文章目录
C++STL详解(一)一一string类的介绍和使用
一、string的定义方式
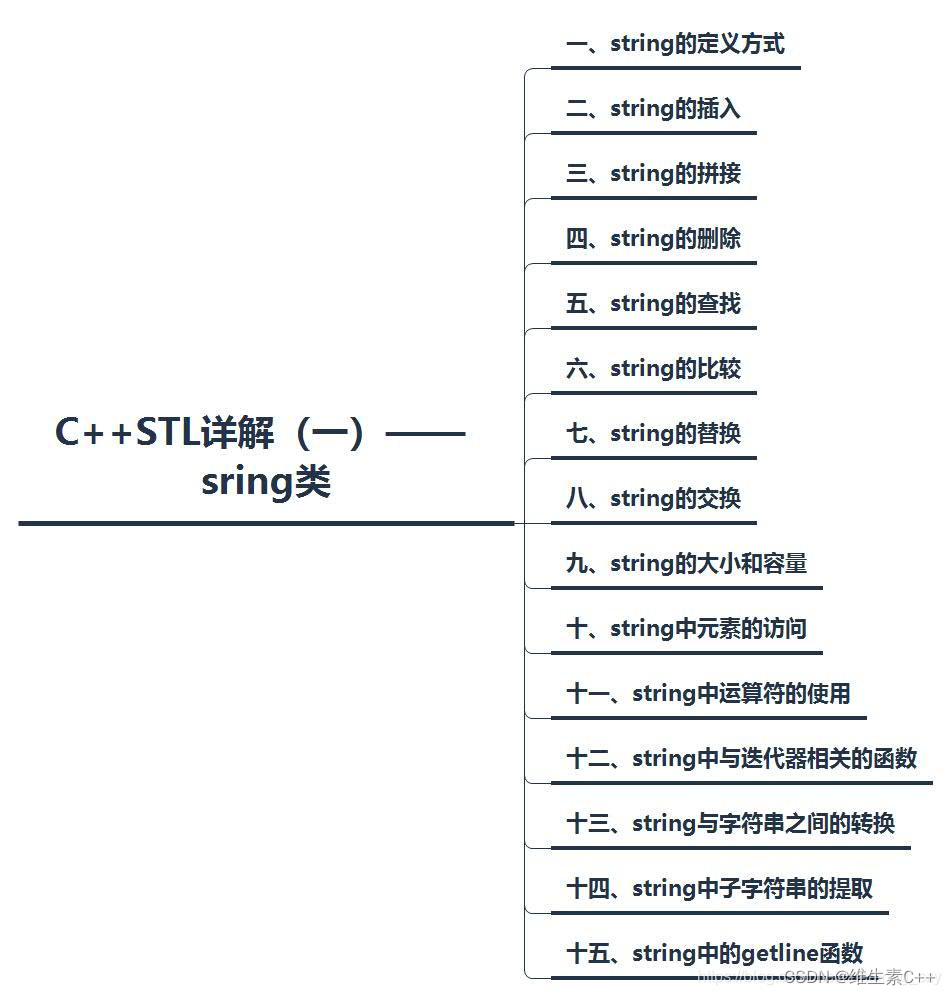
STL中string类实现了多个构造函数的重载,常用六个构造如下:
string(); //构造一个空字符串
string(const string& str); //将str拷贝构造生成一个复制品
string(const string & str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos); //复制str中从字符位置pos开始并跨越len个字符的部分
string(const char* s); //复制s所指的序列
string(const char* s, size_t n); //复制s所指的序列前n个字符
string(size_t n, char c); //生成n个c字符的字符串
使用示例:使用前要包含string头文件

运行结果:
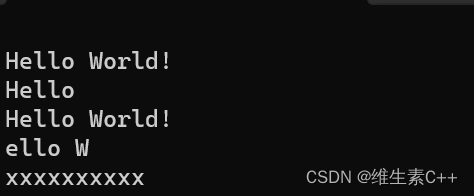
**注意nops是一个无符号的-1转换成有符号是32个比特位全1大小实际是2^32次方约等于4个G,所以我们不可能定义那么长的字符串,所以len缺省值给npos默认取到最后。
二、string的插入
1、使用push_back进行尾插
void push_back (char c);
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
s.push_back('C');
s.push_back('S');
s.push_back('D');
s.push_back('N');
cout << s << endl; //CSDN
return 0;
}
2、使用insert插入
string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str);
string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s);
iterator insert (iterator p, char c);
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("C"); //C
//insert(pos, str)在pos位置插入字符串str
s.insert(1, "S"); //CS
//insert(pos, string)在pos位置插入string对象
string t("D");
s.insert(2, t); //CSD
//insert(pos, char)在pos位置插入字符char
s.insert(s.end(), 'N'); //CSDN
cout << s << endl; //CSDN
return 0;
}
三、string的拼接
使用append函数完成string的拼接:
string& append (const string& str);
string& append (const char* s);
string& append (size_t n, char c);
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("I");
string s2(" like");
//append(string)完成两个string对象的拼接
s1.append(s2); //I like
//append(str)完成string对象和字符串str的拼接
s1.append(" C++"); //I like C++
//append(n, char)将n个字符char拼接到string对象后面
s1.append(3, '!'); //I like C++!!!
cout << s1 << endl; //I like C++!!!
return 0;
}
四、string的删除
1、使用pop_back进行尾删
void pop_back();
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("C++");
s.pop_back();
s.pop_back();
cout << s << endl; //C
return 0;
}
2、使用erase删除
string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);
iterator erase (iterator p);
iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last);
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("I like C++!!!");
//erase(pos, n)删除pos位置开始的n个字符
