本文以FileSystemXmlApplicationContext为例说明
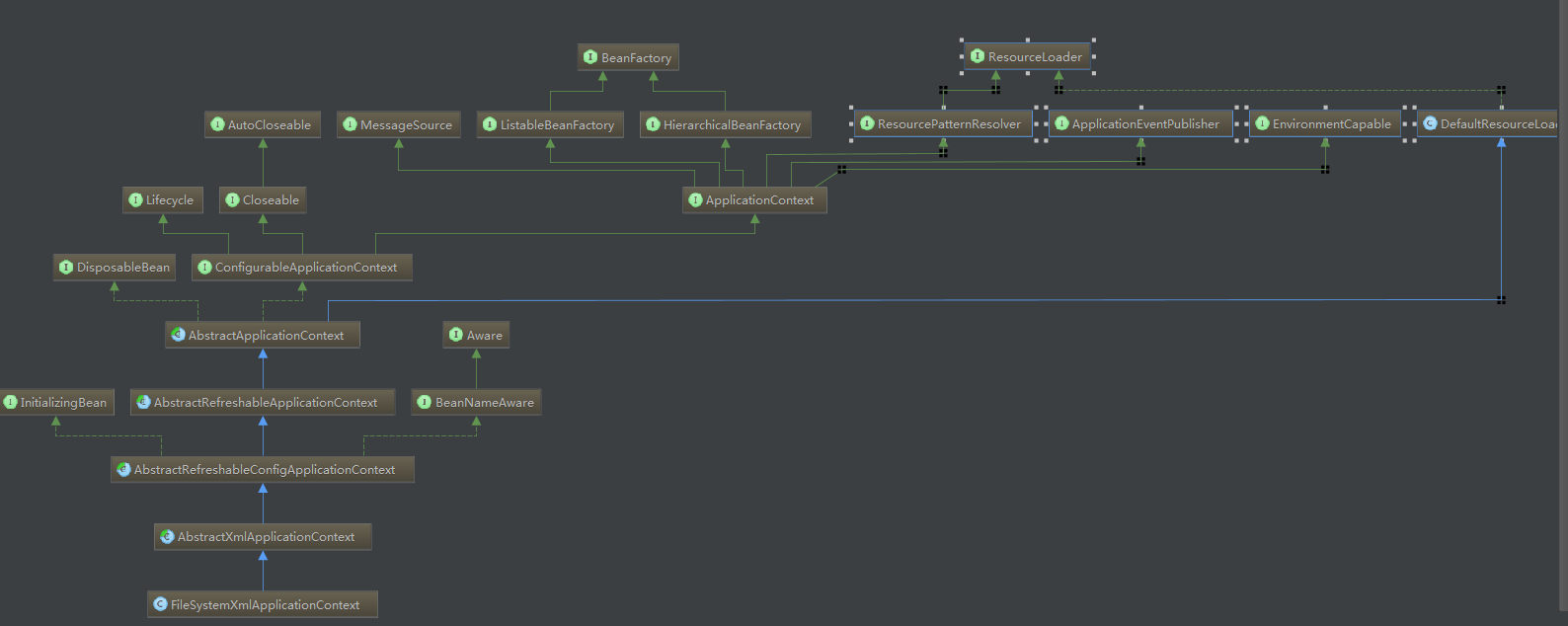
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext继承关系:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
AbstractXmlApplicationContext
AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext(refreshBeanFactory)
AbstractApplicationContext(Refresh)
上面继承层次是从下向上的,有Abstract的全是抽象类
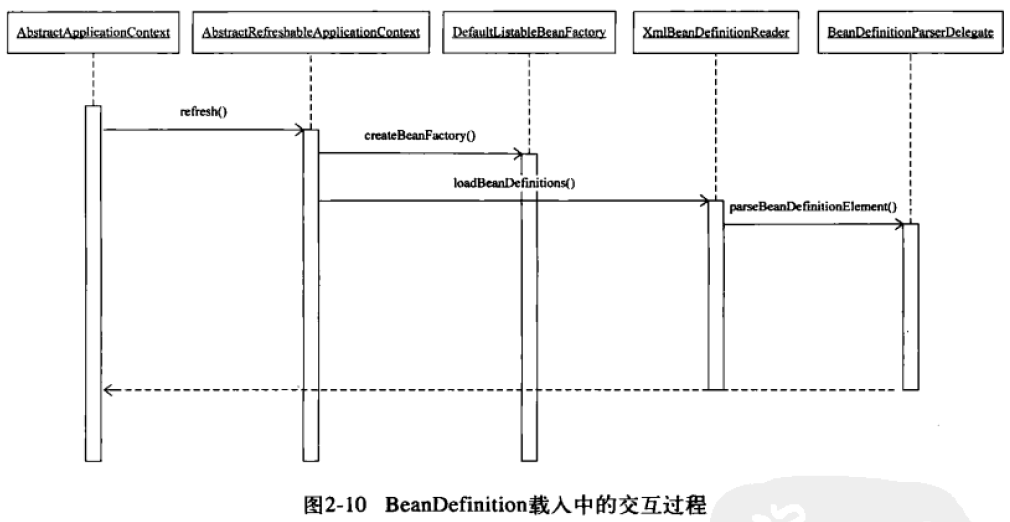
梳理下整个调用关系:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext构造函数
比如new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(“bean.xml”)
public FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
//设置资源文件位置
if (refresh) {
refresh();
//refresh很关键,也是在这里loadBeanDefinition的
}
}AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext的setConfigLocations
把配置文件路径记录在AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext的private String[] configLocations中;
public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法
中间有这么一句:
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// refresh就像重启计算机一样,保证refresh之后使用的是新建立好的IOC容器
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}AbstractApplicationContext的obtainFreshBeanFactory
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的refreshBeanFactory
AbstractApplicationContext中refreshBeanFactory是抽象方法,所以执行的是子类AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
// 创建IOC容器,这里使用的是DefaultListableBeanFactory
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
启动对BeanDefinition的载入
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext的createBeanFactory
// 创建IOC容器
protected DefaultListableBeanFactory createBeanFactory() {
return new DefaultListableBeanFactory(getInternalParentBeanFactory());
}AbstractXmlApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext中loadBeanDefinitions是抽象方法,所以执行的是子类AbstractXmlApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions
这里会new XmlBeanDefinitionReader,用这个类来读取配置
@Override
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}FileSystemXmlApplicationContext的getResourceByPath
找了半天,终于找到了,在继承的最上层,DefaultResourceLoader中。这里调用了模板方法getResourceByPath,这个方法是在FileSystemXmlApplicationContext中重写:
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// Try to parse the location as a URL...
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// No URL -> resolve as resource path.
