为什么要使用树?
因为树既能像链表那样快速的插入和删除,也能像有序数组那样快速查找。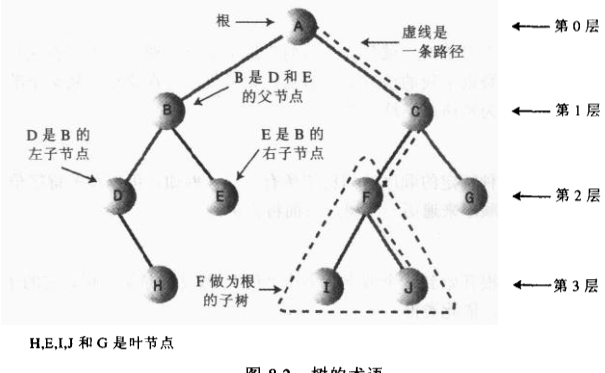
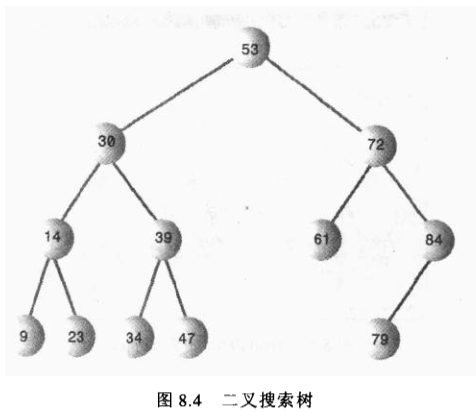
下面是一棵二叉搜索树(二叉查找树BST Binary Search Tree).
二叉查找树的特征可以这样描述:一个节点的左子节点的关键字值小于这个节点,右子节点的关键字值大于或者等于这个父节点。
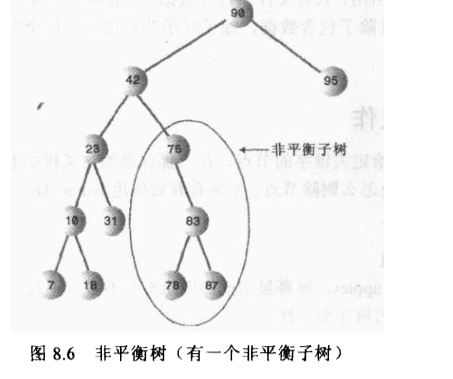
非平衡树,也就是说,它们大部分节点在根的一边或者另一边。
用java代码表示树:
和其他数据结构一样,有很多方法可以在计算机内存中表示树,最常用的方法是把节点存在无关联的存储器中,而通过节点指向中指向自己子节点的引用来连接。
Node类:
首先,需要有一个节点对象的类,这些对象包含数据,数据代表要存储的内容,而且还有指向节点的两个子节点的引用:
public class Node
{
public int iData ; // data item(key)
public double dData; // data item
public Node leftChild; //左子树
public Node rightChild ;//右子树
public void displayNode()
{
System.out.print("{");
System.out.print(iData);
System.out.print(", ");
System.out.println(dData);
System.out.println("} ");
}
}
————————————————————————————————————
Tree类上的操作:
(1)查找节点的java代码
/*
* 二叉树的查找操作
*/
public Node find(int key)// 参数key是要找到的值
{
//查找从根节点开始(只有根节点可以直接访问)
Node current = root;
while(current.iData != key) //key与当前节点的字段值比较
{
if(key <current.iData) // key小于当前数据域的值
//将current设为此节点的左子节点
current =current.leftChild;
else
//将current设为此节点的右子节点
current =current.rightChild;
if(current ==null) //如果没有子节点了
return null; //没有找到,返回空
}
//循环的出口是找到节点来
return current; //否则找到了,返回
}——————————————
(2)二叉树的插入操作
/*
* 程序插入节点的第一步是找到它应该插入的位置
* insert()方法从创建新节点开始,用提供的数据作为参数
* 下一步,必须先确定新节点插入的位置,这段代码与查找节点大致相同
* 区别在于 ,现在要插入一个节点,就在返回前插入
* 要找的值是从参数id传入的,while循环用true做为条件
* 因为它不关心是否会遇到和id值一样的节点;它把那个有相同关键字值的节点当作大的节点处理。
* 插入节点的位置总会找到;找到后,新节点被接到树上。while退出
* 用一个新的变量 parent 用来存储最后一个不是null的节点
*
*/
public void insert(int id,double dd)
{
Node newNode = new Node(); //建立一个新节点
newNode.iData =id; //插入数据
newNode.dData =dd;
if(root ==null)
root = newNode;
else
{
Node current = root; //start at root
Node parent;
while(true)
{
parent =current;
if(id < current.iData)
{
current =current.leftChild;
if(current == null)
{
parent.leftChild =newNode;
return;
}
}
else
{
current = current.rightChild;
if(current ==null)
{
current = current.rightChild;
}
}
}
}
}
——————————
(3)二叉树的遍历操作
/********************************************************/
/*
* 前序遍历
*/
private void preOrder(Node localRoot)
{
if(localRoot != null)
{
//打印出根节点的值
System.out.println(localRoot.iData+” “);
//递归调用自身,打印左右节点的值
preOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
preOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
}
}
/************************************************/
/*
* 中序遍历,先打印左子节点,再打印根节点,再打印右子节点
* 同样使用递归调用的方式
*/
private void inOrder(Node localRoot)
{
if(localRoot != null)
{
inOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
System.out.println(localRoot.iData+" ");
inOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
}
}