s.erase(8, 5); //I like C
//erase(pos)删除pos位置的字符
s.erase(s.end()-1); //I like
//erase(pos1, pos2)删除[pos1pos2)上所有字符
s.erase(s.begin() + 1, s.end()); //I
cout << s << endl; //I
return 0;
}
五、string的查找
1、使用find函数正向搜索第一个匹配项
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");
//find(string)正向搜索与string对象所匹配的第一个位置
string s2("www");
size_t pos1 = s1.find(s2);
cout << pos1 << endl; //7
//find(str)正向搜索与字符串str所匹配的第一个位置
char str[] = "cplusplus.com";
size_t pos2 = s1.find(str);
cout << pos2 << endl; //11
//find(char)正向搜索与字符char所匹配的第一个位置
size_t pos3 = s1.find(':');
cout << pos3 << endl; //4
return 0;
}
2、使用rfind函数反向搜索第一个匹配项
size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = npos) const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");
//rfind(string)反向搜索与string对象所匹配的第一个位置
string s2("string");
size_t pos1 = s1.rfind(s2);
cout << pos1 << endl; //42
//rfind(str)反向搜索与字符串str所匹配的第一个位置
char str[] = "reference";
size_t pos2 = s1.rfind(str);
cout << pos2 << endl; //25
//rfind(char)反向搜索与字符char所匹配的第一个位置
size_t pos3 = s1.rfind('/');
cout << pos3 << endl; //53
return 0;
}
六、string的比较
使用compare函数完成比较:
int compare (const string& str) const;
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str) const;
int compare (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen) const;
比较规则:
1、比较字符串中第一个不匹配的字符值较小,或者所有比较字符都匹配,但比较字符串较短,则返回小于0的值。
2、比较字符串中第一个不匹配的字符值较大,或者所有比较字符都匹配,但比较字符串较长,则返回大于0的值。
3、比较的两个字符串相等,则返回0。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hello CSDN");
//"hello world"和"hello CSDN"比较
cout << s1.compare(s2) << endl; //1
//"ell"和"hello CSDN"比较
cout << s1.compare(1, 3, s2) << endl; //-1
//"hello"和"hello"比较
cout << s1.compare(0, 4, s2, 0, 4) << endl; //0
return 0;
}

注意:除了支持string类之间进行比较,compare函数还支持string类和字符串进行比较。
七、string的替换
使用replace函数完成string的替换:
string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s);
string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, size_t n, char c);
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello world");
//replace(pos, len, str)将pos位置开始的len个字符替换为字符串str
s.replace(6, 4, "CSDN"); //hello CSDNd
//replace(pos, len, n, char)将pos位置开始的len个字符替换为n个字符char
s.replace(10, 1, 3, '!'); //hello CSDN!!!
