前言
众所周知,HDFS作为一个分布式文件系统.存储着海量的数据,每天的IO读写操作次数当然是非常高的.所以在之前的文章中,我们提到了用HDFS的异构存储来做冷热数据的分类存储,但比较好的一点是,他们还是隶属于同一个集群.那么问题来了,是否我还可以做进一步的改进,优化呢,因为有的数据文件访问在某个时间段是大家公用的,访问频率甚至比一般的热点文件还要高很多.但是过了那个时间点,就又会变为普通的文件.本文就来分享HDFS对于这一需求点的解决方案,HDFS中心缓存管理.这一方面的功能属性,可能也被很多人所忽视了.
HDFS缓存适用场景
首先,我们先要了解HDFS的缓存所适用的场景,换句话说,他能解决我们哪些具体的问题.
缓存HDFS中的热点公共资源文件和短期临时的热点数据文件第一种case: 公共资源文件. 这些文件可以是一些存放于HDFS中的依赖资源jar包,或是一些算法学习依赖.so文件等等.像这类的数据文件,放在HDFS上的好处是,我可以在HDFS上全局共享嘛,不用到本地机器上去依赖,而且好管理,我可以直接更新到HDFS上.但是这种场景更好的做法是把它做成distributed cache,否则在程序中将会发送大量的请求到NameNode中去获取这些资源文件的和内容.而且这种请求量是非常恐怖的,不是说请求一次就够了,而是调用一次,请求一次.
第二种case: 短期临时的热点数据文件.比如集群中每天需要统计的报表数据,需要读取前一天的或是最近一周的数据做离线分析,但是过了这个期限内的基本就很少再用到了,就可以视为冷数据了.那么这个时候就可以把符合这个时间段的数据做缓存处理,然后过期了,就直接从缓存中清除.
以上2种场景,都是HDFS Cache非常适用的场景.
HDFS缓存的结构设计
在HDFS中,最终缓存的本质上还是一个INodeFile文件.但是在逻辑上,引出了下面几个概念.
CacheDirective
CacheDirective是缓存的基本单元,但是这里cacheDirective不一定是一个目录,也可以是一个文件.其中包括以下主要的变量:
public final class CacheDirective implements IntrusiveCollection.Element {
// 惟一标识Id
private final long id;
// 目标缓存路径
private final String path;
// 对应路径的文件副本数
private final short replication;
// 所属CachePool
private CachePool pool;
// 过期时间
private final long expiryTime;
// 相关统计指标
private long bytesNeeded;
private long bytesCached;
private long filesNeeded;
private long filesCached;
...在这里,我们看到了一个新的概念,CachePool,可以得出下面一个结论:
CacheDirective属于对应的CachePool缓存池CachePool
下面就是CachePool概念的定义了
public final class CachePool {
// 缓存池名称
@Nonnull
private final String poolName;
// 所属用户名
@Nonnull
private String ownerName;
// 所属组名
@Nonnull
private String groupName;
// 缓存池权限
/**
* Cache pool permissions.
*
* READ permission means that you can list the cache directives in this pool.
* WRITE permission means that you can add, remove, or modify cache directives
* in this pool.
* EXECUTE permission is unused.
*/
@Nonnull
private FsPermission mode;
// 缓存池最大允许缓存字节数
/**
* Maximum number of bytes that can be cached in this pool.
*/
private long limit;
// 过期时间
/**
* Maximum duration that a CacheDirective in this pool remains valid,
* in milliseconds.
*/
private long maxRelativeExpiryMs;
// 变量统计相关值
private long bytesNeeded;
private long bytesCached;
private long filesNeeded;
private long filesCached;
...
// 缓存对象列表
@Nonnull
private final DirectiveList directiveList = new DirectiveList(this);
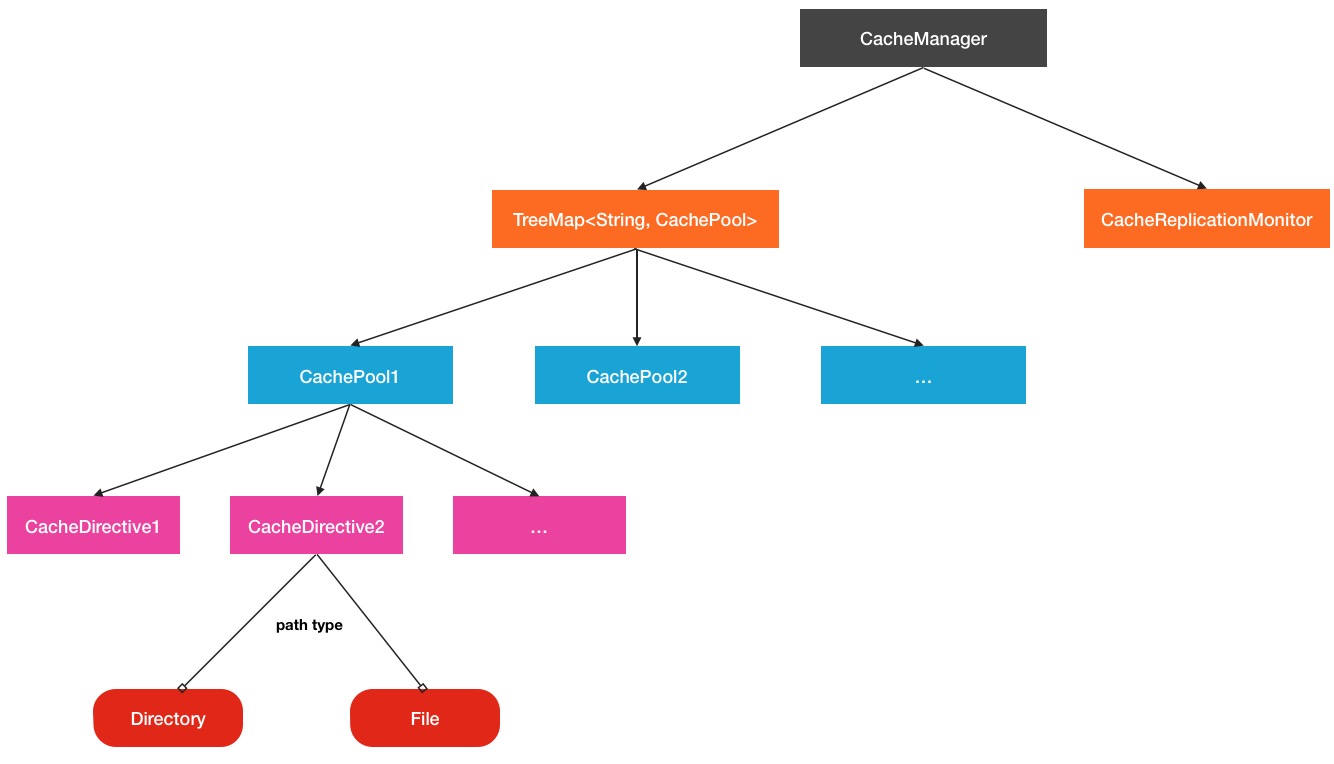
