Pascal's Travels
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 981 Accepted Submission(s): 416
Problem Description
An n x n game board is populated with integers, one nonnegative integer per square. The goal is to travel along any legitimate path from the upper left corner to the lower right corner of the board. The integer in any one square dictates how large a step away from that location must be. If the step size would advance travel off the game board, then a step in that particular direction is forbidden. All steps must be either to the right or toward the bottom. Note that a 0 is a dead end which prevents any further progress.
Consider the 4 x 4 board shown in Figure 1, where the solid circle identifies the start position and the dashed circle identifies the target. Figure 2 shows the three paths from the start to the target, with the irrelevant numbers in each removed.
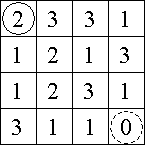
Figure 1
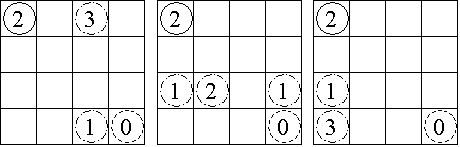
Figure 2
Consider the 4 x 4 board shown in Figure 1, where the solid circle identifies the start position and the dashed circle identifies the target. Figure 2 shows the three paths from the start to the target, with the irrelevant numbers in each removed.


Input
The input contains data for one to thirty boards, followed by a final line containing only the integer -1. The data for a board starts with a line containing a single positive integer n, 4 <= n <= 34, which is the number of rows in this board. This is followed by n rows of data. Each row contains n single digits, 0-9, with no spaces between them.
Output
The output consists of one line for each board, containing a single integer, which is the number of paths from the upper left corner to the lower right corner. There will be fewer than 2^63 paths for any board.
Sample Input
4 2331 1213 1231 3110 4 3332 1213 1232 2120 5 11101 01111 11111 11101 11101 -1
Sample Output
3 0 7Brute force methods examining every path will likely exceed the allotted time limit. 64-bit integer values are available as "__int64" values using the Visual C/C++ or "long long" values using GNU C/C++ or "int64" values using Free Pascal compilers.HintHint
Source
Recommend
mcqsmall
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char map[40][40];
__int64 dp[40][40];
int main(void) {
int n;
while (scanf("%d", &n), n + 1) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%s", map[i]);
memset(dp, 0, sizeof (dp));
dp[0][0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
if (map[i][j] - '0') {
if (i + map[i][j] - '0' < n)
dp[i + map[i][j] - '0'][j] += dp[i][j];
if (j + map[i][j] - '0' < n)
dp[i][j + map[i][j] - '0'] += dp[i][j];
}
printf("%I64d\n", dp[n - 1][n - 1]);
}
return 0;
}




















 62
62











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