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}AbstractXmlApplicationContext的loadBeanDefinitions
和步骤6的函数参数不一样,重载了,这里传的是XmlBeanDefinitionReader
先从resource找,如果没有;再从location找,从location最后也需要调用从resource找
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions
这里的最后一步了,loadBeanDefinitions(Resource)是一个模板方法,具体实现需要在子类中重写
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified XML file.
* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the XML file,
* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(encodedResource, "EncodedResource must not be null");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading XML bean definitions from " + encodedResource.getResource());
}
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<EncodedResource>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的doLoadBeanDefinitions
主要是:
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的doLoadDocument
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());DefaultDocumentLoader中的loadDocument
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}XmlBeanDefinitionReader中的registerBeanDefinitions
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}这里分成两部分:
首先调用xml解析器得到document,也就是通用xml解析。
然后按照Spring规则进行解析,在documentReader中实现
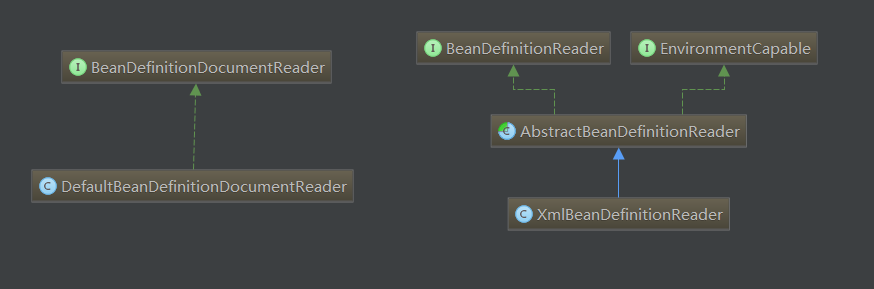
XmlBeanDefinitionReader的createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader
protected BeanDefinitionDocumentReader createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader() {
return BeanDefinitionDocumentReader.class.cast(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(this.documentReaderClass));
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的registerBeanDefinitions
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的doRegisterBeanDefinitions
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的parseBeanDefinitions
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的parseDefaultElement
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的processBeanDefinition
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseBeanDefinitionElement
对Bean元素进行解析
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//这里取得<bean>元素定义的id、name和aliase的值
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<String>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
//这个方法会引发bean元素的详细解析
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix.