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
八、string的交换
使用swap函数完成两个string类的交换:
void swap (string& x, string& y);算法里面库里的swap函数
void swap (string& str);string的成员函数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello");
string s2("CSDN");
//使用string类的成员函数swap交换s1和s2
s1.swap(s2);
cout << s1 << endl; //CSDN
cout << s2 << endl; //hello
//使用非成员函数swap交换s1和s2
swap(s1, s2);
cout << s1 << endl; //hello
cout << s2 << endl; //CSDN
return 0;
}
九、string的大小和容量
1、使用size函数或length函数获取当前有效字符的个数
size_t size() const;
size_t length() const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
cout << s.size() << endl; //4
cout << s.length() << endl; //4
return 0;
}
以后用size()和length()是一样效果都是求个数,但是建议使用size(),因为链表什么地址不是连续说长度不合理,以后都使用size()求个数
2、使用max_size函数获取string对象对多可包含的字符数
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
cout << s.max_size() << endl; //4294967294
return 0;
}
3、使用capacity函数获取当前对象所分配的存储空间的大小
size_t capacity() const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
cout << s.capacity() << endl; //15
return 0;
}
4、使用resize改变当前对象的有效字符的个数
void resize (size_t n);
void resize (size_t n, char c);
resize规则:
1、当n大于对象当前的size时,将size扩大到n,扩大的字符为c,若c未给出,则默认为’\0’。
2、当n小于对象当前的size时,将size缩小到n。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("CSDN");
//resize(n)n大于对象当前的size时,将size扩大到n,扩大的字符默认为'\0'
s1.resize(20);
cout << s1 << endl; //CSDN
cout << s1.size() << endl; //20
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //31
string s2("CSDN");
//resize(n, char)n大于对象当前的size时,将size扩大到n,扩大的字符为char
s2.resize(20, 'x');
cout << s2 << endl; //CSDNxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
cout << s2.size() << endl; //20
cout << s2.capacity() << endl; //31
string s3("CSDN");
//resize(n)n小于对象当前的size时,将size缩小到n
s3.resize(2);
cout << s3 << endl; //CS
cout << s3.size() << endl; //2
cout << s3.capacity() << endl; //15
return 0;
}
注意:若给出的n大于对象当前的capacity,则capacity也会根据自己的增长规则进行扩大。
5、使用reserve改变当前对象的容量大小
void reserve (size_t n = 0);
reserve规则:
1、当n大于对象当前的capacity时,将capacity扩大到n或大于n。
2、当n小于对象当前的capacity时,什么也不做。
g++编译器会缩容,但是不会影响数据,缩容代价很大一般不会缩容,vs不会,看编译器
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
cout << s << endl; //CSDN
cout << s.size() << endl; //4
cout << s.capacity() << endl; //15
//reverse(n)当n大于对象当前的capacity时,将当前对象的capacity扩大为n或大于n
s.reserve(20);
cout << s << endl; //CDSN
cout << s.size() << endl; //4
cout << s.capacity() << endl; //31
//reverse(n)当n小于对象当前的capacity时,什么也不做
s.reserve(2);
cout << s << endl; //CDSN
cout << s.size() << endl; //4
cout << s.capacity() << endl; //31
return 0;
}
注意:此函数对字符串的size没有影响,并且无法更改其内容
6、使用clear删除对象的内容,删除后对象变为空字符串
void clear();
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
//clear()删除对象的内容,该对象将变为空字符串
