支持自定义类型对象转换成bool类型
bool ret2 = d2; 支持自定义类型对象转换成bool类型
cout << ret1 << endl; 打印结果:0(false)
cout << ret2 << endl; 打印结果:1(true)
if (d1) 这里本质上也是调用了operator bool,d1的Date类型转成了bool类型去做判断
{
}
return 0;
}二.C++文件IO流

1.文件读取 ifstream
(1)ifstream继承istream

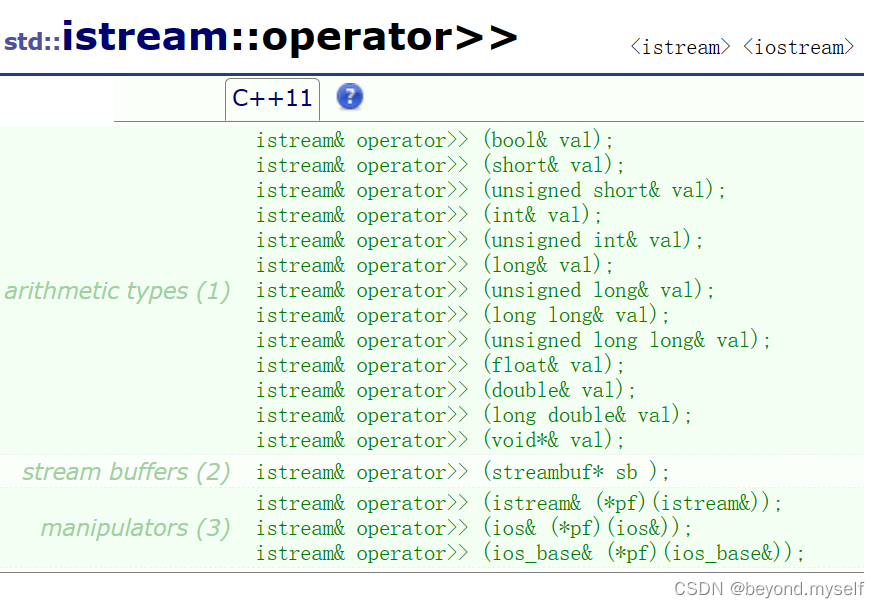

operator>>使用
char str[256];
ifstream ifs("test.cpp");
ifs>>str; 把文件test.cpp"内容读到str中(2)ifstream 构造函数

①ifstream()
先创建一个无参的ifstream对象,再open打开响应文件。
②explicit ifstream (const char* filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::in);
直接传参:filename:文件名称。mode:打开方式,可以不传。(把filename中内容读取到ifstream对象中)
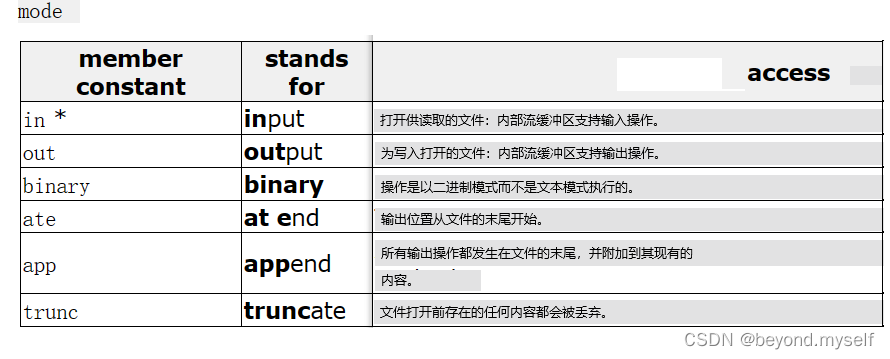
input从头开始读,output输出不是给ifstream用的,binary 打开图片视频等,at end 追加写,
(3)ifstream,get读取整个文件
get()每次读一个字符
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream ifs("Test.cpp");
while (ifs)
{
char ch = ifs.get();
cout << ch;
}
return 0;
}
(4)>> 读取文件
>> 自动过滤空格和换行: >>认为空格/换行只是一个间隔,会自动忽略
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ifstream ifs("Test.cpp");
char ch;
while (ifs>>ch)
{
cout << ch;
}
return 0;
}
2.文件输入 ofstream
(1)ofstream继承ostream

operator<<使用
char str[256]="hello";
ofstream ofs("Copy.cpp");
ofs<<str; 把文件str内容输入到"Copy.cpp"中(2)ofstream 构造函数