// This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility.
String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null;
}
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
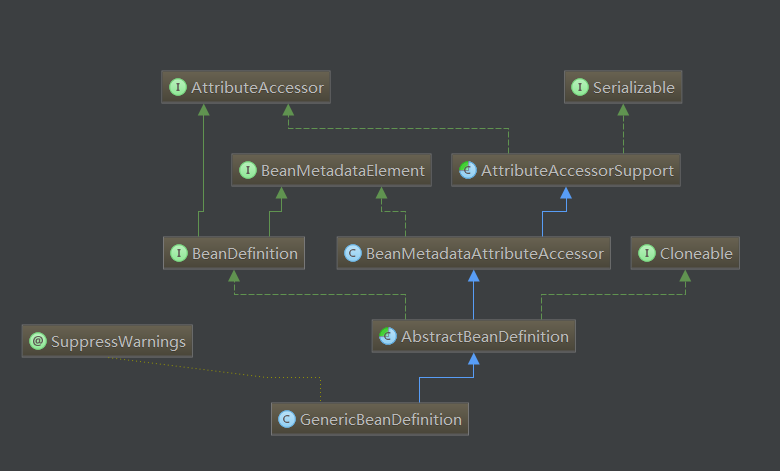
}BeanDefinition的数据封装
这里就是BeanDefinition根据xml定义被创建的过程,BeanDefinition可以看成是对Bean的抽象,可以看到BeanDefinition的数据封装:
public abstract class AbstractBeanDefinition extends BeanMetadataAttributeAccessor
implements BeanDefinition, Cloneable {
public static final String SCOPE_DEFAULT = "";
/**
* Constant that indicates no autowiring at all.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_NO = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_NO;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by name.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by type.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring a constructor.
* @see #setAutowireMode
*/
public static final int AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR;
/**
* Constant that indicates determining an appropriate autowire strategy
* through introspection of the bean class.
* @see #setAutowireMode
* @deprecated as of Spring 3.0: If you are using mixed autowiring strategies,
* use annotation-based autowiring for clearer demarcation of autowiring needs.
*/
@Deprecated
public static final int AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT = AutowireCapableBeanFactory.AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT;
/**
* Constant that indicates no dependency check at all.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE = 0;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for object references.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_OBJECTS = 1;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for "simple" properties.
* @see #setDependencyCheck
* @see org.springframework.beans.BeanUtils#isSimpleProperty
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_SIMPLE = 2;
/**
* Constant that indicates dependency checking for all properties
* (object references as well as "simple" properties).
* @see #setDependencyCheck
*/
public static final int DEPENDENCY_CHECK_ALL = 3;
/**
* Constant that indicates the container should attempt to infer the
* {@link #setDestroyMethodName destroy method name} for a bean as opposed to
* explicit specification of a method name. The value {@value} is specifically
* designed to include characters otherwise illegal in a method name, ensuring
* no possibility of collisions with legitimately named methods having the same
* name.
* <p>Currently, the method names detected during destroy method inference
* are "close" and "shutdown", if present on the specific bean class.
