提问:假设只有一个构造方法,如果将之私有化会有什么后果
- 对于当前类,它是无法实例化的
- 对于它的子类,子类也是无法实例化的
构造函数与是否能够实例化有关
准备
对于单个类
- 正常情况下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
EventDispatcher noticeCenter1;
EventDispatcher *noticeCenter2 = new EventDispatcher;
noticeCenter1.test_printf();
noticeCenter2->test_printf();
}
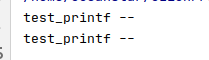
- 构造函数私有化
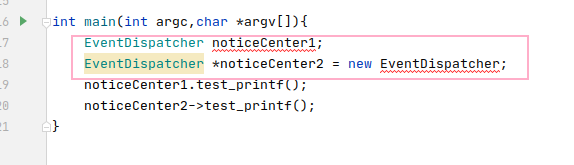
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
private:
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
EventDispatcher noticeCenter1;
EventDispatcher *noticeCenter2 = new EventDispatcher;
noticeCenter1.test_printf();
noticeCenter2->test_printf();
}
编译通不过,因为无论是在栈还是堆上,都无法调用构造函数来生成对象
私有化与继承
- 正常情况下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
class NoticeCenter : public EventDispatcher{
public:
void test_Center(){
std::cout << "test_Center --\r\n";
}
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
NoticeCenter noticeCenter1;
NoticeCenter *noticeCenter2 = new NoticeCenter;
noticeCenter1.test_printf();
noticeCenter2->test_printf();
noticeCenter1.test_Center();
noticeCenter2->test_Center();
}
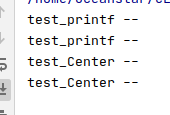
2. 父类构造函数私有化,而且子类没有提供public的构造函数----》 子类的构造函数也是私有化的
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
private:
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
class NoticeCenter : public EventDispatcher{
public:
void test_Center(){
std::cout << "test_Center --\r\n";
}
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
NoticeCenter noticeCenter1;
NoticeCenter *noticeCenter2 = new NoticeCenter;
noticeCenter1.test_printf();
noticeCenter2->test_printf();
noticeCenter1.test_Center();
noticeCenter2->test_Center();
}
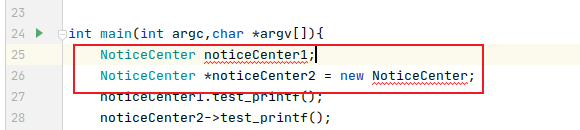
- 父类构造函数私有化,而且子类提供public的构造函数----》编译还是不能通过
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
private:
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
class NoticeCenter : public EventDispatcher{
public:
void test_Center(){
std::cout << "test_Center --\r\n";
}
public:
NoticeCenter() = default; //没有作用
//此时子类无法提供除了默认构造函数之外的函数,比如 NoticeCenter(int a)
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
NoticeCenter noticeCenter1;
NoticeCenter *noticeCenter2 = new NoticeCenter;
noticeCenter1.test_printf();
noticeCenter2->test_printf();
noticeCenter1.test_Center();
noticeCenter2->test_Center();
}
结论:只要继承了一个无法实例化的父类,不管子类怎么折腾,都无法实例化。 这也是noncopyable类的由来
成员变量与私有化
- 正常情况下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
class NoticeCenter {
public:
void test_Center(){
a.test_printf();
std::cout << "test_Center --\r\n";
}
EventDispatcher a;
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
NoticeCenter noticeCenter1;
NoticeCenter *noticeCenter2 = new NoticeCenter;
noticeCenter1.test_Center();
noticeCenter2->test_Center();
}
2. 如果当前类的某个成员变量是无法实例化的,那么当前类也无法实例化(正常,某个组件无法实例化,那么整个构建就会出问题)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
private:
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
class NoticeCenter {
public:
void test_Center(){
std::cout << "test_Center --\r\n";
a.test_printf();
}
EventDispatcher a;
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
NoticeCenter noticeCenter1;
NoticeCenter *noticeCenter2 = new NoticeCenter;
noticeCenter1.test_Center();
noticeCenter2->test_Center();
}

- 解决方法:友元类可以访问某个类的私有成员,所以将令构件为某个组件的友元类,这样构件就可以去访问组件私有的构造函数,将之构造出来了
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class EventDispatcher {
friend class NoticeCenter ;
public:
void test_printf(){
std::cout << "test_printf --\r\n";
}
private:
EventDispatcher() = default;
};
class NoticeCenter {
public:
void test_Center(){
std::cout << "test_Center --\r\n";
a.test_printf();
}
EventDispatcher a;
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[]){
NoticeCenter noticeCenter1;
NoticeCenter *noticeCenter2 = new NoticeCenter;
noticeCenter1.test_Center();
noticeCenter2->test_Center();
}





















 726
726











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