...我们可以看到,在cachePool中,也确实维护了一个cacheDirective缓存单元列表.而这些cachePool缓存池则是被CacheManager所掌管.CacheManager在这里就好比是一个总管理者的角色.当然,在CacheManager中还有运行着一个很重要的服务,就是CacheReplicationMonitor,这个监控程序会周期扫描当前的最新的缓存路径,并分发到对应的DataNode节点上,这个线程服务在后面还会具体提到.所以HDFS Cache的总的结构关系如下图所示:
HDFS缓存管理机制分析
其实之前本人已经写过一篇关于HDFS缓存管理机制方面的文章,HDFS缓存机制,但是现在来看,还并不是很全面,之前的文章完全遗漏了CacheAdmin这块的东西.所以在本小节中,要补充2方面的分析介绍.
- CacheAdmin CLI命令在CacheManager的实现
- CacheMAnager的CacheReplicationMonitor如何将目标缓存文件缓存到DataNode中
下面先来看第一点涉及到的内容
CacheAdmin CLI命令在CacheManager的实现
在CacheAdmin中的每个操作命令,最后通过RPC调用都会对应到CacheManager的一个具体操作方法.所以在此过程中,要解决下面几个主要疑点:
- CacheManager维护了怎样的CachePool列表,CacheDirective关系
- 添加新的CacheDirective,CachePool有哪些特殊的细节
对于第一个问题,CacheManager确实维护了多种映射关系的CachePool,CacheDirective列表关系,如下:
public final class CacheManager {
...
// CacheDirective id对CacheDirective的映射关系
/**
* Cache directives, sorted by ID.
*
* listCacheDirectives relies on the ordering of elements in this map
* to track what has already been listed by the client.
*/
private final TreeMap<Long, CacheDirective> directivesById =
new TreeMap<Long, CacheDirective>();
//缓存路径对CacheDirective列表的映射关系,说明一个文件/目录路径可以同时被多次缓存
...
/**
* Cache directives, sorted by path
*/
private final TreeMap<String, List<CacheDirective>> directivesByPath =
new TreeMap<String, List<CacheDirective>>();
// 缓存池名称对CachePool的映射
/**
* Cache pools, sorted by name.
*/
private final TreeMap<String, CachePool> cachePools =
new TreeMap<String, CachePool>();
...以上的3大映射关系就是CacheManager对象中存储着的,第二条关系缓存路径对缓存对象列表的映射是一开始我感到奇怪的,后来发现,对同一个缓存路径,是可以多次缓存的.由于定义了这3类结构关系,所以在添加CacheDirective实例对象时候会涉及到一些更新操作.以addDirective方法为例
public CacheDirectiveInfo addDirective(
CacheDirectiveInfo info, FSPermissionChecker pc, EnumSet<CacheFlag> flags)
throws IOException {
assert namesystem.hasWriteLock();
CacheDirective directive;
try {
// 获取所属缓存池
CachePool pool = getCachePool(validatePoolName(info));





 本文详细介绍了HDFS的中心缓存管理,包括适用场景、结构设计和管理机制。适用于公共资源文件和短期热点数据文件的缓存,通过CacheDirective和CachePool进行管理,由CacheManager和CacheReplicationMonitor服务协同工作,实现高效的数据缓存和监控。
本文详细介绍了HDFS的中心缓存管理,包括适用场景、结构设计和管理机制。适用于公共资源文件和短期热点数据文件的缓存,通过CacheDirective和CachePool进行管理,由CacheManager和CacheReplicationMonitor服务协同工作,实现高效的数据缓存和监控。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1931
1931

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