①ofstream()
先创建一个无参的ofstream对象,再open打开响应文件。
②explicit ifstream (const char* filename, ios_base::openmode mode = ios_base::in);
直接传参:filename:文件名称。mode:打开方式,可以不传。(把filename中内容读取到ifstream对象中)
(3)拷贝文件 ifstream 搭配 ofstream
ofstream 向Copy.cpp文件中输入

3.二进制读写
注意:二进制读写只能用数组,不能string,string是指针,进程A写入,进程B读取string时就是野指针;文本读写可以用string,WriteText 中调的流插入 ofs << info._address << endl; 调用了string的operator<<重载
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
struct ServerInfo
{
char _address[256];
这里只能用数组,不能string,string是指针,进程A写入,进程B读取string时就是野指针
//string _address;
int _port;
};
struct ConfigManager
{
public:
ConfigManager(const char* filename)
:_filename(filename)
{}
void WriteBin(const ServerInfo& info)
{
// 1 2 4 8 16
ofstream ofs(_filename, ios_base::out | ios_base::binary); 打开一个文件
ofs.write((const char*)&info, sizeof(info)); 向该文件写入 info的内容
}
void ReadBin(ServerInfo& info)
{ 把_filename文件读入ifs中,read把该文件内容读到info中去
ifstream ifs(_filename, ios_base::in | ios_base::binary);
ifs.read((char*)&info, sizeof(info));
}
private:
string _filename; // 配置文件
};
int main()
{
ServerInfo winfo = { "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/ios/ios/eof/", 80 };
二进制写:
ConfigManager cf_bin("test.bin"); 打开文件test.bin即可看到
cf_bin.WriteBin(winfo);
因为是二进制写入,80整形被一个一个字节读到文件中就显示不出来
二进制读:
ServerInfo rbinfo;
cf_bin.ReadBin(rbinfo);
cout << rbinfo._address << " " << rbinfo._port << " ";
return 0;
}test.bin文件:(因为是二进制写入,80整形被一个一个字节读到文件中就显示不出来)
 把test.bin文件中二进制的内容再二进制读出来的结果:
把test.bin文件中二进制的内容再二进制读出来的结果:

4.文本读写
文本读写:转成字符串
注意:二进制读写只能用数组,不能string,string是指针,进程A写入,进程B读取string时就是野指针;文本读写可以用string,WriteText 中调的流插入 ofs << info._address << endl; 调用了string的operator<<重载
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
// 支持Date对象转换成bool
operator bool()
{
// 这里是随意写的,假设输入_year为0,则结束
if (_year < 1)
return false;
else
return true;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day;
return out;
}
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————下面是重点内容
struct ServerInfo
{
string _address;
int _port;
Date _d;
};
struct ConfigManager
{
public:
ConfigManager(const char* filename)
:_filename(filename)
{}
// 文本读写
void WriteText(const ServerInfo& info)
{
// 1 2 4 8 16
ofstream ofs(_filename);
ofs << info._address << endl; 调用了string的operator<<重载
ofs << info._port << endl; 底层会把int转成字符串再读取到ofs文件中
ofs << info._d << endl; 调用了Date友元的operator<<
(注意:这里 流插入<< 务必加上<<endl,因为下面ReadText读取时按空格或换行读取)
}
void ReadText(ServerInfo& info)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename);
ifs >> info._address;
ifs >> info._port;
ifs >> info._d;
}
private:
string _filename; // 配置文件
};
int main()
{
ServerInfo winfo = { "https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/ios/ios/eof/"
, 80, {2022, 10, 11} };
ConfigManager cf_txt("test.txt");
cf_txt.WriteText(winfo); 把winfo中内容以文本形式写入"test.txt"文件
ConfigManager cf_text("test.txt");
ServerInfo rtinfo;
cf_text.ReadText(rtinfo); 把"test.txt"文件中内容以文本形式读到rtinfo
cout << rtinfo._address << " " << rtinfo._port << " " << rtinfo._d << endl;
return 0;
}text.txt文件中写入了内容

