单个物理维度可以被事实表多次引用,每个引用连接逻辑上存在差异的角色维度。例如,事实表可以有多个日期,每个日期通过外键引用不同的日期维度,原则上每个外键表示不同的日期维度视图,这样引用具有不同的含义。这些不同的维度视图具有唯一的代理键列名,被称为角色,相关维度被称为角色扮演维度。
当一个事实表多次引用一个维度表时会用到角色扮演维度。例如,一个销售订单有一个是订单日期,还有一个请求交付日期,这时就需要引用日期维度表两次。
我们期望在每个事实表中设置日期维度,因为总是希望按照时间来分析业务情况。在事务型事实表中,主要的日期列是事务日期,例如,订单日期。有时会发现其它日期也可能与每个事实关联,例如,订单事务的请求交付日期。每个日期应该成为事实表的外键。
本篇说明两类角色扮演维度的实现,分别是表别名和数据库视图。表别名是在SQL语句里引用维度表多次,每次引用都赋予维度表一个别名。而数据库视图,则是按照事实表需要引用维度表的次数,建立相同数量的视图。我先修改销售订单数据库模式,添加一个请求交付日期字段,并对数据抽取和装载脚本做相应的修改。这些表结构修改好后,插入测试数据,演示别名和视图在角色扮演维度中的用法。
RDS和TDS中的内部表直接使用ALTER TABLE语句增加请求交付日期列。因为HAWQ的ADD COLUMN不支持after语法,新增的字段会加到所有已存在字段的后面。修改后数据仓库模式如图1所示。

从图中可以看到,销售订单事实表和日期维度表之间有两条连线,表示订单日期和请求交付日期都是引用日期维度表的外键。注意,虽然图中显示了表之间的关联关系,但HAWQ中并不支持主外键数据库约束。
函数做了以下两点修改:
可以看到只有三个新的销售订单具有request_delivery_date_sk值,6360对应的日期是2017年5月30日。
其次,合并的日期维度表不再适合其它经常使用的日、周、月等日期维度。日期维度表每行记录的含义不再指唯一一天,因此无法在同一张表中标识出周、月等一致性维度,进而无法简单地处理按时间维度的上卷、聚合等需求。
当一个事实表多次引用一个维度表时会用到角色扮演维度。例如,一个销售订单有一个是订单日期,还有一个请求交付日期,这时就需要引用日期维度表两次。
我们期望在每个事实表中设置日期维度,因为总是希望按照时间来分析业务情况。在事务型事实表中,主要的日期列是事务日期,例如,订单日期。有时会发现其它日期也可能与每个事实关联,例如,订单事务的请求交付日期。每个日期应该成为事实表的外键。
本篇说明两类角色扮演维度的实现,分别是表别名和数据库视图。表别名是在SQL语句里引用维度表多次,每次引用都赋予维度表一个别名。而数据库视图,则是按照事实表需要引用维度表的次数,建立相同数量的视图。我先修改销售订单数据库模式,添加一个请求交付日期字段,并对数据抽取和装载脚本做相应的修改。这些表结构修改好后,插入测试数据,演示别名和视图在角色扮演维度中的用法。
一、修改数据库模式
1. 修改源库表结构
执行下面的脚本,给源库中销售订单表sales_order增加request_delivery_date字段。use source;
alter table sales_order add request_delivery_date datetime after order_date ;2. 修改数据仓库表结构
-- 修改外部表
drop external table ext.sales_order;
create external table ext.sales_order
(
order_number int,
customer_number int,
product_code int,
order_date timestamp,
request_delivery_date timestamp,
entry_date timestamp,
order_amount decimal(10 , 2 ),
order_quantity int
)
location ('pxf://mycluster/data/ext/sales_order?profile=hdfstextsimple')
format 'text' (delimiter=e',', null='null');
comment on table ext.sales_order is '销售订单外部表';
comment on column ext.sales_order.order_number is '订单号';
comment on column ext.sales_order.customer_number is '客户编号';
comment on column ext.sales_order.product_code is '产品编码';
comment on column ext.sales_order.order_date is '订单日期';
comment on column ext.sales_order.request_delivery_date is '请求交付日期';
comment on column ext.sales_order.entry_date is '登记日期';
comment on column ext.sales_order.order_amount is '销售金额';
comment on column ext.sales_order.order_quantity is '销售数量';
-- 修改rds.sales_order
alter table rds.sales_order add column request_delivery_date timestamp default null;
comment on column rds.sales_order.request_delivery_date is '请求交付日期';
-- 修改tds.sales_order_fact
alter table tds.sales_order_fact add column request_delivery_date_sk bigint default null;
comment on column tds.sales_order_fact.request_delivery_date_sk is '请求交付日期维度代理键';
comment on column tds.sales_order_fact.order_date_sk is '订单日期维度代理键';RDS和TDS中的内部表直接使用ALTER TABLE语句增加请求交付日期列。因为HAWQ的ADD COLUMN不支持after语法,新增的字段会加到所有已存在字段的后面。修改后数据仓库模式如图1所示。

图1
从图中可以看到,销售订单事实表和日期维度表之间有两条连线,表示订单日期和请求交付日期都是引用日期维度表的外键。注意,虽然图中显示了表之间的关联关系,但HAWQ中并不支持主外键数据库约束。
二、修改定期数据装载函数
create or replace function fn_regular_load ()
returns void as
$$
declare
-- 设置scd的生效时间
v_cur_date date := current_date;
v_pre_date date := current_date - 1;
v_last_load date;
begin
-- 分析外部表
analyze ext.customer;
analyze ext.product;
analyze ext.sales_order;
-- 将外部表数据装载到原始数据表
truncate table rds.customer;
truncate table rds.product;
insert into rds.customer select * from ext.customer;
insert into rds.product select * from ext.product;
insert into rds.sales_order
select order_number,
customer_number,