*/
public static final String INFER_METHOD = "(inferred)";
private volatile Object beanClass;
private String scope = SCOPE_DEFAULT;
private boolean abstractFlag = false;
private boolean lazyInit = false;
private int autowireMode = AUTOWIRE_NO;
private int dependencyCheck = DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE;
private String[] dependsOn;
private boolean autowireCandidate = true;
private boolean primary = false;
private final Map<String, AutowireCandidateQualifier> qualifiers =
new LinkedHashMap<String, AutowireCandidateQualifier>(0);
private boolean nonPublicAccessAllowed = true;
private boolean lenientConstructorResolution = true;
private ConstructorArgumentValues constructorArgumentValues;
private MutablePropertyValues propertyValues;
private MethodOverrides methodOverrides = new MethodOverrides();
private String factoryBeanName;
private String factoryMethodName;
private String initMethodName;
private String destroyMethodName;
private boolean enforceInitMethod = true;
private boolean enforceDestroyMethod = true;
private boolean synthetic = false;
private int role = BeanDefinition.ROLE_APPLICATION;
private String description;
private Resource resource;
}
Bean的属性通过解析之后,数据已经在IOC容器中准备大显身手了
之后是对BeanDefinition中定义元素的处理:
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parseBeanDefinitionElement
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
//只读取定义的Bean设置的class名字,然后载入到BeanDefinition中,只是做个记录,不涉及对象的实例化
//实例化是在依赖注入时完成的
String className = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
try {
String parent = null;
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
//生成需要的BeanDefinition对象,为Bean定义信息的载入做准备
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//对当前Bean元素进行属性解析,并设置description信息
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
//对各种Bean元素信息进行解析的地方
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析Bean构造函数设置
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
//解析Bean的property设置
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parsePropertyElements
这里是解析Bean属性
public void parsePropertyElements(Element beanEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
//解析所有Bean元素下定义的property元素
NodeList nl = beanEle.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (isCandidateElement(node) && nodeNameEquals(node, PROPERTY_ELEMENT)) {
//在判断是property元素后对其进行解析的过程
parsePropertyElement((Element) node, bd);
}
}
}
public void parsePropertyElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd) {
//取得property的名字
String propertyName = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(propertyName)) {
error("Tag 'property' must have a 'name' attribute", ele);
return;
}
this.parseState.push(new PropertyEntry(propertyName));
try {
//如果一个Bean已经有同名的property存在,则不进行解析
//只会解析第一个property
if (bd.getPropertyValues().contains(propertyName)) {
error("Multiple 'property' definitions for property '" + propertyName + "'", ele);
return;
}
//解析property值,value会封装到PropertyValue对象中,然后设置到BeanDefinitionHolder中
Object val = parsePropertyValue(ele, bd, propertyName);
PropertyValue pv = new PropertyValue(propertyName, val);
parseMetaElements(ele, pv);
pv.setSource(extractSource(ele));
bd.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(pv);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
}
//取得property元素的值,也许是个list或其他
public Object parsePropertyValue(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String propertyName) {
String elementName = (propertyName != null) ?
"<property> element for property '" + propertyName + "'" :
"<constructor-arg> element";
// Should only have one child element: ref, value, list, etc.
NodeList nl = ele.getChildNodes();
Element subElement = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT) &&
!nodeNameEquals(node, META_ELEMENT)) {
// Child element is what we're looking for.
if (subElement != null) {
error(elementName + " must not contain more than one sub-element", ele);
}
else {
subElement = (Element) node;
}
}
}
//这里判断property属性,是ref还是value,不允许同时是ref或value
boolean hasRefAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean hasValueAttribute = ele.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasRefAttribute && hasValueAttribute) ||
((hasRefAttribute || hasValueAttribute) && subElement != null)) {
error(elementName +
" is only allowed to contain either 'ref' attribute OR 'value' attribute OR sub-element", ele);
}
//如果是ref,创建一个ref数据对象RuntimeBeanReference,这个对象封装了ref信息
if (hasRefAttribute) {
String refName = ele.getAttribute(REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error(elementName + " contains empty 'ref' attribute", ele);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
//如果是value数据对象,创建一个value的数据对象TypeStringValue,这个对象封装了Value信息
else if (hasValueAttribute) {
TypedStringValue valueHolder = new TypedStringValue(ele.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE));
valueHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return valueHolder;
}
//如果还有子元素,就触发对子元素的解析
else if (subElement != null) {
return parsePropertySubElement(subElement, bd);
}
else {
// Neither child element nor "ref" or "value" attribute found.
