深入Struts2
++YONG原创,转载请注明
1. 深入Struts2的配置文件
1.1 包配置
1.2 命名空间配置
1.3 包含配置
1.5 常量配置
2. Struts2的Action
2.1 实现Action类
2.2 Action访问Servlet API
3. 一个Action内包含多个请求处理方法的处理
3.1 动态方法调用
3.1.1 示例
3.2 为Action配置method属性
3.3 使用通配符映射(wildcard mappings)方式
4. 处理结果
4.1 配置处理结果
4.2 处理结果类型
4.3 动态返回结果
5. 属性驱动和模型驱动
5.1 属性驱动
5.2 模型驱动
6. Struts2的异常处理机制
6.1 异常映射也分为两种
6.2 输出异常信息
6.3 示例
1) 把UserAciton.java中的regist方法改成
2) 修改struts.xml文件
3) 新增一页面:exception.jsp
4) 运行regist.jsp进行调试
1. 深入Struts2的配置文件
1.1 包配置
1.2 命名空间配置
1.3 包含配置
1.5 常量配置
2. Struts2的Action
2.1 实现Action类
2.2 Action访问Servlet API
3. 一个Action内包含多个请求处理方法的处理
3.1 动态方法调用
3.1.1 示例
3.2 为Action配置method属性
3.3 使用通配符映射(wildcard mappings)方式
4. 处理结果
4.1 配置处理结果
4.2 处理结果类型
4.3 动态返回结果
5. 属性驱动和模型驱动
5.1 属性驱动
5.2 模型驱动
6. Struts2的异常处理机制
6.1 异常映射也分为两种
6.2 输出异常信息
6.3 示例
1) 把UserAciton.java中的regist方法改成
2) 修改struts.xml文件
3) 新增一页面:exception.jsp
4) 运行regist.jsp进行调试
1. 深入Struts2的配置文件
本部分主要介绍struts.xml的常用配置。
1.1. 包配置:
Struts2框架中核心组件就是Action、拦截器等,Struts2框架使用包来管理Action和拦截器等。每个包就是多个Action、多个拦截器、多个拦截器引用的集合。
在struts.xml文件中package元素用于定义包配置,每个package元素定义了一个包配置。它的常用属性有:
l name:必填属性,用来指定包的名字。
l extends:可选属性,用来指定该包继承其他包。继承其它包,可以继承其它包中的Action定义、拦截器定义等。
l namespace:可选属性,用来指定该包的命名空间。
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<!-- struts2
的
action
必须放在一个指定的包空间下定义
-->
<
package
name
=
"default"
extends
=
"struts-default"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"login"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
如上示例的配置,配置了一个名为default的包,该包下定义了一个Action。
1.2. 命名空间配置:
考虑到同一个Web应用中需要同名的Action,Struts2以命名空间的方式来管理Action,同一个命名空间不能有同名的Action。
Struts2通过为包指定namespace属性来为包下面的所有Action指定共同的命名空间。
把上示例的配置改为如下形式:
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<!-- struts2
的
action
必须放在一个指定的包空间下定义
-->
<
package
name
=
"qiujy"
extends
=
"struts-default"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"login"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"backLogin"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
如上配置了两个包:default和my,配置my包时指定了该包的命名空间为/manage。
对于包default:没有指定namespace属性。如果某个包没有指定namespace属性,即该包使用默认的命名空间,默认的命名空间总是""。
对于包my:指定了命名空间/manage,则该包下所有的Action处理的URL应该是“命名空间/Action名”。如上名为
backLogin的Action,它处理的URL为:
http://localhost:8080/userlogin_struts2
/manage/backLogin.action
Struts2的命名空间的作用等同于struts1里模块的作用。
1.3. 包含配置:
在Struts2中可以将一个配置文件分解成多个配置文件,那么我们必须在struts.xml中包含其他配置文件。
|
<
struts
>
<
include
file
=
"struts-default.xml"
/>
<
include
file
=
"struts-user.xml"
/>
<
include
file
=
"struts-book.xml"
/>
<
include
file
=
"struts-shoppingCart.xml"
/>
......
