Description
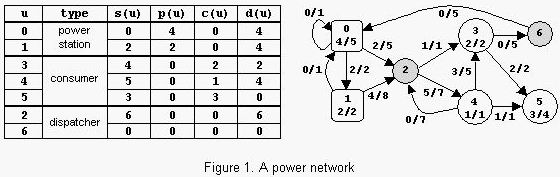
An example is in figure 1. The label x/y of power station u shows that p(u)=x and p max(u)=y. The label x/y of consumer u shows that c(u)=x and c max(u)=y. The label x/y of power transport line (u,v) shows that l(u,v)=x and l max(u,v)=y. The power consumed is Con=6. Notice that there are other possible states of the network but the value of Con cannot exceed 6.
Input
Output
Sample Input
2 1 1 2 (0,1)20 (1,0)10 (0)15 (1)20
7 2 3 13 (0,0)1 (0,1)2 (0,2)5 (1,0)1 (1,2)8 (2,3)1 (2,4)7
(3,5)2 (3,6)5 (4,2)7 (4,3)5 (4,5)1 (6,0)5
(0)5 (1)2 (3)2 (4)1 (5)4
Sample Output
15 6
Hint
The sample input contains two data sets. The first data set encodes a network with 2 nodes, power station 0 with pmax(0)=15 and consumer 1 with cmax(1)=20, and 2 power transport lines with lmax(0,1)=20 and lmax(1,0)=10. The maximum value of Con is 15. The second data set encodes the network from figure 1.
题目大意:
一个电力网络,有m条输电线路,每条线路的参数为(u,v)z,分别表示输电线路的起点终点以及最高输电容量;有n个节点,其中有np个发电站,每个发电站的参数为(u)z,分别表示节点编号和最大发电量,有nc个用户,每个用户的参数为(u)z,分别表示节点编号和最大接受量,问发电站通过该网络到达用户的最多电量。
网络流模板题,典型的增广路算法,需要处理的部分是发电站和用户节点,因为这些节点出现了容量限制,不能直接建图,所以要引入一个源点和一个汇点,源点与所有的发电站建立单向边,所有的用户与汇点建立单向边,建图,在新引入的源点汇点上跑一遍最大流即可。另外还需要注意的是题目的奇葩的格式输入,搞不好就会崩掉。。。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <bitset>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <list>
#include <ctime>
#define STD_REOPEN() freopen("../in.in","r",stdin)
#define STREAM_REOPEN fstream cin("../in.in")
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define _INF 63
#define eps 1e-4
#define MAX_V 100010
#define MAX_P 2010
#define MAX_E 4001000
#define MAX 32000
#define MOD_P 3221225473
#define MOD 9901
using namespace std;
struct edge
{
int from,to,cap,flow;
edge(int u,int v,int c,int f):from(u),to(v),cap(c),flow(f){}
};
struct EdmondsKarp
{
int n,m;
vector<edge> edges;
vector<int> g[MAX_P];
int a[MAX_P];
int p[MAX_P];
void init(int n)
{
this->n=n;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
g[i].clear();
edges.clear();
}
void AddEdge(int from,int to,int cap)
{
edges.push_back(edge(from,to,cap,0));
edges.push_back(edge(to,from,0,0));
m=edges.size();
g[from].push_back(m-2);
g[to].push_back(m-1);
}
int MaxFlow(int s,int t)
{
int flow=0;
while(1)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
queue<int> q;
q.push(s);
a[s]=INF;
while(!q.empty())
{
int x=q.front();
q.pop();
int len=g[x].size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
edge &e=edges[g[x][i]];
if(!a[e.to]&&e.cap>e.flow)
{
p[e.to]=g[x][i];
a[e.to]=min(a[x],e.cap-e.flow);
q.push(e.to);
}
}
if(a[t])
break;
}
if(!a[t])
break;
for(int u=t;u!=s;u=edges[p[u]].from)
{
edges[p[u]].flow+=a[t];
edges[p[u]^1].flow-=a[t];
}
flow+=a[t];
}
return flow;
}
}fl;
int main()
{
//STD_REOPEN();
int n,np,nc,m,u,v,c;
while(~scanf("%d %d %d %d",&n,&np,&nc,&m))
{
fl.init(n+4);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
{
scanf(" (%d,%d)%d",&u,&v,&c);
fl.AddEdge(u,v,c);
}
int ss=n,tt=n+1;
for(int i=0;i<np;i++)
{
scanf(" (%d)%d",&v,&c);
fl.AddEdge(ss,v,c);
}
for(int i=0;i<nc;i++)
{
scanf(" (%d)%d",&u,&c);
fl.AddEdge(u,tt,c);
}
printf("%d\n",fl.MaxFlow(ss,tt));
}
return 0;
}























 460
460

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








