一、Android控件架构
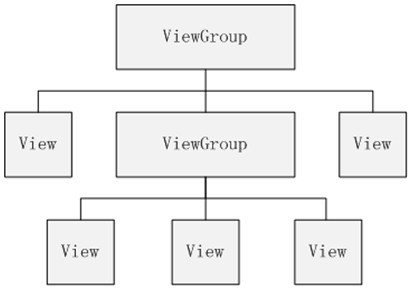
如图所示啦,上面就是我们常见的控件树,上层控件负责下层子控件的测量与绘制,并传递交互事件。
通常在Activity中使用 findViewById() 的方法在控件树中以树的深度优先遍历来查找对应的元素。
每棵树的顶部其实还有一个ViewParent对象,它是整棵树的控制核心,图中并没有标识出来,所有的交互管理事件都由它来统一调度和分配,从而可以对整个视图进行整体控制。
通常情况下,在Activity中使用setContentView()方法来设置一个布局,在调用该方法后,布局内容才真正的显示出来。
这是Android界面的架构图:
1、其中DecorView作为窗口界面的顶层视图,封装了一些窗口操作的通用方法。
可以说,DecorView将要显示的具体内容呈现在了PhoneWindow上,这里面的所有的View的监听事件,都通过WindowManagerService进行接收,并通过Activity对象来回调相应的onClickListener。
2、其中ContentView,是一个ID为content的FrameLayout,activity_main.xml 就是设置在这样一个FrameLayout里,所以之前在布局优化中讲过,最外层是一个FrameLayout,所以当activity_main.xml最外层是一个FrameLayout会造成层次层叠,用merge来代替FrameLayout进行布局的优化。
3、所以这也就说明了,用户通过设置 requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); 来设置全屏显示的时候,它一定要放在 setContentView() 方法之前才能生效。
4、在代码中,当程序在 onCreat() 方法中调用 setContentView()方法后,ActivityManagerService会回调 onResume()方法,此时系统才会把整个DecorView添加到 PhoneWindow中,并让其显示出来,从而最终完成界面的绘制。
5、在源码中ViewGroup是继承自View的!!!!!
二、ViewRoot和DecorView介绍
1、ViewRoot简介:
(1)ViewRoot对应于ViewRootImpl 类,它是连接 WindowManager 和 DecorView的纽带,View的三大流程(measure测量、layout布局、draw绘制)都是通过ViewRoot来完成的。
(2)在ActivityThread 中,当Activity对象被创建完毕后,会将 DecorView 添加到Window中,同时会创建 ViewRootImpl对象,并将 ViewRootImpl对象和DecorView建立关联,看源码(没找到呀,惭愧):
root = new ViewRootImpl(view.getContext(), display);
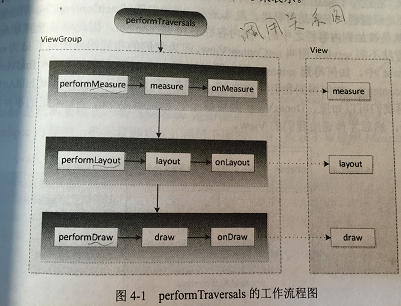
root.setView(view, wparams, panelParentView);它经过 measure、layout和draw三个过程才能最终将一个View绘制出来,
其中measure用来测量View的宽高,
layout用来确定View在父容器中的放置位置,
draw负责将View绘制在屏幕上。
(4)下面是performTraversals 的大致流程:
源码位置:sources\android\view\ViewRootImpl.java
在onMeasure方法中会对所有的子元素进行measure过程,这个时候measure流程就从父容器传递到子元素中了,这样就完成了一次measure过程。接着子元素又会重复父容器的measure过程,如此反复就完成了整个View树的遍历。
performDraw的传递过程是在draw方法中通过dispatchDraw来实现的。
(4)Measure完成后,可以通过 getMeasuredWidth 和getMeasuredHeight 方法来获取到 View 测量后的宽高。
Layout完成后,可以通过 getTop、getBottom、getLeft和getRight 来拿到View的四个顶点的位置,并可以通过 getWidth 和getHeight方法来拿到View的最终宽高。
Draw完成后,View显示在屏幕上。
2、DecorView简介:
(1)DecorView作为顶级View,它内部是一个竖直的LinearLayout,其中包含TitleBar和Content。
(2)其中Activity中设置 setContentView 就是将布局文件加载到内容栏的。
(3)内容栏是一个FrameLayout,可以布局优化。
(4)如何获得Content?
