B+树是从B树修改而来的。对 B 树的建立会了的话,对 B+ 树的操作可以类比着进行。
关于 B 树,可以参看之前写的文章:对B树的插入删除理解和c/c++代码实践
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangzhangkeji/article/details/119767646
B+ 树的节点的结构体定义如下:
struct Node {
int numKeys;
int keyArray[MAX];
Node* ptChildren[MAX] = {NULL}; //?????????指针需要初始化么?
Node* ptParent;
Node* ptRightBrother;
};
m 阶 B+ 树的特点是:
(1)树里节点最多有 m 个 指针 ,指向 m 个子节点 。
(2)分支节点最少可以有 ceil(m/2) 个指针 。如 m = 9, 则最少有5 个指针。m = 10 也最少有 5 个指针 。根节点若也是叶节点,最少可以没有;若根节点是分支节点,最少有2个指针。
(3)节点里关键字个数 和指针个数是相等的。关键字的值是其对应指针指向的子树的最大关键字值。所以,节点里有几个元素,就有几个子树。关键字就是元素。
(4)如 m = 9 则非根节点最少含有 5 个关键字, m = 10 ,则非根节点最少含有 5 个关键字。当一个节点太小,与相邻节点合并时,刚好可以两个最小节点合并成一个最大节点或仅比最大节点少一个元素。一个最大节点刚好也可以拆分成两个最小节点。这也是最小指针数与最大阶数成 二分之一 关系的意义。
(5)B+ 树 始终有两个头指针,一个指向根节点,另一个指向含有最小元素的叶节点,即最左边的叶节点。所以,既可以从根节点开始对关键字进行跳跃式查找。也可以对所有叶节点里的关键字进行顺序查找。
(6)B+ 树里 关键字是重复的。 所有分支节点里的关键字都会在叶节点里再出现一次。所有叶节点含有了不重复的树里所有关键字。分支节点里的关键字,更像是索引,指示了其所有子树的关键字的取值范围。这也为跳跃式查找提供了选择依据。
(7)B+ 树的插入,也是插入到合适的叶节点里,若叶节点太大,则拆分成两个叶节点,并在其父母节点里插入一个元素和一个指向新的节点的指针。如果父母节点太大,则拆分父母节点,依次类推,直到根节点被拆分,生成新的根节点,树的高度加一。若插入的是叶节点里最大的元素,则要修改其祖先节点里元素的值,分支节点里元素值代表对应子树的最大元素值。
(8)B+ 树的所有叶节点,也要求在同一条水平线上,即在树里同样的深度上。
(9)B+ 树的删除,只能对叶节点里的元素进行直接删除。若删除的元素是叶节点的最大元素,因为其也出现在分支节点,需要把分支节点里的该值也删除,修改为叶节点新的最大值。若删除后,叶节点太小,则可以从其左右兄弟叶节点借一个元素。若其左右兄弟节点都是最小节点,则合并该节点和其右兄弟节点(这只是规定,合并其和左兄弟节点也可以,但同一个程序,只能选择一个方向,保持一致性和程序计算的简单化),并从其父母节点里删除一个元素,一个指针。若父母节点也太小了,则合并父母节点和父母节点的右兄弟节点。若合并后的父母节点太大,则还需要拆分父母节点。使父母节点有合适的爷爷奶奶节点。若根节点太大被拆分,则生成新的根。分支节点里出现的元素被删除时,因为其代表子树的最大元素,所以要用子树里的第二最大元素替代之。
(10)合并节点的操作不一定非得是两个最小节点。对于分支节点的合并,必须考虑合并后的分支节点太大的问题。
(11)程序建立 B+ 树正确的话,对叶节点里关键字的遍历,依据根节点从上往下从左往右遍历到叶节点,和直接对叶节点的顺序遍历,其结果是相同的。
(12)因为要求可以对所有叶节点从左到右顺序遍历,所有节点类型里还要有一个指针指向其右侧兄弟节点,当然对于叶节点,这个指针才有意义。只需要对叶节点建立右指针的连接。
(13)B+ 树已经不适合再用中序遍历了,因为对于典型的二叉树中序遍历(左根右),B+ 树的指针数目和关键字数目是相同的。而且B+ 树可以直接对叶节点进行顺序遍历。中序递归遍历的存在对于 B+ 树已经不重要了。
(14)复杂的程序,在编写之前,最好可以列出流程图,明确程序执行步骤,逐步细化,也降低了大脑的想象力负担。
接着给出B+ 树插入操作的流程图:

然后是B+ 树删除操作的流程图:

各函数功能如下:
函数searchNode : 从节点中查找元素应该存在的位置。
函数searchTree : 从整棵树中查找某个元素的位置。
函数newRootVerti:生成新的根节点。
函数split : 拆分过大的节点。
函数insertNode : 往节点里插入元素和指针。
函数insertTree : 往树里添加元素。
函数dispalyCommaExp:显示一棵树的逗号表达式。以检验程序是否正确。
函数sequenTraverseLeafNodes:顺序遍历叶节点。
函数deleteKeyFromNode : 从节点里删除元素和指针。