error(elementName + " must specify a ref or value", ele);
return null;
}
}这里是property子元素的解析过程,Array,List,Set,Map,Prop都会在这里解析,会生成对应的数据对象:ManagedArray,ManagedList,ManagedSet等。
Array、List、Collection等集合元素的parse
对应的解析方法分别是parseArrayElement、parseListElement、parseCollectionElements、parseSetElement、parseMapElement
public Object parseArrayElement(Element arrayEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
String elementType = arrayEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
NodeList nl = arrayEle.getChildNodes();
ManagedArray target = new ManagedArray(elementType, nl.getLength());
target.setSource(extractSource(arrayEle));
target.setElementTypeName(elementType);
target.setMergeEnabled(parseMergeAttribute(arrayEle));
parseCollectionElements(nl, target, bd, elementType);
return target;
}
public List<Object> parseListElement(Element collectionEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
String defaultElementType = collectionEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
NodeList nl = collectionEle.getChildNodes();
ManagedList<Object> target = new ManagedList<Object>(nl.getLength());
target.setSource(extractSource(collectionEle));
target.setElementTypeName(defaultElementType);
target.setMergeEnabled(parseMergeAttribute(collectionEle));
parseCollectionElements(nl, target, bd, defaultElementType);
return target;
}
public Set<Object> parseSetElement(Element collectionEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
String defaultElementType = collectionEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
NodeList nl = collectionEle.getChildNodes();
ManagedSet<Object> target = new ManagedSet<Object>(nl.getLength());
target.setSource(extractSource(collectionEle));
target.setElementTypeName(defaultElementType);
target.setMergeEnabled(parseMergeAttribute(collectionEle));
parseCollectionElements(nl, target, bd, defaultElementType);
return target;
}
protected void parseCollectionElements(
NodeList elementNodes, Collection<Object> target, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultElementType) {
for (int i = 0; i < elementNodes.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = elementNodes.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element && !nodeNameEquals(node, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)) {
target.add(parsePropertySubElement((Element) node, bd, defaultElementType));
}
}
}
/**
* Parse a map element.
*/
public Map<Object, Object> parseMapElement(Element mapEle, BeanDefinition bd) {
String defaultKeyType = mapEle.getAttribute(KEY_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
String defaultValueType = mapEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
List<Element> entryEles = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(mapEle, ENTRY_ELEMENT);
ManagedMap<Object, Object> map = new ManagedMap<Object, Object>(entryEles.size());
map.setSource(extractSource(mapEle));
map.setKeyTypeName(defaultKeyType);
map.setValueTypeName(defaultValueType);
map.setMergeEnabled(parseMergeAttribute(mapEle));
for (Element entryEle : entryEles) {
// Should only have one value child element: ref, value, list, etc.
// Optionally, there might be a key child element.
NodeList entrySubNodes = entryEle.getChildNodes();
Element keyEle = null;
Element valueEle = null;
for (int j = 0; j < entrySubNodes.getLength(); j++) {
Node node = entrySubNodes.item(j);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element candidateEle = (Element) node;
if (nodeNameEquals(candidateEle, KEY_ELEMENT)) {
if (keyEle != null) {
error("<entry> element is only allowed to contain one <key> sub-element", entryEle);
}
else {
keyEle = candidateEle;
}
}
else {
// Child element is what we're looking for.
if (nodeNameEquals(candidateEle, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT)) {
// the element is a <description> -> ignore it
}
else if (valueEle != null) {
error("<entry> element must not contain more than one value sub-element", entryEle);
}
else {
valueEle = candidateEle;
}
}
}
}
// Extract key from attribute or sub-element.
Object key = null;
boolean hasKeyAttribute = entryEle.hasAttribute(KEY_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean hasKeyRefAttribute = entryEle.hasAttribute(KEY_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasKeyAttribute && hasKeyRefAttribute) ||
((hasKeyAttribute || hasKeyRefAttribute)) && keyEle != null) {
error("<entry> element is only allowed to contain either " +
"a 'key' attribute OR a 'key-ref' attribute OR a <key> sub-element", entryEle);
}
if (hasKeyAttribute) {
key = buildTypedStringValueForMap(entryEle.getAttribute(KEY_ATTRIBUTE), defaultKeyType, entryEle);
}
else if (hasKeyRefAttribute) {
String refName = entryEle.getAttribute(KEY_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<entry> element contains empty 'key-ref' attribute", entryEle);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(entryEle));
key = ref;
}
else if (keyEle != null) {
key = parseKeyElement(keyEle, bd, defaultKeyType);
}
else {
error("<entry> element must specify a key", entryEle);
}
// Extract value from attribute or sub-element.