</
struts
>
|
1.4. 拦截器配置:
见后面章节介绍。
1.5. 常量配置:
Struts2 框架有两个核心配置文件,其中struts.xml文件主要负责管理应用中的Action映射, 及Action处理结果和物理资源之间的映射关系。除此之外,Struts2框架还包含了一个struts.properties文件,该文件主义了 Struts2框架的大量常量属性。但通常推荐也是在struts.xml文件中来配置这些常量属性。
如:后面会讲到Struts2的国际化,它的资源文件位置就用常量属性来指定:
|
<
struts
>
......
<
constant
name
=
"struts.custom.i18n.resources"
value
=
"messages"
/>
</
struts
>
|
表示指定了资源文件的放置在classes目录下,基本名是messages,则在classes目录下您就应该放置类似messages_zh_CN.properties,message_en.properties名的文件。
2. Struts2的Action
2.1. 实现Action类:
Struts2中Action是核心内容,它包含了对用户请求的处理逻辑,我们也称Action为业务控制器。
Struts2 中的Action采用了低侵入式的设计,Struts2不要求Action类继承任何的Struts2的基类或实现Struts2接口。(但是,我们为了 方便实现Action,大多数情况下都会继承com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport类,并重写此类里的 public String execute() throws Exception方法。因为此类中实现了很多的实用接口,提供了很多默认方法,这些默认方法包括获取国际化信息的方法、数据校验的方法、默认的处理用户 请求的方法等,这样可以大大的简化Action的开发。)
Struts2 中通常直接使用Action来封装HTTP请求参数,因此,Action类里还应该包含与请求参数对应的属性,并且为属性提供对应的getter和 setter方法。(当然,Action类中还可以封装处理结果,把处理结果信息当作一属性,提供对应的getter和setter方法)
修改第一部分的用户登录示例:把Action改成如下:
|
package
org.qiujy.web.struts2.action;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
@author
qiujy
*
@version
1.0
*/
public
class
LoginAction
extends
ActionSupport
{
private
String
userName
;
private
String
password
;
private
String
msg
;
//
结果信息属性
/**
*
@return
the
msg
*/
public
String getMsg() {
return
msg
;
}
/**
*
@param
msg
the
msg
to
set
*/
public
void
setMsg(String msg) {
this
.
msg
= msg;
}
/**
*
@return
the
userName
*/
public
String getUserName() {
return
userName
;
}
/**
*
@param
userName
the
userName
to
set
*/
public
void
setUserName(String userName) {
this
.
userName
= userName;
}
/**
*
@return
the
password
*/
public
String getPassword() {
return
password
;
}
/**
*
@param
password
the
password
to
set
*/
public
void
setPassword(String password) {
this
.
password
= password;
}
/**
*
处理用户请求的
excute()
方法
*
@return
结果导航字符串
*
@throws
Exception
*/
public
String execute()
throws
Exception{
if
(
"test"
.equals(
this
.
userName
) &&
"test"
.equals(
this
.
password
)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+
this
.
userName
;
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
}
|
往success.jsp和error.jsp页面中添加 ${msg} EL表达式来显示结果信息。则最终效果跟以前一样。
2.2. Action访问Servlet API:
Struts2中的Action并没有和任何Servlet API耦合,这样框架更具灵活性,更易测试。
但 是,对于web应用的控制器而言,不访问Servlet API几乎是不可能的,例如跟踪HTTP Session状态等。Struts2框架提供了一种更轻松的方式来访问Servlet API。Struts2中提供了一个ActionContext类(当前Action的上下文对象),通过这个类可以访问Servlet API。下面是该类中提供的几个常用方法:
l public static ActionContext getContext() :获得当前Action的ActionContext实例。
l public Object get(Object key) :此方法类似于调用HttpServletRequest的getAttribute(String name)方法。
l public void put(Object key, Object value) :此方法类似于调用HttpServletRequest 的setAttribute(String name, Object o)。
l public Map getParameters() :获取所有的请求参数。类似于调用HttpServletRequest对象的getParameterMap() 方法。
l public Map getSession() :返回一个Map对象,该Map对象模拟了HttpSession实例。
l public void setSession(Map session) : 直接传入一个Map实例,将该Map实例里的key-value对转换成session的属性名-属性值对。
l public Map getApplication() :返回一个Map对象,该对象模拟了该应用的ServletContext实例。
l public void setApplication(Map application) :直接传入一个Map实例,将该Map实例里的key-value对转换成application的属性名-属性值对。
修改以上用户登录验证示例的Action类中的execute方法:
|
public
String execute()
throws
Exception{
if
(
"test"
.equals(
this
.
userName
) &&
"test"
.equals(
this
.
password
)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+
this
.
userName
;
//
获取
ActionContext
实例,通过它来访问
Servlet API
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
//
看
session
中是否已经存放了用户名,如果存放了:说明已经登录了;
//
否则说明是第一次登录成功
if
(
null
!= context.getSession().get(
"uName"
)){
msg
=
this
.
userName
+
"
:你已经登录过了
!!!"