函数smallNode:处理出现的过小节点。
函数deleteKeyFromTree:从树里删除元素。
以下是完整代码。先是main函数所在源文件代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 8
#define ORDER 5
#define MAXKEYS ORDER
#define MINKEYS (ORDER + 1) / 2
struct Node {
int numKeys;
int keyArray[MAX];
Node* ptChildren[MAX] = {NULL}; //?????????指针需要初始化么?
Node* ptParent;
Node* ptRightBrother;
};
struct Result {
Node* pt;
int index;
bool findOrNot;
};
extern int searchNode(Node*& pt, int key);
extern Result searchTree(Node * & rootVerti,int key);
extern void newRootVerti(Node*& rootVerti, int keyLeft, Node* ptLeft, int keyRight ,Node* ptRight);
extern void split(Node*& rootVerti, Node* ptLeft);
extern void insertNode(Node * &rootVerti,Node* pt, int index, int key, Node* ptKey);
extern void insertTree(Node*& rootVerti, int key,Node * & rootHoriz);
extern void dispalyCommaExp(Node * & rootVerti);
extern void sequenTraverseLeafNodes(Node*& rootHoriz);
extern void deleteKeyFromNode(Node*& rootVerti, Node* pt, int index, Node* ptIndex);
extern void smallNode(Node * & rootVerti,Node* pt);
extern bool deleteKeyFromTree(Node*& rootVerti,int key,Node * & rootHoriz);
extern void combine(Node*& rootVerti, Node* ptParent, int indexLeft, int indexRight, Node* ptLeft, Node* ptRight);
int main() {
Node* rootVerti = NULL, * rootHoriz = NULL;
// Result result;
// int array[] = { 4, 9, 0, 1, 8, 6, 3, 5, 2, 7,10},length = 11;
// int array[] = { 1, 8, 5, 2, 7,10}, length = 6;
// int array[] = { 4},length = 1 ;
// int array[] = { 4,0,9,6},length = 4 ;
int array[] = { 1,2,6,7,11,4,8,13,10,5,17,9,16,20,3,12,14,18,19,15,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30},length = 30;
// int array[] = { 1,2,6,7,11,4,8,13,10,5,17,9,16,20,3,12,14,18,19,15 }, length = 20;
for (int i = 0; i < length ; i++)
insertTree(rootVerti, array[i],rootHoriz);
dispalyCommaExp(rootVerti);
cout << endl;
sequenTraverseLeafNodes(rootHoriz);
cout << endl;
cout << "input number after 'next' to continue test,but 100 means stop test.eg.next:100";
cout << endl << "input the number you want to delete : ";
int input;
do{
cin >>input ;
cout << endl;
if (input == 100)
break;