product_code,
order_date,
entry_date,
order_amount,
order_quantity,
request_delivery_date
from ext.sales_order;
-- 分析rds模式的表
analyze rds.customer;
analyze rds.product;
analyze rds.sales_order;
-- 设置cdc的上限时间
select last_load into v_last_load from rds.cdc_time;
truncate table rds.cdc_time;
insert into rds.cdc_time select v_last_load, v_cur_date;
-- 装载客户维度
insert into tds.customer_dim
(customer_number,
customer_name,
customer_street_address,
customer_zip_code,
customer_city,
customer_state,
shipping_address,
shipping_zip_code,
shipping_city,
shipping_state,
isdelete,
version,
effective_date)
select case flag
when 'D' then a_customer_number
else b_customer_number
end customer_number,
case flag
when 'D' then a_customer_name
else b_customer_name
end customer_name,
case flag
when 'D' then a_customer_street_address
else b_customer_street_address
end customer_street_address,
case flag
when 'D' then a_customer_zip_code
else b_customer_zip_code
end customer_zip_code,
case flag
when 'D' then a_customer_city
else b_customer_city
end customer_city,
case flag
when 'D' then a_customer_state
else b_customer_state
end customer_state,
case flag
when 'D' then a_shipping_address
else b_shipping_address
end shipping_address,
case flag
when 'D' then a_shipping_zip_code
else b_shipping_zip_code
end shipping_zip_code,
case flag
when 'D' then a_shipping_city
else b_shipping_city
end shipping_city,
case flag
when 'D' then a_shipping_state
else b_shipping_state
end shipping_state,
case flag
when 'D' then true
else false
end isdelete,
case flag
when 'D' then a_version
when 'I' then 1
else a_version + 1
end v,
v_pre_date
from (select a.customer_number a_customer_number,
a.customer_name a_customer_name,
a.customer_street_address a_customer_street_address,
a.customer_zip_code a_customer_zip_code,
a.customer_city a_customer_city,
a.customer_state a_customer_state,
a.shipping_address a_shipping_address,
a.shipping_zip_code a_shipping_zip_code,
a.shipping_city a_shipping_city,
a.shipping_state a_shipping_state,
a.version a_version,
b.customer_number b_customer_number,
b.customer_name b_customer_name,
b.customer_street_address b_customer_street_address,
b.customer_zip_code b_customer_zip_code,
b.customer_city b_customer_city,
b.customer_state b_customer_state,
b.shipping_address b_shipping_address,
b.shipping_zip_code b_shipping_zip_code,
b.shipping_city b_shipping_city,
b.shipping_state b_shipping_state,
case when a.customer_number is null then 'I'
when b.customer_number is null then 'D'
else 'U'
end flag
from v_customer_dim_latest a
full join rds.customer b on a.customer_number = b.customer_number
where a.customer_number is null -- 新增
or b.customer_number is null -- 删除
or (a.customer_number = b.customer_number
and not
(coalesce(a.customer_name,'') = coalesce(b.customer_name,'')
and coalesce(a.customer_street_address,'') = coalesce(b.customer_street_address,'')
and coalesce(a.customer_zip_code,0) = coalesce(b.customer_zip_code,0)
and coalesce(a.customer_city,'') = coalesce(b.customer_city,'')
and coalesce(a.customer_state,'') = coalesce(b.customer_state,'')
and coalesce(a.shipping_address,'') = coalesce(b.shipping_address,'')
and coalesce(a.shipping_zip_code,0) = coalesce(b.shipping_zip_code,0)
and coalesce(a.shipping_city,'') = coalesce(b.shipping_city,'')
and coalesce(a.shipping_state,'') = coalesce(b.shipping_state,'')
))) t
order by coalesce(a_customer_number, 999999999999), b_customer_number limit 999999999999;
-- 重载PA客户维度
truncate table pa_customer_dim;