;
}
else
{
context.getSession().put(
"uName"
,
this
.
userName
);
}
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
|
Struts2中通过ActionContext来访问Servlet API,让Action彻底从Servlet API 中分离出来,最大的好处就是可以脱离Web容器测试Action。
另外,Struts2中还提供了一个ServletActionContext类,Action只要继承自该类,就可以直接访问Servlet API。具体方法参看struts2的API文档。
3. 一个Action内包含多个请求处理方法的处理
Struts1提供了DispatchAction,从而允许一个Action内包含多个请求处理方法。Struts2也提供了类似的功能。处理方式主要有以下三种方式:
3.1. 动态方法调用:
DMI:Dynamic Method Invocation 动态方法调用。
动态方法调用是指:表单元素的action不直接等于某个Action的名字,而是以如下形式来指定对应的动作名:
|
<form method="post"
action="userOpt!login.action">
|
则用户的请求将提交到名为”userOpt”的Action实例,Action实例将调用名为”login”方法来处理请求。同时login方法的签名也是跟execute()一样,即为public String login() throws Exception。
注意:要使用动态方法调用,必须设置Struts2允许动态方法调用,通过设置struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation常量来完成,该常量属性的默认值是true。
3.1.1. 示例:
修改用户登录验证示例,多增加一个注册用户功能。
1. 修改Action类:
|
package
org.qiujy.web.struts2.action;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
/**
*
@author
qiujy
*
@version
1.0
*/
public
class
LoginAction
extends
ActionSupport{
private
String
userName
;
private
String
password
;
private
String
msg
;
//
结果信息属性
/**
*
@return
the
msg
*/
public
String getMsg() {
return
msg
;
}
/**
*
@param
msg
the
msg
to
set
*/
public
void
setMsg(String msg) {
this
.
msg
= msg;
}
/**
*
@return
the
userName
*/
public
String getUserName() {
return
userName
;
}
/**
*
@param
userName
the
userName
to
set
*/
public
void
setUserName(String userName) {
this
.
userName
= userName;
}
/**
*
@return
the
password
*/
public
String getPassword() {
return
password
;
}
/**
*
@param
password
the
password
to
set
*/
public
void
setPassword(String password) {
this
.
password
= password;
}
/**
*
处理用户请求的
login()
方法
*
@return
结果导航字符串
*
@throws
Exception
*/
public
String login()
throws
Exception{
if
(
"test"
.equals(
this
.
userName
) &&
"test"
.equals(
this
.
password
)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+
this
.
userName
;
//
获取
ActionContext
实例,通过它来访问
Servlet API
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
//
看
session
中是否已经存放了用户名,如果存放了:说明已经登录了;
//
否则说明是第一次登录成功
if
(
null
!= context.getSession().get(
"uName"
)){
msg
=
this
.
userName
+
"
:你已经登录过了
!!!"
;
}
else
{
context.getSession().put(
"uName"
,
this
.
userName
);
}
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
public
String regist()
throws
Exception{
//
将用户名,密码添加到数据库中
//...