if(deleteKeyFromTree(rootVerti,input,rootHoriz) == false)
cout << "list does not have this key : "<<input<<'.';
else {
cout << "逗号表达式:";
dispalyCommaExp(rootVerti);
cout << endl;
cout << "叶节点遍历:";
sequenTraverseLeafNodes(rootHoriz);
}
cout<< " next :";
} while (1 == 1);
return 0;
}
接着是各函数所在源文件代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 8
#define ORDER 5
#define MAXKEYS ORDER
#define MINKEYS (ORDER + 1) / 2
struct Node {
int numKeys;
int keyArray[MAX];
Node* ptChildren[MAX] = {NULL};
Node* ptParent;
Node* ptRightBrother;
};
struct Result {
Node* pt;
int index;
bool findOrNot;
};
int searchNode(Node*& pt, int key) {
int index;
for (index = 0; index < pt->numKeys && pt->keyArray[index] < key; index++);
return index;
}
Result searchTree(Node*& rootVerti, int key) { //返回的是其应该在叶节点中的插入位置
Result result; //或者其在树中第一次出现的位置
Node* pt = rootVerti, * ptParent = NULL;
int index = 0;
while (pt != NULL) {
index = searchNode(pt, key);
if (index == pt->numKeys) {
while (pt->ptChildren[0] != NULL)
pt = pt->ptChildren[pt->numKeys - 1];
result.findOrNot = false;
result.pt = pt;
result.index = pt->numKeys;
return result;
}
else if (pt->keyArray[index] != key) {
ptParent = pt;
pt = pt->ptChildren[index];
}
else
break;
}
if (pt == NULL) {
result.findOrNot = false;
result.pt = ptParent;
}
else {
result.findOrNot = true;
result.pt = pt;
}
result.index = index;
return result;
}
void newRootVerti(Node*& rootVerti, int keyLeft, Node* ptLeft, int keyRight, Node* ptRight) {
rootVerti = new Node;
rootVerti->ptParent = NULL;
rootVerti->numKeys = 2;
rootVerti->keyArray[0] = keyLeft;
rootVerti->keyArray[1] = keyRight;
rootVerti->ptChildren[0] = ptLeft;
ptLeft->ptParent = rootVerti;
rootVerti->ptChildren[1] = ptRight;
ptRight->ptParent = rootVerti;
if (ptLeft->ptChildren[0] == NULL) { //防止根节点以下的就是叶节点,为其建立横向连接
ptRight->ptRightBrother = ptLeft->ptRightBrother;
ptLeft->ptRightBrother = ptRight;
}
}
void split(Node*& rootVerti, Node* ptLeft) {
void insertNode(Node * &rootVerti, Node * pt, int index, int key, Node * ptKey);
Node* ptRight = new Node;
ptRight->numKeys = MINKEYS;
ptLeft->numKeys = ptLeft->numKeys - MINKEYS;
ptRight->ptParent = ptLeft->ptParent;