/************************************************/
/*
* 后序遍历
*/
private void postOrder(Node localRoot)
{
if(localRoot != null)
{
postOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
postOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
System.out.println(localRoot.iData+" ");
}
}
————————————————————
删除节点:
* 删除节点:
* 删除节点要从查找要删的节点开始,方法与前面的find()和insert()相同
* 但是找到节点后,这个要删除的节点有三种情况要考虑:
* 1.该节点是叶节点(没有子节点) 2.该节点有一个子节点3 该节点有两个子节点
*
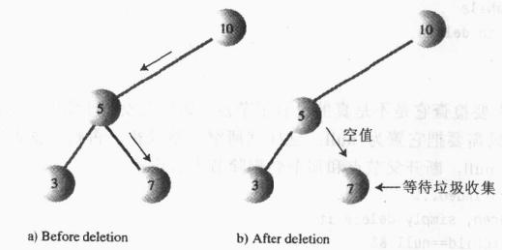
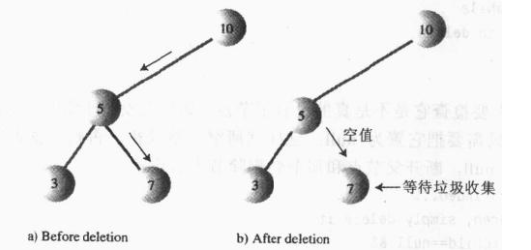
情况1:删除没有子节点的节点。
要删除叶节点,只需要改变该节点的父节点的对应子字段的值,由指向该节点改为null就可以了,要删除的节点仍然存在,但已经不是树的一部分了
因为java语言有垃圾自动回收的机制,所以不需要非得把节点给删掉。一旦java意识到程序不再与这个节点有关联,就会自动把它清理出存储器。
delete()方法的第一部分和find()和insert()很像,它查找要删除的节点。和insert()一样,需要保存要删 节点的父节点,这样姐可以修改它的子字段的值了。如果找到节点了,就从while循环中退出,parent保存要删除的节点,如果找不到要删除的节点,就从delete()方法中返回false。
情况2:删除有一个子节点的节点
这个节点只有两个连接,连向父节点的和连向它唯一的子节点的。需要从这个序列中剪断这个节点,把它的子节点连接到它的父节点上。这个过程要求改变父节点适当的引用(左子节点还是右子节点),指向要删除节点的子节点。
用代码处理有一个子节点的情况。有四种不同的情况:要删除节点的子节点可能有左子节点或者右子节点。并且每种情况中要删除节点也可能是自己父亲节点的左子节点或者右子节点。
还有一种特殊情况:被删除的节点可能是根,它没有父亲节点,只是被合适的子树说代替。
情况3:
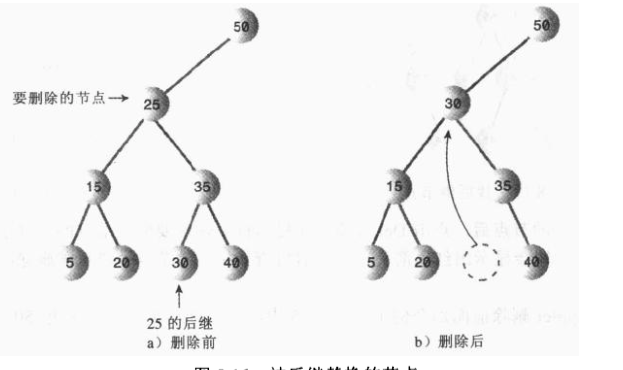
删除有两个子节点的节点
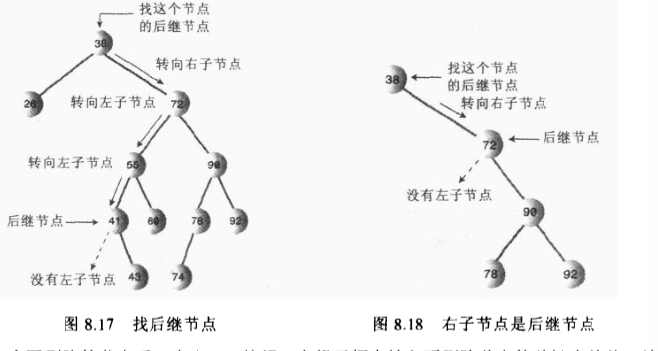
关键:找后继节点
算法:首先,程序找到初始节点的右子节点,它的关键字值一定比初始节点大。然后转到初始节点的右子节点(如果有的话),然后找到这个左子节点的左子节点,依次类推,顺着左子节点的路径一直向下找,这个路径的最后一个左子节点就是初始节点的后继。
如果初始节点 的右子节点没有左子节点,那么这个右子节点本身就是后继。
3)删除节点的代码(包含三种情况)
public boolean delete(int key)
{
Node current =root;
Node parent =root;
boolean isLeftChild = true;
while(current.iData != key)
{
parent = current;
if(key <current.dData)
{
isLeftChild =true;
current = current.leftChild;
}
else
{
isLeftChild = false;
current = current.rightChild;
}
if(current == null)
return false;
/*
* 找到节点后,先要检查它是不是真的没有子节点,如果没有,还要检查它是不是根
* 是根,只需将其设置为null;这样就清空了整棵树,否则,就把叶节点的leftChild
* 或者rightChild字段设置为null,断开父节点和要删除节点的连接
*/
if(current.leftChild == null && current.rightChild ==null)
{
if(current ==root)
root= null;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =null;
else
parent.rightChild = null;
}
//若果没有右孩子
else if(current.rightChild == null)
if(current == root)
root = current.leftChild;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =current.leftChild;
else
parent.rightChild =current.leftChild;
//
else if(current.leftChild == null)
{
if(current == root)
root = current.rightChild;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =current.rightChild;
else
parent.rightChild =current.rightChild;
//two children
{
Node successor = getSuccessor(current);
if(current == root)
root = successor;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =successor;
else
parent.rightChild = successor;
successor.leftChild =current.leftChild;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/*