msg
=
"
注册成功。
"
;
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
}
|
2. struts.xml文件:没有什么变化,跟以前一样配置
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<!--
定义处理请求
URL
为
login.action
的
Action -->
<
action
name
=
"userOpt"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
>
<!--
定义处理结果字符串和资源之间的映射关系
-->
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
3. 页面:
index.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"UTF-8"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
用户登录页面
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
用户入口
</
h2
>
<
hr
>
<
form
action
=
"manage/userOpt!login.action"
method
=
"post"
>
<
table
border
=
"1"
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
用户名:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"text"
name
=
"userName"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
密码:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"password"
name
=
"password"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
colspan
=
"2"
>
<
input
type
=
"submit"
value
=
"
确定
"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
</
table
>
</
form
>
</
body
>
</
html
>
|
regist.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"UTF-8"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
用户注册页面
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
用户注册
</
h2
>
<
hr
>
<
form
action
=
"manage/userOpt!regist.action"
method
=
"post"
>
<
table
border
=
"1"
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
用户名:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"text"
name
=
"userName"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
密码:
</
td
>
<
td
><
input
type
=
"password"
name
=
"password"
/></
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
colspan
=
"2"
>
<
input
type
=
"submit"
value
=
"
注册
"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
</
table
>
</
form
>
</
body
>
</
html
>
|
4. 运行结果:


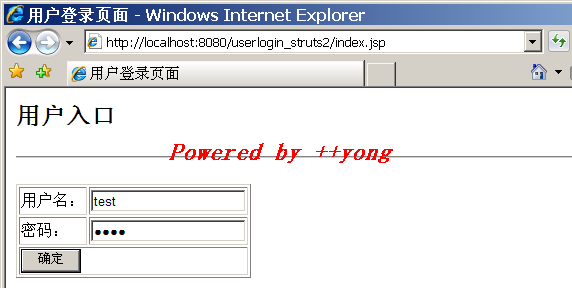
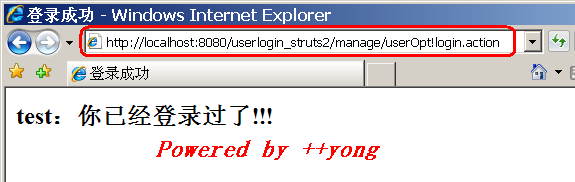
3.2. 为Action配置method属性:
将Action类中的每一个处理方法都定义成一个逻辑Action方法。
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<
action
name
=
"userLogin"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
method
=
"login"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
<
action
name
=
"userRegist"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.LoginAction"
method
=
"regist"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
如 上,把LoginAction中的login和regist方法都配置成逻辑Action。要调用login方法,则相应的把index.jsp中表单元 素的action设置为"manage/userLogin.action";要调用regist方法,把regist.jsp中表单元素的action 设置为"manage/userRegist.action"。
3.3. 使用通配符映射(wildcard mappings)方式:
在struts.xml文件中配置<action…>元素时,它的name、class、method属性都可支持通配符,这种通配符的方式是另一种形式的动态方法调用。
当我们使用通配符定义Action的name属性时,相当于用一个元素action定义了多个逻辑Action:
|
<
action
name
=
"user_*"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.UserAction"
method
=
"{1}"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
|
如 上,<action name=”user_*”>定义一系列请求URL是user_*.action模式的逻辑Action。同时method属性值为一个表达式 {1},表示它的值是name属性值中第一个*的值。例如:用户请求URL为user_login.action时,将调用到UserAction类的 login方法;用户请求URL为user_regist.action时,将调用到UserAction类的regist方法。
4. 处理结果
Struts2的Action处理完用户请求后,将返回一个普通字符串,整个普通字符串就是一个逻辑视图名。Struts2通过配置逻辑视图名和物理视图资源之间的映射关系,一旦系统收到Action返回的某个逻辑视图名,系统就会把对应的物理视图资源呈现给浏览者。
4.1. 配置处理结果:
Struts2的Action处理用户请求结束后,返回一个普通字符串-逻辑视图名,必须在struts.xml文件中完成逻辑视图和物理视图资源的映射,才可让系统转到实际的视图资源。
Struts2通过在struts.xml文件中使用<result …/>元素来配置结果。Struts2提供了两种结果。