for (int i = 0, j = ptLeft->numKeys; i < MINKEYS; i++) {
ptRight->keyArray[i] = ptLeft->keyArray[j + i];
ptRight->ptChildren[i] = ptLeft->ptChildren[j + i];
if (ptRight->ptChildren[i] != NULL)
ptRight->ptChildren[i]->ptParent = ptRight;
}
if (ptLeft == rootVerti) //根节点被拆分,生成新根
newRootVerti(rootVerti,ptLeft->keyArray[ptLeft->numKeys - 1],ptLeft,
ptRight->keyArray[ptRight->numKeys - 1],ptRight);
else {
int i = searchNode(ptLeft->ptParent,ptLeft->keyArray[ptLeft->numKeys - 1]);
ptLeft->ptParent->keyArray[i] = ptLeft->keyArray[ptLeft->numKeys - 1];
insertNode(rootVerti,ptRight->ptParent,i + 1,
ptRight->keyArray[ptRight->numKeys - 1],ptRight);
}
}
void insertNode(Node*& rootVerti, Node* pt, int index, int key, Node* ptKey) {
int i;
for (i = pt->numKeys; i > index; i--) {
pt->keyArray[i] = pt->keyArray[i - 1];
pt->ptChildren[i] = pt->ptChildren[i - 1];
}
pt->keyArray[index] = key;
pt->numKeys++;
pt->ptChildren[index] = ptKey;
if (ptKey != NULL && ptKey->ptChildren[0] == NULL) { //说明插入的是叶节点
pt->ptChildren[index]->ptRightBrother = pt->ptChildren[index - 1]->ptRightBrother;
pt->ptChildren[index - 1]->ptRightBrother = pt->ptChildren[index];
}
if (pt->ptChildren[0] == NULL &&
key == pt->keyArray[pt->numKeys - 1]) {//插入的是叶节点最大元素
Node* ptTemp = pt->ptParent; //也许也是整棵树最大元素
int index,keyOld = pt->keyArray[pt->numKeys - 2];
while (ptTemp != NULL) {
index = searchNode(ptTemp, keyOld);
ptTemp->keyArray[index] = key;
if (index < ptTemp->numKeys - 1)
break;
ptTemp = ptTemp->ptParent;
}
}
if (pt->numKeys > ORDER)
split(rootVerti, pt);
}
void insertTree(Node*& rootVerti, int key, Node*& rootHoriz) {
Result result = searchTree(rootVerti,key);
if (result.findOrNot == false)
if (rootVerti == NULL) {
rootHoriz = rootVerti = new Node;
rootHoriz->ptRightBrother = NULL;
rootVerti->ptParent = NULL;
rootHoriz->numKeys = 1;
rootVerti->keyArray[0] = key;
}
else
insertNode(rootVerti,result.pt,result.index,key,NULL);
}
void dispalyCommaExp(Node*& rootVerti) {
if (rootVerti == NULL)
return;
int i;
cout << '[';
for (i = 0; i < rootVerti->numKeys - 1; i++)
cout << rootVerti->keyArray[i] << ' ';
cout << rootVerti->keyArray[i] << ']';
