手写线性回归
使用numpy随机生成数据
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 生成模拟数据
np.random.seed(42)
X = 2 * np.random.rand(200, 1)
y = 4 + 3 * X + np.random.randn(200, 1)
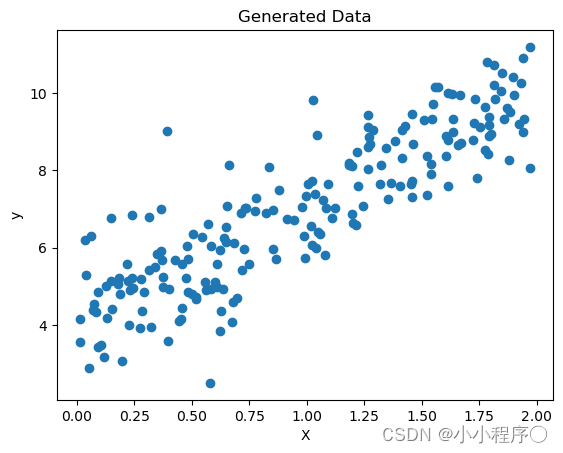
# 可视化数据
plt.scatter(X, y)
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.title('Generated Data')
plt.show()
定义线性回归参数并实现梯度下降
对于线性拟合,其假设函数为:
h
θ
(
x
)
=
θ
1
x
+
θ
0
h_θ(x)=θ_1x+θ_0
hθ(x)=θ1x+θ0
这其中的
θ
θ
θ是假设函数当中的参数。
也可以简化为:
h
θ
(
x
)
=
θ
1
x
h_θ(x)=θ_1x
hθ(x)=θ1x
代价函数,在统计学上称为均方根误差函数。当假设函数中的系数
θ
θ
θ取不同的值时,
1
2
m
\frac{1}{2m}
2m1倍假设函数预测值
h
θ
(
x
(
i
)
)
h_θ(x^{(i)})
hθ(x(i))和真实值
y
(
i
)
y^{(i)}
y(i)的差的平方的和之间的函数关系表示为代价函数
J
J
J。
J
(
θ
0
,
θ
1
)
=
1
2
m
∑
i
=
1
m
(
h
θ
(
x
(
i
)
)
−
y
(
i
)
)
2
J(θ_0,θ_1)=\frac{1}{2m}∑_{i=1}^m(h_θ(x^{(i)})-y^{(i)})^2
J(θ0,θ1)=2m1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))2
#x跟b
X_b=np.c_[np.ones((200,1)),X]
rate = 0.05 #学习率
iterations =1000 #迭代次数
m = 200 #样本数量
#参数theta
theta = np.random.randn(2,1)
#代价函数的梯度下降
for i in range(iterations):
temp=1/m*X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta)-y)
theta=theta-rate*temp
print("参数是:",theta)
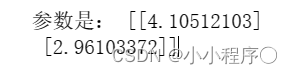
y=2.96103372*x+4.10512103
绘制预测完的图像
# 可视化结果
plt.plot(X_new, y_hat, "r-", label="Predictions")
plt.scatter(X, y, label="Training Data")
plt.xlabel('X')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Linear Regression using Gradient Descent')
plt.show()
实现多元线性回归
多元线性回归的梯度下降算法:
θ j ≔ θ j − α ∂ J ( θ ) ∂ θ j θ_j≔θ_j−α\frac{∂J(θ)}{∂θ_j} θj:=θj−α∂θj∂J(θ)
对 ∂ J ( θ ) ∂ θ j \frac{∂J(θ)}{∂θ_j} ∂θj∂J(θ)进行等价变形:
θ j ≔ θ j − α 1 m ∑ i = 1 m ( h θ ( x ( i ) ) − y ( i ) ) x j i θ_j≔θ_j−α\frac{1}{m}∑_{i=1}^m(h_θ (x^{(i)} )−y^{(i)}) x_j^i θj:=θj−αm1i=1∑m(hθ(x(i))−y(i))xji
#x跟b
X_b=np.c_[np.ones((200,1)),X]
rate = 0.05 #学习率
iterations =1000 #迭代次数
m = 200 #样本数量
#参数theta
theta = np.random.randn(4,1)
#梯度下降
for i in range(iterations):
temp=1/m*X_b.T.dot(X_b.dot(theta)-y)
theta=theta-rate*temp
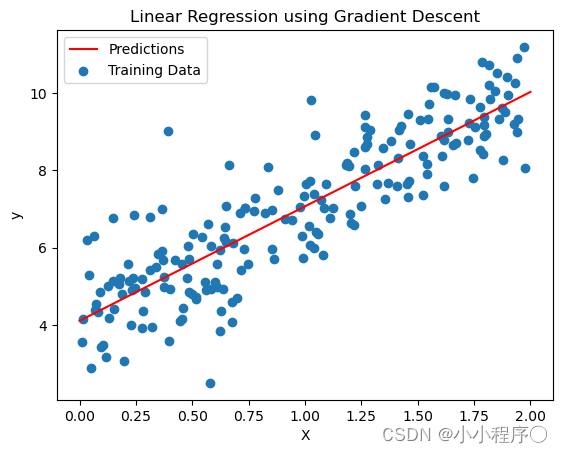
print("参数是:",theta)
X_new=np.array([[1,1.3,3],[1.2,1.3,1.4],[1.1,1.2,1.88]])
X_b_new = np.c_[np.ones((3,1)),X_new]
y_hat = X_b_new.dot(theta)
# 可视化结果
plt.scatter(X[:, 0], y, label='Actual')
plt.scatter(X_new[0, 1], y_predict, color='red', label='Prediction')
plt.scatter(X_new[1, 2], y_predict, color='red', label='Prediction')
plt.scatter(X_new[2, 2], y_predict, color='red', label='Prediction')
plt.xlabel('Feature 1')
plt.ylabel('Target')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Multiple Linear Regression Prediction')
plt.show()























 5644
5644











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