l 局部结果:将<result …/>作为<action …>元素的子元素配置。
l 全局结果:将<result …/>作为<global-results …>元素的子元素配置。
在package元素中配置<global-results>子元素:
|
<global-results>
<result name="error">/Error.jsp</result>
<result name="invalid.token">/Error.jsp</result>
<result name="login" type="redirect-action">Logon!input</result>
</global-results>
|
4.2. 处理结果类型:
Struts2提供了对不同种类返回结果的支持,常见的有JSP,FreeMarker,Velocity等。
Struts2支持的不同类型的返回结果为:
|
名字
|
说明
|
|
chain
|
用来处理Action链
|
|
dispatcher
|
用来转向页面,通常处理JSP
,这是默认的结果类型
|
|
freeMarker
|
处理FreeMarker模板
|
|
httpHeader
|
用来控制特殊的Http行为
|
|
redirect
|
重定向到一个URL
|
|
redirect-action
|
重定向到一个Action
|
|
stream
|
向浏览器发送InputSream对象,通常用来处理文件下载
|
|
velocity
|
处理Velocity模板
|
|
xslt
|
处理XML/XLST模板
|
|
plaintext
|
显示原始文件内容,例如文件源代码
|
|
tiles
|
结合Tile使用
|
另外第三方的Result类型还包括JasperReports Plugin,专门用来处理JasperReport类型的报表输出;Jfreechart Plugin;JSF Plugin。
4.3. 动态返回结果
有些时候,只有当Action执行完毕的时候我们才知道要返回哪个结果,这个时候我们可以在Action内部定义一个属性,这个属性用来存储Action执行完毕之后的result值,例如:
|
private String nextAction;
public String getNextAction() {
return nextAction;
}
|
在strutx.xml配置文件中,我们可以使用${nextAction}来引用到Action中的属性,通过${nextAction}表示的内容来动态的返回结果,例如:
|
<action name="fragment" class="FragmentAction">
<result name="next" type="redirect-action">${nextAction}</result>
</action>
|
上述Action的execute方法返回next的时候,还需要根据nextAction的属性来判断具体定位到哪个Action。
5. 属性驱动和模型驱动
不管属性驱动还是模型驱动,Struts2框架都是通过拦截器负责提取请求参数,并将请求数据封装到相应的Action实例的属性或专门的模型的属性。
5.1. 属性驱动:
属性驱动就是属性(property)作为贯穿MVC流程的信息携带者。简单的说,就是使用Action实例来封装请求参数和处理结果信息。前面我们做的示例都属于属性驱动模式。
5.2. 模型驱动:
模型驱动就是使用单独的javaBean作为贯穿整个MVC流程的信息携带者。也就是说,使用单独的VO(值对象)来封装请求参数和处理结果信息。
示例:继续修改用户登录验证:
1. 新增一用户域模型对象:User.java
|
package
org.qiujy.domain;
public
class
User {
private
String
userName
;
private
String
password
;
/**
*
@return
the
userName
*/
public
String getUserName() {
return
userName
;
}
/**
*
@param
userName
the
userName
to
set
*/
public
void
setUserName(String userName) {
this
.
userName
= userName;
}
/**
*
@return
the
password
*/
public
String getPassword() {
return
password
;
}
/**
*
@param
password
the
password
to
set
*/
public
void
setPassword(String password) {
this
.
password
= password;
}
}
|
2. 业务控制器:UserAction.java
|
package
org.qiujy.web.struts2.action;
import
org.qiujy.domain.User;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext;
import
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport;
public
class
UserAction
extends
ActionSupport{
//
定义用于封装请求参数的模型对象
private
User
user
=
new
User();
private
String
msg
;
//
结果信息属性
/**
*
@return
the
user
*/
public
User getUser() {
return
user
;
}
/**
*
@param
user
the
user
to
set
*/
public
void
setUser(User user) {
this
.
user
= user;
}
/**
*
@return
the
msg
*/
public
String getMsg() {
return
msg
;
}
/**
*
@param
msg
the
msg
to
set
*/
public
void
setMsg(String msg) {
this
.
msg
= msg;
}
/**
*
处理用户请求的
login()
方法
*
@return
结果导航字符串
*
@throws
Exception
*/
public
String login()
throws
Exception{
String userName =
user
.getUserName();
String password =
user
.getPassword();
if
(
"test"
.equals(userName) &&
"test"
.equals(password)){
msg
=
"
登录成功,欢迎
"
+ userName;
//
获取
ActionContext
实例,通过它来访问
Servlet API
ActionContext context = ActionContext.getContext();
//
看
session
中是否已经存放了用户名,如果存放了:说明已经登录了;否则说明是第一次登录成功
if
(
null
!= context.getSession().get(
"uName"
)){
msg
= userName +
"
:你已经登录过了
!!!"
;
}
else
{
context.getSession().put(
"uName"
, userName);
}
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
else
{
msg
=
"
登录失败,用户名或密码错
"
;
return
this
.
