驱动模块添加:
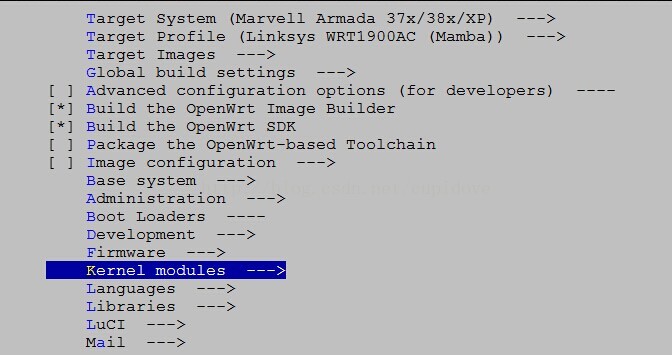
1:make menuconfig中的 kernel modules
其中的各个配置选项来自于下面目录中的.mk文件
这里以other.mk为对照,后续我们添加的驱动模块,添加到other分支当中
2:建立模块目录,路径是package/kernel/example。mkdir -p package/kernel/example
3:进行package/kernel/example目录,建立Makefile文件,内容如下
#Kernel module example
include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/kernel.mk
PKG_NAME:=example
PKG_RELEASE:=1
include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
EXTRA_CFLAGS:= \
$(patsubst CONFIG_%, -DCONFIG_%=1, $(patsubst %=m,%,$(filter %=m,$(EXTRA_KCONFIG)))) \
$(patsubst CONFIG_%, -DCONFIG_%=1, $(patsubst %=y,%,$(filter %=y,$(EXTRA_KCONFIG)))) \
MAKE_OPTS:=ARCH="$(LINUX_KARCH)" \
CROSS_COMPILE="$(TARGET_CROSS)" \
SUBDIRS="$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)" \
EXTRA_CFLAGS="$(EXTRA_CFLAGS)"
define KernelPackage/example
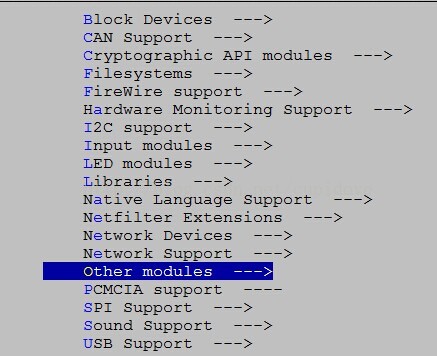
SUBMENU:=Other modules
TITLE:=Support Module for example
# DEPENDS:=@XXX #如果有依赖,这个名字可去make menuconfig里面找到 Symbol:XXX
FILES:=$(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/example.ko
AUTOLOAD:=$(call AutoLoad,81,example) #系统启动时自动装载
endef
#PKG_BUILD_DIR:/build_dir/target-mipsel_24kec+dsp_uClibc-0.9.33.2/linux-ramips_mt7621/example
#建立 PKG_BUILD_DIR ,并将代码拷贝到此处
define Build/Prepare
mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/
$(CP) -R ./src/* $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/
endef
define Build/Compile
$(MAKE) -C "$(LINUX_DIR)" $(MAKE_OPTS) CONFIG_EXAMPLE=m modules
endef
$(eval $(call KernelPackage,example))4:在package/kernel/example目录下建立src目录,mkdir -p package/kernel/example/src
5:在package/kernel/example/src目录下建立源码文件example.c和对应的Makefile,Kconfig
example.c
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/version.h>
#include <linux/kmod.h>
static int __init example_init(void)
{
printk("hello example openwrt\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit example_exit(void)
{
printk("hello example openwrt exit\n");
}
module_init(example_init);
module_exit(example_exit);
MODULE_AUTHOR("hello world");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("example driver");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_ALIAS("platform:" DRV_NAME);
obj-${CONFIG_EXAMPLE}+= example.o
Kconfig:
config EXAMPLE
tristate "Just a example"
help
This is a example, for debugging kernel model.
If unsure, say N.
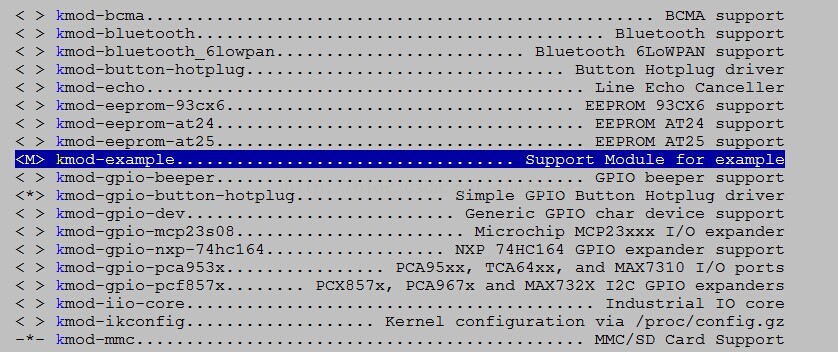
6:在trunk目录make menuconfig-->kernel module-->other module-->kmod-example选中。保存Config后,输入make ./package/kernel/example/compile V=s进行编译
应用程序编译
1:在trunk/package应用目录。参考其他的应用文件。创建helloworld文件夹,并进入。创建Makefile:
##############################################
# OpenWrt Makefile for helloworld program
#
#
# Most of the variables used here are defined in
# the include directives below. We just need to
# specify a basic description of the package,
# where to build our program, where to find
# the source files, and where to install the
# compiled program on the router.
#
# Be very careful of spacing in this file.
# Indents should be tabs, not spaces, and
# there should be no trailing whitespace in
# lines that are not commented.
#
##############################################
include $(TOPDIR)/rules.mk
# Name and release number of this package
PKG_NAME:=helloworld
PKG_RELEASE:=1
