本文是观看斯坦福大学吴恩达老师的机器学习视频后的一些心得体会和总结,以及作业题中的关键代码,大家可以共同讨论进步。
之前的线形回归是对结果为连续量的数据集做出一个拟合,比如拟合出一条直线,而逻辑回归是要对结果为离散量的数据集能够产生一个预测机制,比如输出为0或者1,这就是一个离散量的输出,不管输入何值,输出必然是0或者是1,所以,逻辑回归要做的事情就是预测结果是0还是1,进一步说,就是做一个分类器。
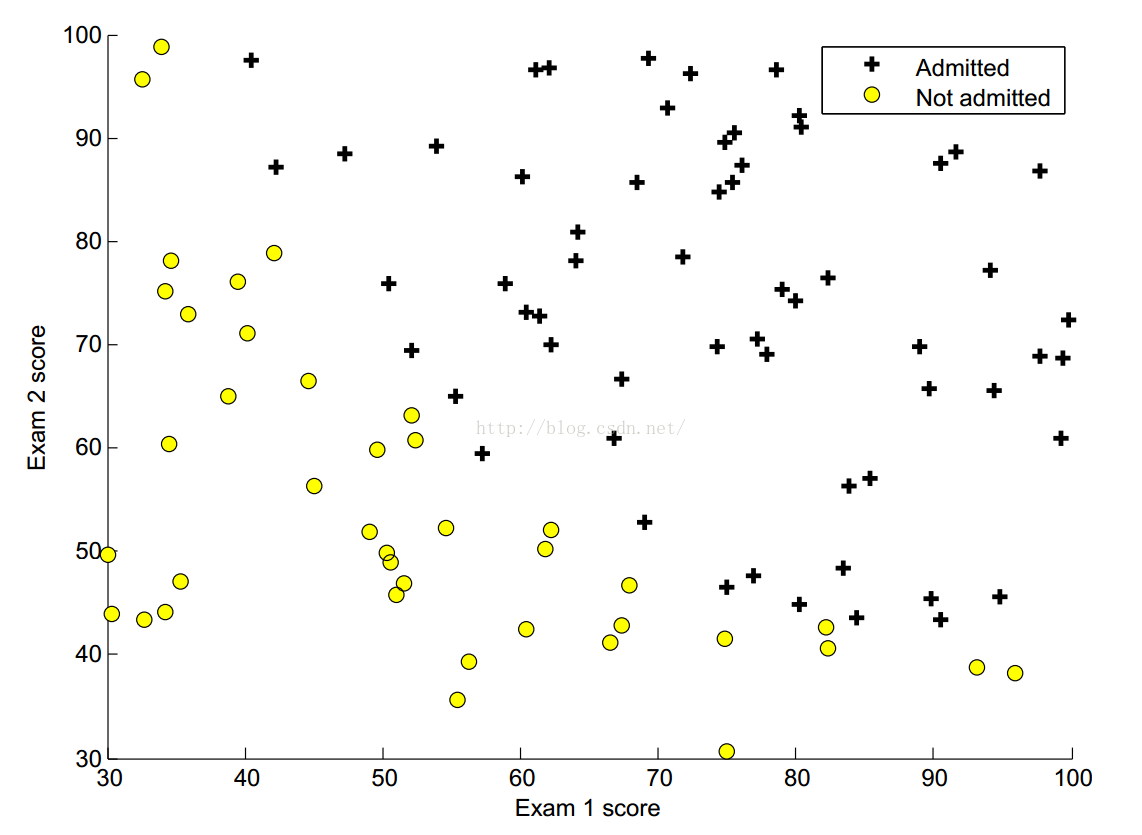
作业中,我们有这样一个数据集,输入为X1,X2,而输出则是0或是1,我们可以运用如下代码,画出更为直观的图像。
% Find Indices of Positive and Negative Examples
pos = find(y==1); neg = find(y == 0);
% Plot Examples
plot(X(pos, 1), X(pos, 2), 'k+','LineWidth', 2, ...
'MarkerSize', 7);
plot(X(neg, 1), X(neg, 2), 'ko', 'MarkerFaceColor', 'y', ...
'MarkerSize', 7);我们得到的图像
线性回归中,h=X*theta',但是对于我们逻辑回归,由于输出是离散的,所以继续套用这个公式,很明显得到的输出值不是我们想要的,于是我们引入了一个函数sigmoid(z)=1/(1+exp(-z)),我们令z=X*theta‘,则h=sigmoid(X*theta')。由于sigmoid函数大于0小于1,以(0,0.5)中心对称,当h大于0.5时,我们就预测结果是1,反之同理,而这个时候的h就表示是预测的准确率,比如h=0.98,那么结果等于1 的几率就是0.98,h=0.12,我们就可以说结果等于0的概率是0.88 。
那么如何求出我们theta呢,思想还是一样的,最小化代价函数,梯度下降法。
逻辑回归的代价函数,以及梯度和线性回归是不一样的:
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
%
% Note: grad should have the same dimensions as theta
J=-1/m*(y'*log(sigmoid(X*theta))+(1-y)'*log(1-sigmoid(X*theta)));
grad=-1/m*X'*(y-sigmoid(X*theta));
然后在作业中,老师已经给我们写好了使用fminuc函数的代码,通过计算,就可以得到最优的theta
% Set options for fminunc
options = optimset('GradObj', 'on', 'MaxIter', 400);
% Run fminunc to obtain the optimal theta
% This function will return theta and the cost
[theta, cost] = ...
fminunc(@(t)(costFunction(t, X, y)), initial theta, options);将我们的模型画到图像上更直观的来看,就是一个分类器,划分出不同区域。