insert into pa_customer_dim
select customer_sk,
customer_number,
customer_name,
customer_street_address,
customer_zip_code,
customer_city,
customer_state,
isdelete,
version,
effective_date,
shipping_address,
shipping_zip_code,
shipping_city,
shipping_state
from customer_dim
where customer_state = 'pa';
-- 装载产品维度
insert into tds.product_dim
(product_code,
product_name,
product_category,
isdelete,
version,
effective_date)
select case flag
when 'D' then a_product_code
else b_product_code
end product_code,
case flag
when 'D' then a_product_name
else b_product_name
end product_name,
case flag
when 'D' then a_product_category
else b_product_category
end product_category,
case flag
when 'D' then true
else false
end isdelete,
case flag
when 'D' then a_version
when 'I' then 1
else a_version + 1
end v,
v_pre_date
from (select a.product_code a_product_code,
a.product_name a_product_name,
a.product_category a_product_category,
a.version a_version,
b.product_code b_product_code,
b.product_name b_product_name,
b.product_category b_product_category,
case when a.product_code is null then 'I'
when b.product_code is null then 'D'
else 'U'
end flag
from v_product_dim_latest a
full join rds.product b on a.product_code = b.product_code
where a.product_code is null -- 新增
or b.product_code is null -- 删除
or (a.product_code = b.product_code
and not
(a.product_name = b.product_name
and a.product_category = b.product_category))) t
order by coalesce(a_product_code, 999999999999), b_product_code limit 999999999999;
-- 装载order维度
insert into order_dim (order_number, version, effective_date)
select t.order_number, t.v, t.effective_date
from (select order_number, 1 v, order_date effective_date
from rds.sales_order, rds.cdc_time
where entry_date >= last_load and entry_date < current_load) t;
-- 装载销售订单事实表
insert into sales_order_fact
select order_sk,
customer_sk,
product_sk,
e.date_sk,
e.year * 100 + e.month,
order_amount,
order_quantity,
f.date_sk
from rds.sales_order a,
order_dim b,
v_customer_dim_his c,
v_product_dim_his d,
date_dim e,
date_dim f,
rds.cdc_time g
where a.order_number = b.order_number
and a.customer_number = c.customer_number
and a.order_date >= c.effective_date
and a.order_date < c.expiry_date
and a.product_code = d.product_code
and a.order_date >= d.effective_date
and a.order_date < d.expiry_date
and date(a.order_date) = e.date
and date(a.request_delivery_date) = f.date
and a.entry_date >= g.last_load and a.entry_date < g.current_load;
-- 分析tds模式的表
analyze customer_dim;
analyze product_dim;
analyze order_dim;
analyze sales_order_fact;
-- 更新时间戳表的last_load字段
truncate table rds.cdc_time;
insert into rds.cdc_time select v_cur_date, v_cur_date;
end;
$$
language plpgsql;函数做了以下两点修改:
- 在装载rds.sales_order时显式指定了列的顺序,因为外部表与内部表列的顺序不一致。
- 在装载销售订单事实表时,关联了日期维度表两次,分别赋予别名e和f。事实表和两个日期维度表关联,取得日期代理键。e.date_sk表示订单日期代理键,f.date_sk表示请求交付日期的代理键。
三、测试
1. 在源库中生成测试数据
执行下面的SQL脚本在源库中增加三个带有交货日期的销售订单。use source;
/*** 新增订单日期为昨天的3条订单。***/
set @start_date := unix_timestamp(date_add(current_date, interval -1 day));
set @end_date := unix_timestamp(current_date);
drop table if exists temp_sales_order_data;
create table temp_sales_order_data as select * from sales_order where 1=0;
set @order_date := from_unixtime(@start_date + rand() * (@end_date - @start_date));
set @request_delivery_date := from_unixtime(unix_timestamp(date_add(current_date, interval 5 day)) + rand() * 86400);
set @amount := floor(1000 + rand() * 9000);
set @quantity := floor(10 + rand() * 90);
insert into temp_sales_order_data