注意!!!:流提取>> 读取时按空格或换行读取
WriteText流插入<< 务必加上<<endl,因为下面ReadText的 流提取>> 读取时按空格或换行读取
// 文本读写
void WriteText(const ServerInfo& info)
{
// 1 2 4 8 16
ofstream ofs(_filename);
ofs << info._address << endl; 调用了string的operator<<重载
ofs << info._port << endl; 底层会把int转成字符串再读取到ofs文件中
ofs << info._d << endl; 调用了Date友元的operator<<
(注意:这里 流插入<< 务必加上<<endl,因为下面ReadText读取时按空格或换行读取)
}
void ReadText(ServerInfo& info)
{
ifstream ifs(_filename);
ifs >> info._address;
ifs >> info._port;
ifs >> info._d;
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
ConfigManager cf_text("test.txt");
ServerInfo rtinfo;
cf_text.ReadText(rtinfo); 把"test.txt"文件中内容以文本形式读到rtinfo
cout << rtinfo._address << " " << rtinfo._port << " " << rtinfo._d << endl;①如果不加 WriteText 流插入<< 不加<<endl,那么写入文件的内容是:
"https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/ios/ios/eof/"802022 10 11 ,日期类插入时带空格了,则 ReadText 读到ServerInfo rtinfo 中时,
rtinfo._address 读到内容是:"https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/ios/ios/eof/"802022
rtinfo._port 读到内容是: 10
rtinfo._d 读到内容是:_d._year=11,_d._month 和 _d._day 都没读到东西,则值是缺省值1
打印出来就是下面这种错误的情况:

②WriteText流插入<< 加上<<endl 后才能正确打印出

三.stringstream

stringstream 是 istringstream 和 ostringstream 的功能集合版,一般不使用stringstream,就直接用 istringstream 和 ostringstream 即可
1.用途:将 整形/自定义类型 转字符串
int main()
{
int n = 123456789;
char s1[32];
_itoa(n, s1, 10);
char s2[32];
sprintf(s2, "%d", n);
char s3[32];
sprintf(s3, "%f", n);
return 0;
}2.功能使用
(1)将数值类型数据格式化为字符串。

真正用法:自定义类型转字符串
class Date
{
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d);
public:
Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
// 支持Date对象转换成bool
operator bool()
{
// 这里是随意写的,假设输入_year为0,则结束
if (_year < 1)
return false;
else
return true;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
istream& operator >> (istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}
ostream& operator << (ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << " " << d._month << " " << d._day;
return out;
}oss<<d1 借助上面Date内部的 operator << ,就可以转成字符串
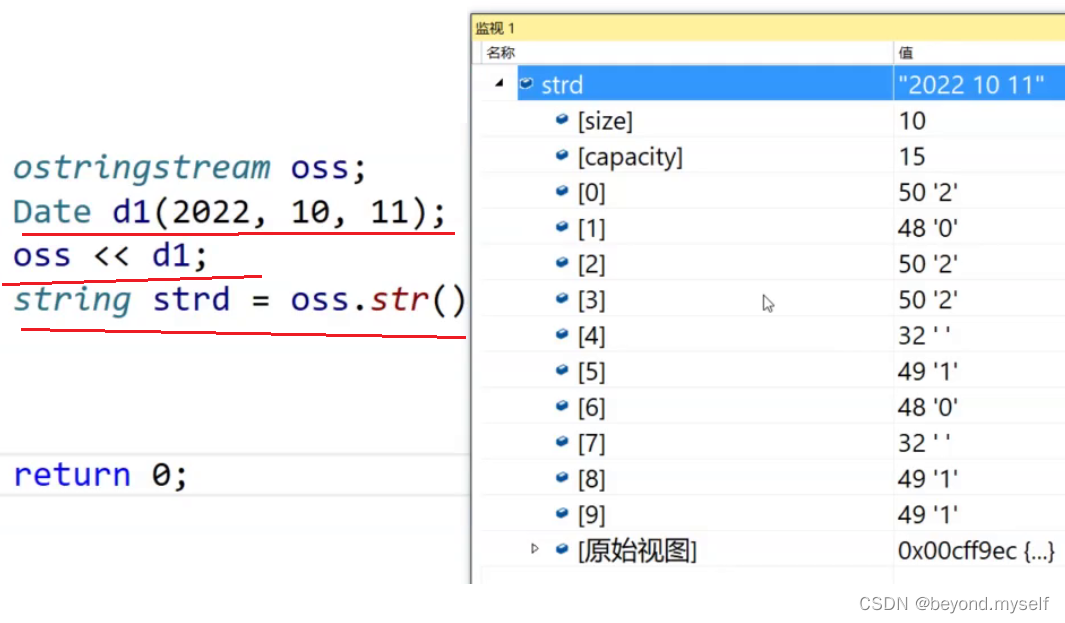
字符串 转 自定义类型





















 959
959











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