if (rootVerti->ptChildren[0] != NULL) {
cout << '(';
for (i = 0; i < rootVerti->numKeys - 1; i++) {
dispalyCommaExp(rootVerti->ptChildren[i]);
cout << ',';
}
dispalyCommaExp(rootVerti->ptChildren[i]);
cout << ')';
}
}
void sequenTraverseLeafNodes(Node*& rootHoriz) {
Node* pt = rootHoriz;
while (pt != NULL) {
for (int i = 0; i < pt->numKeys; i++)
cout << pt->keyArray[i] << ' ';
pt = pt->ptRightBrother;
}
}
void deleteKeyFromNode(Node*& rootVerti, Node* pt, int index,Node * ptIndex) {
void smallNode(Node * &rootVerti, Node * pt);
int max = pt->keyArray[index];
for (int j = index; j < pt->numKeys - 1; j++) {
pt->keyArray[j] = pt->keyArray[j + 1];
pt->ptChildren[j] = pt->ptChildren[j + 1];
}
pt->numKeys--;
if(ptIndex == NULL) //若被删元素是原叶节点最大元素
if (index == pt->numKeys) { //需要修改其祖先节点存储的最大元素值
Node* ptTemp = pt->ptParent;
while (ptTemp != NULL) {
index = searchNode(ptTemp, max);
ptTemp->keyArray[index] = pt->keyArray[pt->numKeys - 1];
if (index < ptTemp->numKeys - 1)
break;
ptTemp = ptTemp->ptParent;
}
}
if (ptIndex != NULL && ptIndex->ptChildren[0] == NULL) //叶节点被删
pt->ptChildren[index - 1]->ptRightBrother = ptIndex->ptRightBrother;
delete ptIndex;
if (pt->ptParent != NULL && pt->numKeys < MINKEYS)
smallNode(rootVerti,pt);
}
void combine(Node*& rootVerti, Node* ptParent, int indexLeft,int indexRight,Node* ptLeft, Node* ptRight) {
for (int i = 0; i < ptRight->numKeys; i++) {
ptLeft->keyArray[ptLeft->numKeys + i] = ptRight->keyArray[i];
ptLeft->ptChildren[ptLeft->numKeys + i] = ptRight->ptChildren[i];
if (ptLeft->ptChildren[0] != NULL)
ptRight->ptChildren[i]->ptParent = ptLeft;
}
ptLeft->numKeys = ptLeft->numKeys + ptRight->numKeys;
ptParent->keyArray[indexLeft] = ptRight->keyArray[ptRight->numKeys - 1];
if (ptParent == rootVerti && rootVerti->numKeys == 2) {
if (ptLeft->ptChildren[0] == NULL) //如果根节点以下就是叶节点
ptLeft->ptRightBrother = ptRight->ptRightBrother;
delete rootVerti;
delete ptRight;
rootVerti = ptLeft;
rootVerti->ptParent = NULL;
}
else
deleteKeyFromNode(rootVerti,ptParent,indexRight,ptRight);
if (ptLeft->numKeys > MAXKEYS)
split(rootVerti,ptLeft);
}
void smallNode(Node*& rootVerti, Node* pt) {