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
% your learned logistic regression parameters.
% You should set p to a vector of 0's and 1's
%
p=sigmoid(X*theta);
for iter=1:m
if p(iter,1)>=0.5
p(iter,1)=1;
else
p(iter,1)=0;
end
end以上是一个线形分类器,因为我们的theta是两个值的,所以最后得到的分类器也就是一条直线,当我们碰到另一种数据集。
很明显,划分的界限不是线形的,,这时候我们就要把X1,X2的多项式也加到输入里面来,同时增加对应特征值,这时候我们用之前的J和grad去求我们的最优解,我们很容易出现过度拟合(overfit),或者欠拟合(underfit)的情况,所以我们对加入正则化项(regularization)来进行计算。这里有一个lambda,可以进行调节,来控制拟合的情况,防止不良情况出现。
% ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
% Instructions: Compute the cost of a particular choice of theta.
% You should set J to the cost.
% Compute the partial derivatives and set grad to the partial
% derivatives of the cost w.r.t. each parameter in theta
h=sigmoid(X*theta);
J=-1/m*(y'*log(h)+(1-y)'*log(1-h))+lambda/(2*m)*(theta(2:end)'*theta(2:end));
theta_temp=theta;
theta_temp(1)=0;
grad=-1/m*X'*(y-h)+lambda/m*theta_temp;lambda不同时,很明显拟合的情况出现了变化。
以上就是主要内容,逻辑回归以及正则化。








 本文基于吴恩达的机器学习课程,探讨逻辑回归在分类问题中的应用,包括理解逻辑回归从线性回归的差异,sigmoid函数的引入,以及如何通过梯度下降法优化代价函数。此外,还讨论了正则化在防止过拟合和欠拟合中的作用,并通过实例展示了不同lambda值对模型拟合的影响。
本文基于吴恩达的机器学习课程,探讨逻辑回归在分类问题中的应用,包括理解逻辑回归从线性回归的差异,sigmoid函数的引入,以及如何通过梯度下降法优化代价函数。此外,还讨论了正则化在防止过拟合和欠拟合中的作用,并通过实例展示了不同lambda值对模型拟合的影响。

























 795
795

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