Object value = null;
boolean hasValueAttribute = entryEle.hasAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean hasValueRefAttribute = entryEle.hasAttribute(VALUE_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean hasValueTypeAttribute = entryEle.hasAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
if ((hasValueAttribute && hasValueRefAttribute) ||
((hasValueAttribute || hasValueRefAttribute)) && valueEle != null) {
error("<entry> element is only allowed to contain either " +
"'value' attribute OR 'value-ref' attribute OR <value> sub-element", entryEle);
}
if ((hasValueTypeAttribute && hasValueRefAttribute) ||
(hasValueTypeAttribute && !hasValueAttribute) ||
(hasValueTypeAttribute && valueEle != null)) {
error("<entry> element is only allowed to contain a 'value-type' " +
"attribute when it has a 'value' attribute", entryEle);
}
if (hasValueAttribute) {
String valueType = entryEle.getAttribute(VALUE_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(valueType)) {
valueType = defaultValueType;
}
value = buildTypedStringValueForMap(entryEle.getAttribute(VALUE_ATTRIBUTE), valueType, entryEle);
}
else if (hasValueRefAttribute) {
String refName = entryEle.getAttribute(VALUE_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<entry> element contains empty 'value-ref' attribute", entryEle);
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName);
ref.setSource(extractSource(entryEle));
value = ref;
}
else if (valueEle != null) {
value = parsePropertySubElement(valueEle, bd, defaultValueType);
}
else {
error("<entry> element must specify a value", entryEle);
}
// Add final key and value to the Map.
map.put(key, value);
}
return map;
}BeanDefinitionParserDelegate的parsePropertySubElement
这里是对子元素解析
public Object parsePropertySubElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition bd, String defaultValueType) {
if (!isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
return parseNestedCustomElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
BeanDefinitionHolder nestedBd = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, bd);
if (nestedBd != null) {
nestedBd = decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, nestedBd, bd);
}
return nestedBd;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, REF_ELEMENT)) {
// A generic reference to any name of any bean.
String refName = ele.getAttribute(BEAN_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
boolean toParent = false;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// A reference to the id of another bean in the same XML file.
refName = ele.getAttribute(LOCAL_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
// A reference to the id of another bean in a parent context.
refName = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_REF_ATTRIBUTE);
toParent = true;
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(refName)) {
error("'bean', 'local' or 'parent' is required for <ref> element", ele);
return null;
}
}
}
if (!StringUtils.hasText(refName)) {
error("<ref> element contains empty target attribute", ele);
return null;
}
RuntimeBeanReference ref = new RuntimeBeanReference(refName, toParent);
ref.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return ref;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, IDREF_ELEMENT)) {
return parseIdRefElement(ele);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, VALUE_ELEMENT)) {
return parseValueElement(ele, defaultValueType);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, NULL_ELEMENT)) {
// It's a distinguished null value. Let's wrap it in a TypedStringValue
// object in order to preserve the source location.
TypedStringValue nullHolder = new TypedStringValue(null);
nullHolder.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return nullHolder;
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, ARRAY_ELEMENT)) {
return parseArrayElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, LIST_ELEMENT)) {
return parseListElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, SET_ELEMENT)) {
return parseSetElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, MAP_ELEMENT)) {
return parseMapElement(ele, bd);
}
else if (nodeNameEquals(ele, PROPS_ELEMENT)) {
return parsePropsElement(ele);
}
else {
error("Unknown property sub-element: [" + ele.getNodeName() + "]", ele);
return null;
}
}经过逐层解析,在XML中定义的BeanDefinition被整个载入到IOC容器中,并在容器中建立了数据映射。
POJO对象在IOC中完成了抽象,建立了数据结构,这些数据结构可以以AbstractBeanDefinition为入口,让IOC容器执行索引,查询和操作。
这时候,管理Bean对象的数据准备工作完成。
之后还需要注册,就是把BeanDefinition写入Map中。
propertyValue是在AbstractBeanDefinition的propertyValues里,所有propertyValues用Object来存
private final List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList;BeanDefinition在IOC容器中的注册
在DefaultListableBeanFactory中,是通过一个HashMap来持有BeanDefinition的:
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
/** Map of bean definition objects, keyed by bean name */
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>(256);
}























 346
346

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










