
<K,V> —— 键值对。
1、常用方法
代码示例:
package test1_Map;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
/**
* @Auther: zhoulz
* @Description: test1_Map
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
增加:put(K key, V value)
删除:clear()、remove(Object key)
修改:
查看:entrySet()、get(Object key)、keySet()
size()、values()
判断:containsKey(Object key)、containsValue(Object value)
equals(Object o)、isEmpty()
*/
//创建一个Map集合
//Map map = new Map(); //同理,接口不能直接创建对象
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//指定键值对的类型
//1、添加
System.out.println("添加----------");
//map.put("lili1",111111);
System.out.println(map.put("lili1", 111111)); //null
map.put("lili2",222222);
map.put("lili3",333333);
//map.put("lili1",111111666);//名字相同,身份证号不同
//存的是这个lili1,为什么?
System.out.println(map.put("lili1", 111111666)); //111111
map.put("lili4",444444);
map.put("lili5",555555);
System.out.println(map.size()); // 5
System.out.println(map); //结果:无序、唯一
//2、删除
System.out.println("删除----------");
//map.clear();
System.out.println(map);
//map.remove("lili2",222222);
//map.remove("lili2");//直接传入Key即可
System.out.println(map);
//3、判断
System.out.println("判断----------");
System.out.println(map.containsKey("lili4"));
System.out.println(map.containsValue(333333));
//equals(Object o)
Map<String,Integer> map2 = new HashMap<>();//指定键值对的类型
map2.put("lili1",111111);
map2.put("lili2",222222);
map2.put("lili3",333333);
map2.put("lili1",111111666);
map2.put("lili4",444444);
map2.put("lili5",555555); //改动一点
System.out.println(map2);
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println(map == map2); // == 比较地址,肯定不一样
System.out.println(map.equals(map2));
//equals进行了重写,比较的是集合中的值是否一致
System.out.println(map2.isEmpty()); //false
//4、查看
// 1)get(Object key)
System.out.println(map2.get("lili5"));
//先说两个简单的
// 2)keySet() —— 返回值类型为 Set<String>
//返回此地图中包含的键的Set视图
Set<String> set = map2.keySet();
//keySet()对集合中的key进行遍历查看:
for(String s : set){
System.out.println(s);
}
// 3)values()——对集合中的value进行遍历查看:
Collection<Integer> values = map2.values();
for (Integer i : values){
System.out.println(i);
}
System.out.println("-----------------");
//除了values()方法外,遍历集合中value值的方法还有:
//get(Object key)和keySet()结合:
Set<String> set2 = map2.keySet();
for (String s : set2){ //获得key
System.out.println(map2.get(s)); //通过key获取value
}
//还有另一种方法:
// 4)entrySet() — 返回此地图中包含的映射的Set视图
//注意返回值 —— 返回的是set集合,并且其中的每一个元素都是Entry
Set<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> entries = map2.entrySet();
//得到的其实是一对数据
//遍历:
for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> e : entries){
System.out.println(e.getKey()+"---"+e.getValue());
}
}
}
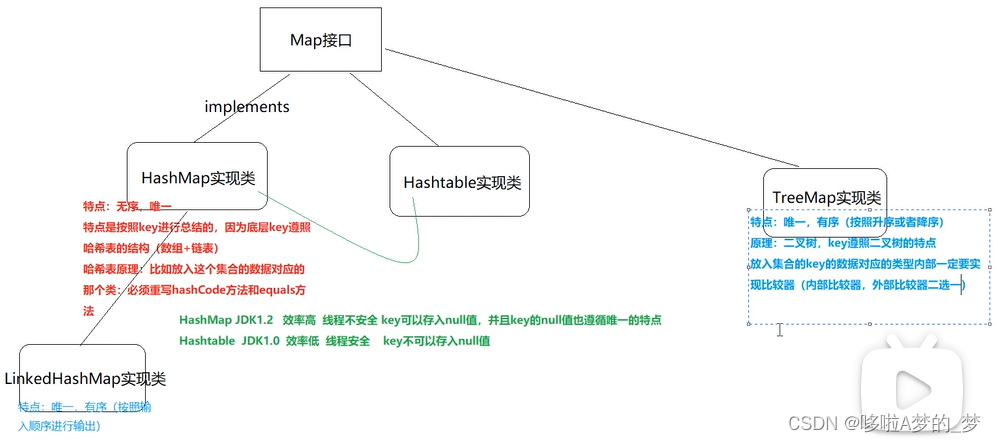
除了HashSet 实现类,还有一个叫 Hashtable 实现类,区别如下图。
另外,如果想要集合按照输入顺序进行输出,可使用LinkedHashMap 实现类。
(同:LinkedHashSet 实现类,在hash表的基础上再加一个总的链表)
2、Map部分整体结构图
3、TreeMap
【1】key的类型为String类型
package test2_TreeMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
/**
* @Auther: zhoulz
* @Description: test2_TreeMap
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put("blili",1111);
map.put("alili",2222);
//map.put("blili",3333);
System.out.println(map.put("blili", 3333));
map.put("clili",5555);
map.put("dlili",4444);
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map); //按照升序进行输出abcd
}
}
【2】key的类型是一个自定义的引用数据类型
(1)内部比较器
Student类:
package test2_TreeMap;
import java.util.Comparator;
/**
* @Auther: zhoulz
* @Description: test2_TreeMap
* @version: 1.0
*/
//内部比较器:
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private int age;
private String name;
private double height;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public Student(int age, String name, double height) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", height=" + height +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
//return 0;
//按照年龄进行排序
//return this.getAge() - o.getAge();
//按照名字进行排序
//return this.getName().compareTo(o.getName());
//按照身高进行排序
return ((Double)(this.getHeight())).compareTo((Double)(o.getHeight()));
}
}测试类:
package test2_TreeMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
/**
* @Auther: zhoulz
* @Description: test2_TreeMap
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<Student,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
map.put(new Student(19,"blili",170.5),1111);
map.put(new Student(18,"blili",171.5),2222);
map.put(new Student(19,"alili",172.5),3333);
map.put(new Student(17,"clili",173.5),4444);
map.put(new Student(16,"dlili",174.5),5555);
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map);
//默认使用的是内部比较器
}
}
(2)外部比较器
Student类:
package test2_TreeMap.external_comparator;
/**
* @Auther: zhoulz
* @Description: test2_TreeMap
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Student {
private int age;
private String name;
private double height;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height) {
this.height = height;
}
public Student(int age, String name, double height) {
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.height = height;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"age=" + age +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", height=" + height +
'}';
}
}
//外部比较器: —— 可以直接在测试类中写!!!
测试类:
package test2_TreeMap.external_comparator;
import test2_TreeMap.Student;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.TreeMap;
/**
* @Auther: zhoulz
* @Description: test2_TreeMap
* @version: 1.0
*/
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//直接将外部比较器定义在这里:
Map<Student,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
//return 0;
//比较身高: — 这时候,两个年龄19岁的都能输出了
return ((Double)(o1.getHeight())).compareTo((Double)(o2.getHeight()));
}
});
map.put(new Student(19,"blili",170.5),1111);
map.put(new Student(18,"blili",171.5),2222);
map.put(new Student(19,"alili",172.5),3333);
map.put(new Student(17,"clili",173.5),4444);
map.put(new Student(16,"dlili",174.5),5555);
System.out.println(map.size());
System.out.println(map);
}
}






















 2882
2882











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








