1.What are the advantages of Object Oriented Programming Languages(OOPL)?
It directly represent the real life objects like Car, Account, Customer etc.
The features of OOPL like polymorphism, inheritance, encapsulation(Tip: remember “Pie”) make it powerful.
2.How does the Object Oriented approach improve software development?
The key benefits are:
Re-use of previous work: using implementation inheritance and object composition.
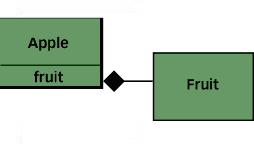
Real mapping to the problem domain: Objects map to real world and represent customers, products etc with encapsulation.
Modular architecture: Objects, systems, frameworks etc are the building blocks of larger systems.
In the conclusion, OO is used to increase the software quality and reduce development time. If 90% of the new application consists of proven existing components then only the remaining 10% of the code have to be tested from scratch.
3. What do you mean by polymorphism, inheritance, encapsulation and dynamic binding?
Polymorphism allows values of different data types to be handled by using a uniform interface. The benefit of polymorphism is that it is very easy to add new classes of derived objects without breaking the calling code.
Dynamic binding is the process used by object-oriented programming languages to implement polymorphism
Inheritance is the inclusion of methods and variables of a base class in a derived class so that they are accessible in that derived class. The benefit of inheritance is that it provides the formal mechanism for code reuse.
Encapsulation refers to keeping all the related members(variables and methods) together in an object. Good encapsulation improves code modularity by preventing objects interacting with each other in an unexpected way.
4. Why would you prefer code reuse via composition over inheritance?
Object composition and inheritance are two techniques for reusing functionality in object-oriented systems.
Figure 1. The inheritance relationship
Figure 2. The composition relationship
| Composition | |
| It is done statically at compile time and is easy to use. | It is done dynamically at run-time. |
| Subclass becomes dependent on the parent class implementation. Inheritance breaks encapsulation. | The implementations can be replaced at run-time. The behavior of the system may be harder to understand just by looking at the source code. |
| This type of reuse is often called white-box reuse. | This type of reuse is often called black-box reuse. |
Overuse inheritance will result in large inheritance hierarchies that can become hard to deal with. Furthermore, due to the flexibility and power of object composition, most design patterns emphasize object composition over inheritance.























 328
328

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