* 下面是getSuccessor()方法的代码,它返回参数delNode的后继节点
* 这个方法默认delNode有右子节点,因为前提就是要删除的节点有两个子节点
* delNode 是要删除节点
*/
private Node getSuccessor(Node delNode)
{
Node successorParent = delNode;
Node successor = delNode;
Node current = delNode.rightChild; //首先找到delNode的右子节点
while(current != null)//循环终止时,succssor就存有delNode的后继
{
//找到后继后,还需要访问它的父节点,所以在while循环中还需要保存当前节点的父节点
successorParent = successor;
successor = current;
current=current.leftChild;
}
if(successor != delNode.rightChild)
{
successorParent.leftChild = successor.rightChild;
successor.rightChild = delNode.rightChild;
}
return successor;
}
————————————
(4)输出树的操作
public void displayTree()
{
Stack globalStack =new Stack();
globalStack.push(root);
int nBlanks =32;
boolean isRowEmpty = false;
System.out.println(“……………………………”);
while(isRowEmpty ==false)
{
Stack localStack =new Stack();
isRowEmpty =true;
for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++)
{
System.out.println(' ');
while(globalStack.isEmpty() == false)
{
Node temp = (Node)globalStack.pop();
if(temp != null)
{
System.out.println(temp.iData);
localStack.push(temp.leftChild);
localStack.push(temp.rightChild);
if(temp.leftChild != null || temp.rightChild != null)
isRowEmpty =false;
}
else
{
System.out.println("..");
localStack.push(null);
localStack.push(null);
}
for (int j = 0; j < nBlanks *2-2; j++)
{
System.out.println(' ');
}
System.out.println();
nBlanks /=2;
while(localStack.isEmpty() ==false)
globalStack.push(localStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(".......................................");
}
}
}
——————————-
二叉树所有操作完整代码:
import java.util.Stack;
public class Tree
{
private Node root; //根节点
public Tree() //构造方法
{
root =null;
}
/*
* 二叉树的查找操作
*/
public Node find(int key)// 参数key是要找到的值
{
//查找从根节点开始(只有根节点可以直接访问)
Node current = root;
while(current.iData != key) //key与当前节点的字段值比较
{
if(key <current.iData) // key小于当前数据域的值
//将current设为此节点的左子节点
current =current.leftChild;
else
//将current设为此节点的右子节点
current =current.rightChild;
if(current ==null) //如果没有子节点了
return null; //没有找到,返回空
}
//循环的出口是找到节点来
return current; //否则找到了,返回
}
/*
* 程序插入节点的第一步是找到它应该插入的位置
* insert()方法从创建新节点开始,用提供的数据作为参数
* 下一步,必须先确定新节点插入的位置,这段代码与查找节点大致相同
* 区别在于 ,现在要插入一个节点,就在返回前插入
* 要找的值是从参数id传入的,while循环用true做为条件
* 因为它不关心是否会遇到和id值一样的节点;它把那个有相同关键字值的节点当作大的节点处理。
* 插入节点的位置总会找到;找到后,新节点被接到树上。while退出
* 用一个新的变量 parent 用来存储最后一个不是null的节点
*
*/
public void insert(int id,double dd)
{
Node newNode = new Node(); //建立一个新节点
newNode.iData =id; //插入数据
newNode.dData =dd;
if(root ==null)
root = newNode;
else
{
Node current = root; //start at root
Node parent;
while(true)
{
