2015年深度学习领域,非常值得学习的一篇文献:《Batch Normalization: Accelerating Deep Network Training by Reducing Internal Covariate Shift》,这个算法目前已经被大量的应用,最新的文献算法很多都会引用这个算法,进行网络训练。
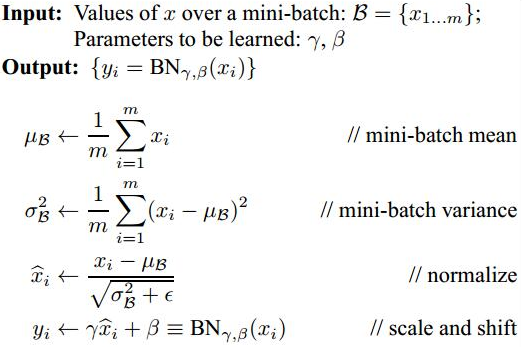
在训练网络的时会将输入减去均值,还有些人甚至会对输入做白化等操作,目的是为了加快训练。白化的方式有好几种,常用的有PCA白化:即对数据进行PCA操作之后,在进行方差归一化。这样数据基本满足0均值、单位方差、弱相关性。作者首先考虑,对每一层数据都使用白化操作,但分析认为这是不可取的。因为白化需要计算协方差矩阵、求逆等操作,计算量很大,此外,反向传播时,白化操作不一定可导。于是,作者采用下面的Normalization方法。整个BN的算法如下:
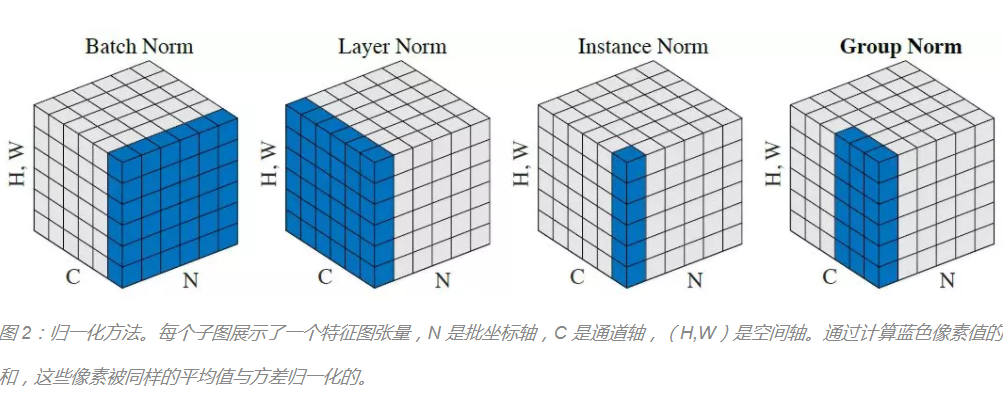
其中的m是batchsize,因此BN是作用在Layer层面的归一化操作,这种操作可以和每个神经元绑定,一个Layer的每个神经元都对应着各自的gamma和beta,用于重构输入数据的分布。这两个参数和W和b一样需要学习出来的。最终的实现中beta和b的功能冗余,故去掉一个。关于BN在CNN中的使用在Group Normalization这篇文章中有直观描述:
算法的TensorFlow实现代码:
def add_layer(inputs, in_size, out_size, activation_function=None, norm=False):
# weights and biases (bad initialization for this case)
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size], mean=0., stddev=1.))
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
# fully connected product
Wx_plus_b = tf.matmul(inputs, Weights) + biases
# normalize fully connected product对每层输出做批正则化
if norm:
# Batch Normalize
fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments(
Wx_plus_b,
axes=[0], # the dimension you wanna normalize, here [0] for batch
# for image, you wanna do [0, 1, 2] for [batch, height, width] but not channel
)
scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([out_size])) #需要训练出来的放缩尺度伽马
shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([out_size]))#需要寻来拿出来的平移变换贝塔
epsilon = 0.001 #防止方差为零
# apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5)
def mean_var_with_update():
ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var])
with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]):
return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var)
mean, var = mean_var_with_update()
Wx_plus_b = tf.nn.batch_normalization(Wx_plus_b, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon)
# similar with this two steps:
# Wx_plus_b = (Wx_plus_b - fc_mean) / tf.sqrt(fc_var + epsilon)
# Wx_plus_b = Wx_plus_b * scale + shift
# activation
if activation_function is None:
outputs = Wx_plus_b
else:
outputs = activation_function(Wx_plus_b)
return outputs
fix_seed(1)
if norm:
# BN for the first input对输入前数据做批正则化
fc_mean, fc_var = tf.nn.moments(
xs, #输入数据
axes=[0],
)
scale = tf.Variable(tf.ones([1]))
shift = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
epsilon = 0.001
# apply moving average for mean and var when train on batch
ema = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(decay=0.5)
def mean_var_with_update():
ema_apply_op = ema.apply([fc_mean, fc_var])
with tf.control_dependencies([ema_apply_op]):
return tf.identity(fc_mean), tf.identity(fc_var)
mean, var = mean_var_with_update()
xs = tf.nn.batch_normalization(xs, mean, var, shift, scale, epsilon)
# record inputs for every layer
layers_inputs = [xs]
# build hidden layers
for l_n in range(N_LAYERS): #循环添加神经网络层
layer_input = layers_inputs[l_n]
in_size = layers_inputs[l_n].get_shape()[1].value
output = add_layer(
layer_input, # input
in_size, # input size
N_HIDDEN_UNITS, # output size
ACTIVATION, # activation function
norm, # normalize before activation
)
layers_inputs.append(output) # add output for next run
# build output layer
prediction = add_layer(layers_inputs[-1], 30, 1, activation_function=None)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices=[1]))
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(cost)
return [train_op, cost, layers_inputs]关于Group Normalization的Tensorflow实现比BN更加简洁:
def GroupNorm(x, gamma, beta, G, eps=1e.5):
# x: input features with shape [N,C,H,W]
# gamma, beta: scale and offset, with shape [1,C,1,1]
# G: number of groups for GN
N, C, H, W = x.shape
x = tf.reshape(x, [N, G, C // G, H, W])
mean, var = tf.nn.moments(x, [2, 3, 4], keep dims=True)
x = (x . mean) / tf.sqrt(var + eps)
x = tf.reshape(x, [N, C, H, W])
return x gamma + beta





















 1269
1269











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