ERROR
;
}
}
public
String regist()
throws
Exception{
//
将用户名,密码添加到数据库中
//...
msg
=
"
注册成功。
"
;
return
this
.
SUCCESS
;
}
}
|
3. 配置文件:struts.xml
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<
action
name
=
"userOpt"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.UserAction"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
4. 页面:
index.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"UTF-8"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
用户登录页面
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
用户入口
</
h2
>
<
hr
>
<
form
action
=
"manage/userOpt!login.action"
method
=
"post"
>
<
table
border
=
"1"
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
用户名:
</
td
>
<
td
>
<
input
type
=
"text"
name
=
"user.userName"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
>
密码:
</
td
>
<
td
>
<input type="password" name="user.password"/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
<
tr
>
<
td
colspan
=
"2"
>
<
input
type
=
"submit"
value
=
"
确定
"
/>
</
td
>
</
tr
>
</
table
>
</
form
>
</
body
>
</
html
>
|
其它页面略。
5. 运行效果:同以前一样。
6. 源代码:
6. Struts2的异常处理机制:
任何成熟的MVC框架都应该提供成就的异常处理机制。Strut2也不例外。Struts2提供了一种声明式的异常处理方式。Struts2也是通过配置的拦截器来实现异常处理机制的。
Struts2的异常处理机制通过在struts.xml文件中配置<exception-mapping …>元素完成的,配置该元素时,需要指定两个属性:
exception:此属性指定该异常映射所设置的异常类型。
result:此属性指定Action出现该异常时,系统转入result属性所指向的结果。
6.1. 异常映射也分为两种:
l 局部异常映射:<exception-mapping…>元素作为<action…>元素的子元素配置。
l 全局异常映射:<exception-mapping…>元素作为<global-exception-mappings>元素的子元素配置。
6.2. 输出异常信息:
使用Struts2的标签来输出异常信息:
l <s:property value="exception.message"/> : 输出异常对象本身。
l <s:property value="exceptionStack"/> : 输出异常堆栈信息。
6.3. 示例:
还是修改用户登录示例:
1) 把UserAciton.java中的regist方法改成:
|
public
String regist()
throws
Exception{
//
将用户名,密码添加到数据库中
//...
//msg = "
注册成功。
";
if
(
true
){
throw new
java.sql.SQLException(
"
没有数据库驱动程序
"
);
}
return this.SUCCESS;
}
|
2) 修改struts.xml文件:
|
<!
DOCTYPE
struts
PUBLIC
"-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.0//EN"
"http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.0.dtd"
>
<
struts
>
<
package
name
=
"my"
extends
=
"struts-default"
namespace
=
"/manage"
>
<!--
定义全局处理结果
-->
<
global-results
>
<!--
逻辑名为
sql
的结果,映射到
/exception.jsp
页面
-->
<
result
name
=
"sql"
>
/exception.jsp
</
result
>
</
global-results
>
<
global-exception-mappings
>
<!--
当
Action
抛出
SQLException
异常时,转入名为
sql
的结果
-->
<
exception-mapping
exception
=
"java.sql.SQLException"
result
=
"sql"
/>
</
global-exception-mappings
>
<
action
name
=
"userOpt"
class
=
"org.qiujy.web.struts2.action.UserAction"
>
<
result
name
=
"success"
>
/success.jsp
</
result
>
<
result
name
=
"error"
>
/error.jsp
</
result
>
</
action
>
</
package
>
</
struts
>
|
3) 新增一页面:exception.jsp
|
<%@
page
language
=
"java"
pageEncoding
=
"utf-8"
%>
<%@
taglib
uri
=
"/struts-tags"
prefix
=
"s"
%>
<
html
>
<
head
>
<
title
>
异常信息
</
title
>
</
head
>
<
body
>
<
h2
>
出现异常啦
</
h2
>
<
hr
/>
<
h3
style
=
"color:red"
>
<!--
获得异常对象
-->
<
s:property
value
=
"exception.message"
/>
</
h3
>
<
br
/>
<!--
异常堆栈信息
-->
<
s:property
value
=
"exceptionStack"
/>
</
html
>
|
4) 运行regist.jsp进行调试:























 1592
1592

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