parent =current;
if(id < current.iData)
{
current =current.leftChild;
if(current == null)
{
parent.leftChild =newNode;
return;
}
}
else
{
current = current.rightChild;
if(current ==null)
{
current = current.rightChild;
}
}
}
}
}
/*
* 遍历树:中序遍历
* 中序遍历二叉搜索树会使所有的节点按关键字值升序被访问到。
* 遍历树的最简单方法是使用递归的方法。
* 用递归的方法遍历整棵树要用一个节点作为参数,初始化时这个节点是根,这个方法只需做三件事
* 1.调用自身来遍历节点的左子树2.访问这个节点3调用自身来遍历节点的右子树
* 此递归的基值条件(递归出口)是,作为参数传入的节点等于null时,就是终止条件。
*/
//
// private void inOrder(Node localRoot)
// {
// if(localRoot != null)
// {
// inOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
// System.out.println(localRoot.iData+" ");
// inOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
// }
// }
//
/*
* 删除节点:
* 删除节点要从查找要删的节点开始,方法与前面的find()和insert()相同
* 但是找到节点后,这个要删除的节点有三种情况要考虑:
* 1.该节点是叶节点(没有子节点) 2.该节点有一个子节点3该节点有两个子节点
*
*
*
*/
public boolean delete(int key)
{
Node current =root;
Node parent =root;
boolean isLeftChild = true;
while(current.iData != key)
{
parent = current;
if(key <current.dData)
{
isLeftChild =true;
current = current.leftChild;
}
else
{
isLeftChild = false;
current = current.rightChild;
}
if(current == null)
return false;
/*
* 找到节点后,先要检查它是不是真的没有子节点,如果没有,还要检查它是不是根
* 是根,只需将其设置为null;这样就清空了整棵树,否则,就把叶节点的leftChild
* 或者rightChild字段设置为null,断开父节点和要删除节点的连接
*/
if(current.leftChild == null && current.rightChild ==null)
{
if(current ==root)
root= null;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =null;
else
parent.rightChild = null;
}
//若果没有右孩子
else if(current.rightChild == null)
if(current == root)
root = current.leftChild;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =current.leftChild;
else
parent.rightChild =current.leftChild;
//
else if(current.leftChild == null)
{
if(current == root)
root = current.rightChild;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =current.rightChild;
else
parent.rightChild =current.rightChild;
//two children
{
Node successor = getSuccessor(current);
if(current == root)
root = successor;
else if(isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild =successor;
else
parent.rightChild = successor;
successor.leftChild =current.leftChild;
}
}
}
return true;
}
/*
* 下面是getSuccessor()方法的代码,它返回参数delNode的后继节点
* 这个方法默认delNode有右子节点,因为前提就是要删除的节点有两个子节点
* delNode 是要删除节点
*/
private Node getSuccessor(Node delNode)
{
Node successorParent = delNode;
Node successor = delNode;
Node current = delNode.rightChild; //首先找到delNode的右子节点
while(current != null)//循环终止时,succssor就存有delNode的后继
{
//找到后继后,还需要访问它的父节点,所以在while循环中还需要保存当前节点的父节点
successorParent = successor;
successor = current;
current=current.leftChild;
}
if(successor != delNode.rightChild)
{
successorParent.leftChild = successor.rightChild;