Node* ptParent = pt->ptParent, * ptLeft, * ptRight;
int index = searchNode(ptParent,pt->keyArray[pt->numKeys - 1]);
if (index == 0) {
ptRight = ptParent->ptChildren[index + 1];
if (pt->ptChildren[0] == NULL && ptRight->numKeys > MINKEYS) {
insertNode(rootVerti, pt, pt->numKeys, ptRight->keyArray[0], NULL);
deleteKeyFromNode(rootVerti, ptRight, 0, NULL);
}
else
combine(rootVerti, ptParent, 0, 1, pt, ptRight);
}
else if (index == ptParent->numKeys - 1) {
ptLeft = ptParent->ptChildren[index - 1];
if (pt->ptChildren[0] == NULL && ptParent->ptChildren[index - 1]->numKeys > MINKEYS) {
insertNode(rootVerti, pt, 0, ptLeft->keyArray[ptLeft->numKeys - 1], NULL);
deleteKeyFromNode(rootVerti, ptLeft, ptLeft->numKeys - 1, NULL);
}
else
combine(rootVerti,ptParent,index - 1,index,ptLeft,pt);
}
else {
ptLeft = ptParent->ptChildren[index - 1];
ptRight = ptParent->ptChildren[index + 1];
if (pt->ptChildren[0] == NULL)
if (ptLeft->numKeys > MINKEYS) {
insertNode(rootVerti, pt, 0, ptLeft->keyArray[ptLeft->numKeys - 1], NULL);
deleteKeyFromNode(rootVerti, ptLeft, ptLeft->numKeys - 1, NULL);
return;
}
else if (ptRight->numKeys > MINKEYS) {
insertNode(rootVerti, pt, pt->numKeys, ptRight->keyArray[0], NULL);
deleteKeyFromNode(rootVerti, ptRight, 0, NULL);
return;
}
combine(rootVerti,ptParent,index,index + 1,pt,ptRight);
}
}
bool deleteKeyFromTree(Node*& rootVerti, int key, Node*& rootHoriz) {
Result result = searchTree(rootVerti,key);
if (result.findOrNot == false)
return false;
if (result.pt->ptChildren[0] != NULL) {
Node* ptTemp = result.pt->ptChildren[result.index];
while (ptTemp->ptChildren[0] != NULL)
ptTemp = ptTemp->ptChildren[ptTemp->numKeys - 1];
deleteKeyFromNode(rootVerti, ptTemp, ptTemp->numKeys - 1,NULL);
}
else if (result.pt == rootVerti && rootVerti->numKeys == 1) {
delete rootVerti;
rootVerti = rootHoriz = NULL;
}
else
deleteKeyFromNode(rootVerti,result.pt,result.index,NULL);
return true;
}
接着是测试结果,30个数字的大 B+ 树。一一从树中删除到空树。足够的测试才可以检验程序全面的性能。
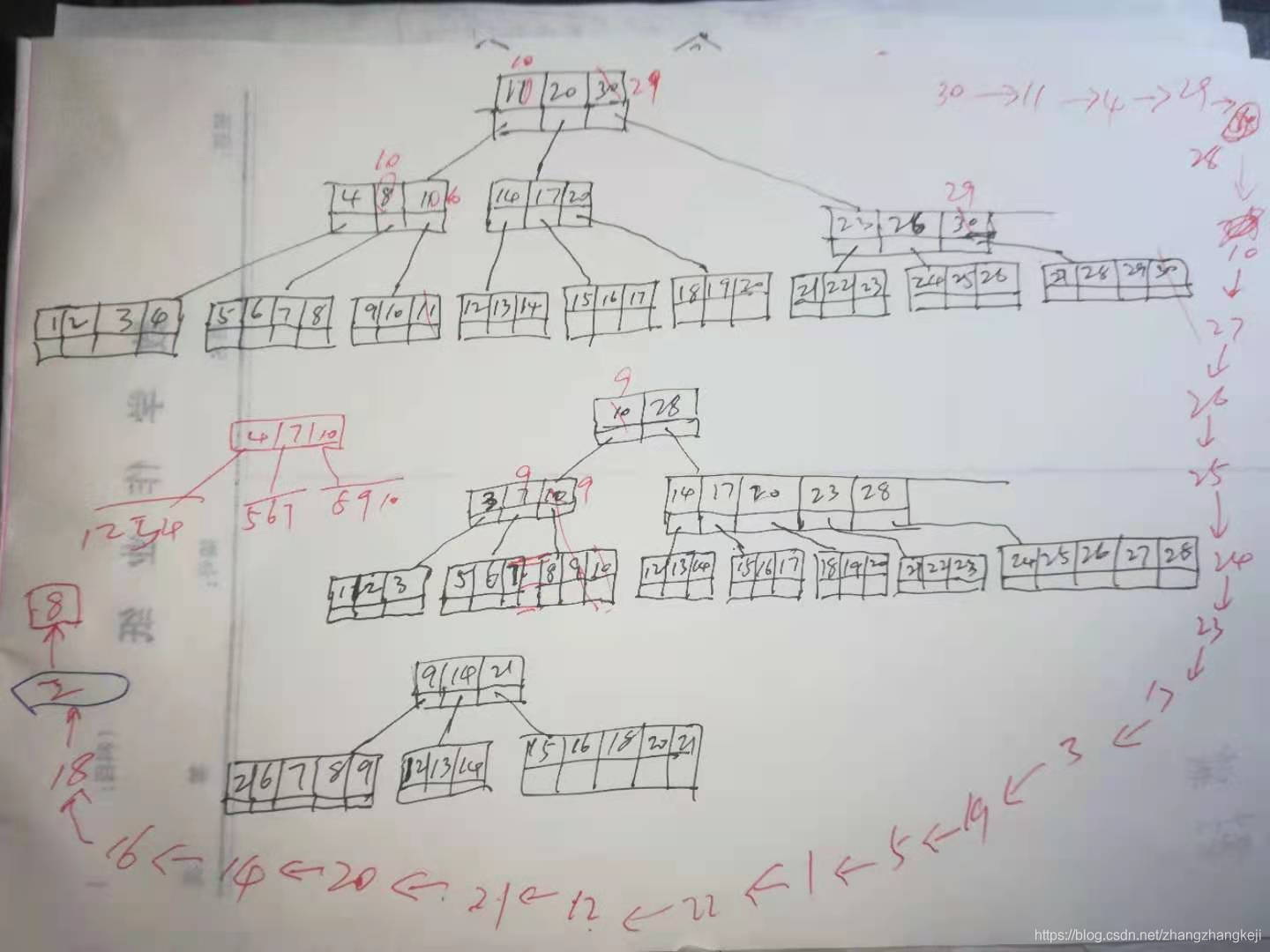

程序变量命名见名知意,易于理解和跟踪程序。
谢谢阅读。





















 2874
2874











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