values (126, 1, 1, @order_date,
@request_delivery_date, @order_date, @amount, @quantity);
set @order_date := from_unixtime(@start_date + rand() * (@end_date - @start_date));
set @request_delivery_date := from_unixtime(unix_timestamp(date_add(current_date, interval 5 day)) + rand() * 86400);
set @amount := floor(1000 + rand() * 9000);
set @quantity := floor(10 + rand() * 90);
insert into temp_sales_order_data
values (127, 2, 2, @order_date,
@request_delivery_date, @order_date, @amount, @quantity);
set @order_date := from_unixtime(@start_date + rand() * (@end_date - @start_date));
set @request_delivery_date := from_unixtime(unix_timestamp(date_add(current_date, interval 5 day)) + rand() * 86400);
set @amount := floor(1000 + rand() * 9000);
set @quantity := floor(10 + rand() * 90);
insert into temp_sales_order_data
values (128, 3, 3, @order_date,
@request_delivery_date, @order_date, @amount, @quantity);
insert into sales_order
select null,customer_number,product_code,order_date,
request_delivery_date,entry_date,order_amount,order_quantity
from temp_sales_order_data order by order_date;
commit ;2. 执行定期装载函数并查看结果
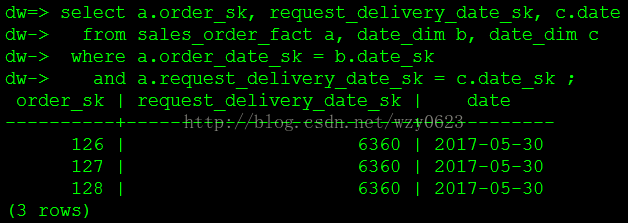
~/regular_etl.shselect a.order_sk, request_delivery_date_sk, c.date
from sales_order_fact a, date_dim b, date_dim c
where a.order_date_sk = b.date_sk
and a.request_delivery_date_sk = c.date_sk ;
图2
可以看到只有三个新的销售订单具有request_delivery_date_sk值,6360对应的日期是2017年5月30日。
四、使用角色扮演维度查询
1. 使用表别名查询
select order_date_dim.date order_date,
request_delivery_date_dim.date request_delivery_date,
sum(order_amount),count(*)
from sales_order_fact a,
date_dim order_date_dim,
date_dim request_delivery_date_dim
where a.order_date_sk = order_date_dim.date_sk
and a.request_delivery_date_sk = request_delivery_date_dim.date_sk
group by order_date_dim.date , request_delivery_date_dim.date
order by order_date_dim.date , request_delivery_date_dim.date;2. 使用视图查询
-- 创建订单日期视图
create view v_order_date_dim
(order_date_sk,
order_date,
month,
month_name,
quarter,
year)
as select * from date_dim;
-- 创建请求交付日期视图
create view v_request_delivery_date_dim
(request_delivery_date_sk,
request_delivery_date,
month,
month_name,
quarter,
year)
as select * from date_dim;
-- 查询
select order_date,request_delivery_date,sum(order_amount),count(*)
from sales_order_fact a,v_order_date_dim b,v_request_delivery_date_dim c
where a.order_date_sk = b.order_date_sk
and a.request_delivery_date_sk = c.request_delivery_date_sk
group by order_date , request_delivery_date
order by order_date , request_delivery_date;上面两种实现方式是等价的。结果如图3所示。
图3
尽管不能连接到单一的日期维度表,但可以建立并管理单独的物理日期维度表,然后使用视图或别名建立两个不同日期维度的描述。注意在每个视图或别名列中需要唯一的标识。例如,订单日期属性应该具有唯一标识order_date以便与请求交付日期request_delivery_date区别。别名与视图在查询中的作用并没有本质的区别,都是为了从逻辑上区分同一个物理维度表。许多BI工具也支持在语义层使用别名。但是,如果有多个BI工具,连同直接基于SQL的访问,都同时在组织中使用的话,不建议采用语义层别名的方法。当某个维度在单一事实表中同时出现多次时,则会存在维度模型的角色扮演。基本维度可能作为单一物理表存在,但是每种角色应该被当成标识不同的视图展现到BI工具中。
五、一种有问题的设计
为处理多日期问题,一些设计者试图建立单一日期维度表,该表使用一个键表示每个订单日期和请求交付日期的组合,例如:create table date_dim (date_sk int, order_date date, delivery_date date);
create table sales_order_fact (date_sk int, order_amount int);订单日期 请求交付日期
2017-05-26 2017-05-29
2017-05-27 2017-05-29
2017-05-28 2017-05-29
2017-05-26 2017-05-30
2017-05-27 2017-05-30
2017-05-28 2017-05-30
2017-05-26 2017-05-31
2017-05-27 2017-05-31
2017-05-28 2017-05-31其次,合并的日期维度表不再适合其它经常使用的日、周、月等日期维度。日期维度表每行记录的含义不再指唯一一天,因此无法在同一张表中标识出周、月等一致性维度,进而无法简单地处理按时间维度的上卷、聚合等需求。

























 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