# This specifies the directory where we're going to build the program.
# The root build directory, $(BUILD_DIR), is by default the build_mipsel
# directory in your OpenWrt SDK directory
PKG_BUILD_DIR := $(BUILD_DIR)/$(PKG_NAME)
include $(INCLUDE_DIR)/package.mk
# Specify package information for this program.
# The variables defined here should be self explanatory.
# If you are running Kamikaze, delete the DESCRIPTION
# variable below and uncomment the Kamikaze define
# directive for the description below
define Package/helloworld
SECTION:=utils
CATEGORY:=Utilities
TITLE:=Helloworld -- prints a snarky message
endef
# Uncomment portion below for Kamikaze and delete DESCRIPTION variable above
define Package/helloworld/description
If you can't figure out what this program does, you're probably
brain-dead and need immediate medical attention.
endef
# Specify what needs to be done to prepare for building the package.
# In our case, we need to copy the source files to the build directory.
# This is NOT the default. The default uses the PKG_SOURCE_URL and the
# PKG_SOURCE which is not defined here to download the source from the web.
# In order to just build a simple program that we have just written, it is
# much easier to do it this way.
define Build/Prepare
mkdir -p $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)
$(CP) ./src/* $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/
endef
define Build/Configure
endef
define Build/Compile
$(MAKE) -C $(PKG_BUILD_DIR) \
CC="$(TARGET_CC)" \
CFLAGS="$(TARGET_CFLAGS) -Wall" \
LDFLAGS="$(TARGET_LDFLAGS)"
endef
# We do not need to define Build/Configure or Build/Compile directives
# The defaults are appropriate for compiling a simple program such as this one
# Specify where and how to install the program. Since we only have one file,
# the helloworld executable, install it by copying it to the /bin directory on
# the router. The $(1) variable represents the root directory on the router running
# OpenWrt. The $(INSTALL_DIR) variable contains a command to prepare the install
# directory if it does not already exist. Likewise $(INSTALL_BIN) contains the
# command to copy the binary file from its current location (in our case the build
# directory) to the install directory.
define Package/helloworld/install
$(INSTALL_DIR) $(1)/bin
$(INSTALL_BIN) $(PKG_BUILD_DIR)/helloworld $(1)/bin/
endef
# This line executes the necessary commands to compile our program.
# The above define directives specify all the information needed, but this
# line calls BuildPackage which in turn actually uses this information to
# build a package.
$(eval $(call BuildPackage,helloworld))2:在helloworld目录创建src文件夹,并进入。创建Makefile和helloworld.c:
# build helloworld executable when user executes "make"
helloworld: helloworld.o
$(CC) $(LDFLAGS) helloworld.o -o helloworld
helloworld.o: helloworld.c
$(CC) $(CFLAGS) -c helloworld.c
# remove object files and executable when user executes "make clean"
clean:
rm *.o helloworldhelloworld.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char**argv)
{
printf("Hell! O' world, why won't my code compile?\n\n");
return 0;
}
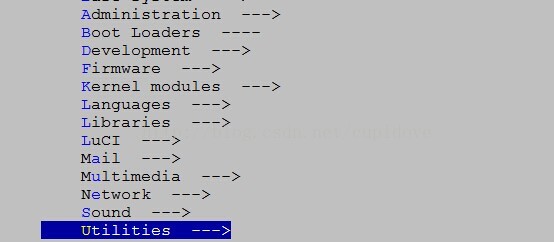
3:返回trunk目录,make menuconfig-->Utilities-->helloworld。然后make ./package/helloworld/compile V=s





 本文详细介绍了如何在OpenWrt系统上添加自定义驱动模块及应用程序的全过程,包括配置选项、目录结构搭建、Makefile编写等内容。
本文详细介绍了如何在OpenWrt系统上添加自定义驱动模块及应用程序的全过程,包括配置选项、目录结构搭建、Makefile编写等内容。

















 3781
3781

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