successor.rightChild = delNode.rightChild;
}
return successor;
}
/* ***********************************************/
public void traverse(int traverseType)
{
switch(traverseType)
{
case 1:System.out.println("\nPreorder traversal; ");
preOrder(root);
break;
case 2:System.out.println("\nInorder traversal; ");
inOrder(root);
break;
case 3:System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal; ");
postOrder(root);
break;
}
System.out.println();
}
/******************************************************************/
/*
* 前序遍历
*/
private void preOrder(Node localRoot)
{
if(localRoot != null)
{
//打印出根节点的值
System.out.println(localRoot.iData+" ");
//递归调用自身,打印左右节点的值
preOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
preOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
}
}
/************************************************/
/*
* 中序遍历,先打印左子节点,再打印根节点,再打印右子节点
* 同样使用递归调用的方式
*/
private void inOrder(Node localRoot)
{
if(localRoot != null)
{
inOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
System.out.println(localRoot.iData+" ");
inOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
}
}
/************************************************/
/*
* 后序遍历
*/
private void postOrder(Node localRoot)
{
if(localRoot != null)
{
postOrder(localRoot.leftChild);
postOrder(localRoot.rightChild);
System.out.println(localRoot.iData+" ");
}
}
public void displayTree()
{
Stack globalStack =new Stack();
globalStack.push(root);
int nBlanks =32;
boolean isRowEmpty = false;
System.out.println(".................................");
while(isRowEmpty ==false)
{
Stack localStack =new Stack();
isRowEmpty =true;
for (int i = 0; i < nBlanks; i++)
{
System.out.println(' ');
while(globalStack.isEmpty() == false)
{
Node temp = (Node)globalStack.pop();
if(temp != null)
{
System.out.println(temp.iData);
localStack.push(temp.leftChild);
localStack.push(temp.rightChild);
if(temp.leftChild != null || temp.rightChild != null)
isRowEmpty =false;
}
else
{
System.out.println("..");
localStack.push(null);
localStack.push(null);
}
for (int j = 0; j < nBlanks *2-2; j++)
{
System.out.println(' ');
}
System.out.println();
nBlanks /=2;
while(localStack.isEmpty() ==false)
globalStack.push(localStack.pop());
}
System.out.println(".......................................");
}
}
}
}











 本文介绍了二叉搜索树(BST)的概念及其特性,包括如何使用Java实现树节点类、插入节点、前序遍历、删除节点以及输出树的操作。二叉搜索树允许快速查找、插入和删除操作,其中删除操作分为删除无子节点、一个子节点和两个子节点的节点三种情况。
本文介绍了二叉搜索树(BST)的概念及其特性,包括如何使用Java实现树节点类、插入节点、前序遍历、删除节点以及输出树的操作。二叉搜索树允许快速查找、插入和删除操作,其中删除操作分为删除无子节点、一个子节点和两个子节点的节点三种情况。















 67
67











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