ViewGroup content = findViewById(R.android.id.content);
(5)如何获得View?
content.getChildAt(0);
三、View的测量
1、MeasureSpec简介:
(1)源码位置:sources\android\view\View.java
(2)Android系统在绘制View前,必须对View进行测量,这个过程在onMeasure()方法中进行,借助的是 MeasureSpec 类。
MeasureSpec类是一个32位的值,其中高2位为测量的模式SpecMode,低30位为测量的大小SpecSize。
public static class MeasureSpec {
// 移位用的,后面表示大小的30位
private static final int MODE_SHIFT = 30;
private static final int MODE_MASK = 0x3 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has not imposed any constraint
* on the child. It can be whatever size it wants.
*/
/*
* dp/px
* 父容器对子元素没有任何约束,子元素可以是任意大小
* */
public static final int UNSPECIFIED = 0 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The parent has determined an exact size
* for the child. The child is going to be given those bounds regardless
* of how big it wants to be.
*/
/*
* match_parent
* 父容器决定了子元素的大小,子元素和父元素一样大
* */
public static final int EXACTLY = 1 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Measure specification mode: The child can be as large as it wants up
* to the specified size.
*/
/*
* wrap_content
* 子元素不可以超过父容器的大小。
* 通常的控件对这个值都会设定一个默认值来表示wrap_content。
* */
public static final int AT_MOST = 2 << MODE_SHIFT;
/**
* Creates a measure specification based on the supplied size and mode.
*
* The mode must always be one of the following:
* <ul>
* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED}</li>
* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}</li>
* <li>{@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST}</li>
* </ul>
*
* <p><strong>Note:</strong> On API level 17 and lower, makeMeasureSpec's
* implementation was such that the order of arguments did not matter
* and overflow in either value could impact the resulting MeasureSpec.
* {@link android.widget.RelativeLayout} was affected by this bug.
* Apps targeting API levels greater than 17 will get the fixed, more strict
* behavior.</p>
*
* @param size the size of the measure specification
* @param mode the mode of the measure specification
* @return the measure specification based on size and mode
*/
/*
* 将size和mode打包成一个32位的int值返回:
* */
public static int makeMeasureSpec(int size, int mode) {
if (sUseBrokenMakeMeasureSpec) {
return size + mode;
} else {
return (size & ~MODE_MASK) | (mode & MODE_MASK);
}
}
/**
* Extracts the mode from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the mode from
* @return {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#UNSPECIFIED},
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#AT_MOST} or
* {@link android.view.View.MeasureSpec#EXACTLY}
*/
public static int getMode(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & MODE_MASK);
}
/**
* Extracts the size from the supplied measure specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to extract the size from
* @return the size in pixels defined in the supplied measure specification
*/
public static int getSize(int measureSpec) {
return (measureSpec & ~MODE_MASK);
}
static int adjust(int measureSpec, int delta) {
return makeMeasureSpec(getSize(measureSpec + delta), getMode(measureSpec));
}
/**
* Returns a String representation of the specified measure
* specification.
*
* @param measureSpec the measure specification to convert to a String
* @return a String with the following format: "MeasureSpec: MODE SIZE"
*/
public static String toString(int measureSpec) {
int mode = getMode(measureSpec);
int size = getSize(measureSpec);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("MeasureSpec: ");
if (mode == UNSPECIFIED)
sb.append("UNSPECIFIED ");
else if (mode == EXACTLY)
sb.append("EXACTLY ");
else if (mode == AT_MOST)
sb.append("AT_MOST ");
else
sb.append(mode).append(" ");
sb.append(size);
return sb.toString();
}
}MeasureSpec的测量模式有三种:
(1)EXACTLY:具体值或者 match_parent。onMeasure()方法默认情况下只支持这种模式。
(2)AT_MOST:wrap_content。不可以比父容器大就可以了,不过通常控件都会有一个默认值。
(3)UNSPECIFIED:View想多大就多大,通常自定义View时使用。
注意点:要让自定义View支持 wrap_content 属性,就必须重写onMeasure()方法来指定wrap_content时的大小。
2、MeasureSpec和LayoutParams的对应关系:
下面来看看顶级View即DecorView在ViewRootImpl中的源码:
(1)DecorView的MeasureSpec创建过程。在measureHierarchy函数中有如下的语句:
if (baseSize != 0 && desiredWindowWidth > baseSize) {
childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(baseSize, lp.width);
childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(desiredWindowHeight, lp.height);
performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);......if下面的两句的作用是获得宽高,第三句就是通过performMeasure来设置宽高了。
(2)接下来看看里面的getRootMeasureSpec 方法:
/**
* Figures out the measure spec for the root view in a window based on it's
* layout params.
*
* @param windowSize
* The available width or height of the window
*
* @param rootDimension
* The layout params for one dimension (width or height) of the
* window.
*
* @return The measure spec to use to measure the root view.
*/
private static int getRootMeasureSpec(int windowSize, int rootDimension) {
int measureSpec;
switch (rootDimension) {
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT:
// Window can't resize. Force root view to be windowSize.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
case ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT:
// Window can resize. Set max size for root view.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(windowSize, MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
break;
default:
// Window wants to be an exact size. Force root view to be that size.
measureSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(rootDimension, MeasureSpec.EXACTLY);
break;
}
return measureSpec;
}下面看看普通的View,这里是指我们布局中的View:
(1)View的measure过程由ViewGroup传递而来,先看一下ViewGroup的measureChildWithMargins 方法:
/**
* Ask one of the children of this view to measure itself, taking into
* account both the MeasureSpec requirements for this view and its padding
* and margins. The child must have MarginLayoutParams The heavy lifting is
* done in getChildMeasureSpec.
*
* @param child The child to measure
* @param parentWidthMeasureSpec The width requirements for this view
* @param widthUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* horizontally (possibly by other children of the parent)
* @param parentHeightMeasureSpec The height requirements for this view
* @param heightUsed Extra space that has been used up by the parent
* vertically (possibly by other children of the parent)
*/
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
/* 也是先获取子元素的MeasureSpec,
* getChildMeasureSpec这里的参数,第一个就变成了父类的大小,
* 第二个参数是上下左右的边距
* 第三个参数是LinearLayout的宽高
*/
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
/*
* 得到子元素的MeasureSpec后,调用子元素的measure来设置宽高。
* */
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}/**
* Does the hard part of measureChildren: figuring out the MeasureSpec to
* pass to a particular child. This method figures out the right MeasureSpec
* for one dimension (height or width) of one child view.
*
* The goal is to combine information from our MeasureSpec with the
* LayoutParams of the child to get the best possible results. For example,
* if the this view knows its size (because its MeasureSpec has a mode of
* EXACTLY), and the child has indicated in its LayoutParams that it wants
* to be the same size as the parent, the parent should ask the child to
* layout given an exact size.
*
* @param spec The requirements for this view
* @param padding The padding of this view for the current dimension and
* margins, if applicable
* @param childDimension How big the child wants to be in the current
* dimension
* @return a MeasureSpec integer for the child
*/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
/*
* 第一个参数是父类的MeasureSpec,所以获取的模式也就是父容器的:
* */
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
//子元素可用大小为父容器尺寸减去padding:
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
/*
* 这里的这个specMode是父类容器的:
* */
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
/*
* 这里的LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT就是子元素它的LinearLayout
* */
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = 0;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}就是说只要子元素的LinearLayout是精确值,那子元素就是精确值。
子元素如果是match_parent,那子元素就和父容器一样大小。
子元素如果是wrap_content,那子元素就不能超过父容器的剩余空间大小。
3、看看具体的onMeasure实现和如何重写这个方法:
(1)原始的onMeasure在源码中是这样的,也就是重写时它自动构成这样:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
} protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}可以发现超类中调用了setMeasuredDimension()方法,它的两个参数是 MeasureSpec 类型变量,这个方法将测量后的宽高值设置进去,从而完成测量工作。
(3)所以当我们想要重写onMeasure()方法时,可以直接重写超类中的setMeasuredDimension()方法,同时自定义两个测量宽高的方法 measureWidth() 和 measureHeight() 来处理 MeasureSpec 类型变量,返回宽高值Size:
在超类中是以getDefaultSize()来处理 MeasureSpec 类型变量的,这里我们换成自己写的 measureWidth() 和 measureHeight() 方法:
(注意啦,这里getDefaultSize返回的是size大小,也就是说将MeasureSpec中的size部分返回。)
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
setMeasuredDimension(
measureWidth(widthMeasureSpec),
measureHeight(heightMeasureSpec));
}(4)下面就看看需要编写的measureWidth()方法如何实现的:
private int measureWidth(int measureSpec) {
int result 







 本文详细介绍了Android控件的架构,包括ViewRoot和DecorView的角色,讲解了View的测量、布局和绘制过程,特别是measure的MeasureSpec概念。此外,探讨了自定义View的注意事项和分类,如扩展现有控件、创建复合控件和全新控件的实现。最后,文章提到了自定义ViewGroup的重点,包括添加子view和响应滑动事件。
本文详细介绍了Android控件的架构,包括ViewRoot和DecorView的角色,讲解了View的测量、布局和绘制过程,特别是measure的MeasureSpec概念。此外,探讨了自定义View的注意事项和分类,如扩展现有控件、创建复合控件和全新控件的实现。最后,文章提到了自定义ViewGroup的重点,包括添加子view和响应滑动事件。


 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 866
866











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