s.clear();
cout << s << endl; //空字符串
return 0;
}
7、使用empty判断对象是否为空
bool empty() const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
cout << s.empty() << endl; //0
//clear()删除对象的内容,该对象将变为空字符串
s.clear();
cout << s.empty() << endl; //1
return 0;
}
十、string中元素的访问
1、[ ]+下标
因为string类对[ ]运算符进行了重载,所以我们可以直接使用[ ]+下标访问对象中的元素。并且该重载使用的是引用返回,所以我们可以通过[ ]+下标修改对应位置的元素。
char& operator[](size_t pos);
const char& operator[](size_t pos) const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
//[]+下标访问对象元素
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
cout << s[i];
}
cout << endl;//结果CSDN
//[]+下标修改对象元素内容
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
s[i] = 'x';
}
cout << s << endl; //结果:xxxx
return 0;
}
2、使用at访问对象中的元素
因为at函数也是使用的引用返回,所以我们也可以通过at函数修改对应位置的元素。
char& at(size_t pos);
const char& at(size_t pos) const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
//at(pos)访问pos位置的元素
cout << s.at(i);
}
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < s.size(); i++)
{
//at(pos)访问pos位置的元素,并对其进行修改
s.at(i) = 'x';
}
cout << s << endl; //xxxx
return 0;
}
3、使用范围for访问对象中的元素(其实就是迭代器,傻瓜式替换成迭代器)
需要特别注意的是:若是需要通过范围for修改对象的元素,则用于接收元素的变量e的类型必须是引用类型,否则e只是对象元素的拷贝,对e的修改不会影响到对象的元素。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
//使用范围for访问对象元素
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e;
}
cout << endl; //CSDN
//使用范围for访问对象元素,并对其进行修改
for (auto& e : s) //需要修改对象的元素,e必须是引用类型
{
e = 'x';
}
cout << s << endl; //xxxx
return 0;
}
4.迭代器访问(深层是指针加模板)
迭代器访问才是主流
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("CSDN");
//使用迭代器访问对象元素
string::iterator it1 = s.begin();
while (it1 != s.end())
{
cout << *it1;
it1++;
}
cout << endl; //CSDN
//使用迭代器访问对象元素,并对其进行修改
string::iterator it2 = s.begin();
while (it2 != s.end())
{
*it2 += 1;
it2++;
}
cout << s << endl; //DTEO
return 0;
}
十一、string中运算符的使用
1、operator=
string类中对=运算符进行了重载,重载后的=运算符支持string类的赋值、字符串的赋值以及字符的赋值。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("CSDN");
//支持string类的赋值
s1 = s2;
cout << s1 << endl; //CSDN
//支持字符串的赋值
s1 = "hello";
cout << s1 << endl; //hello
//支持字符的赋值
s1 = 'x';
cout << s1 << endl; //x
return 0;
}
注意string常用字符串拼接不是append而是+=
2、operator+=
string类中对+=运算符进行了重载,重载后的+=运算符支持string类的复合赋值、字符串的复合赋值以及字符复合的赋值。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello");
//支持string类的复合赋值
s1 += s2;
cout << s1 << endl; //hello
//支持字符串的复合赋值
s1 += " CSDN";
cout << s1 << endl; //hello CSDN
//支持字符的复合赋值
s1 += '!';
cout << s1 << endl; //hello CSDN!
return 0;
}
3、operator+
string类中对+运算符进行了重载,重载后的+运算符支持以下几种类型的操作:
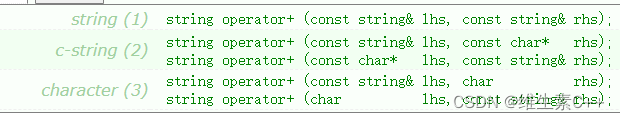
string类 + string类
string类 + 字符串
字符串 + string类
string类 + 字符
字符 + string类
它们相加后均返回一个string类对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
string s1("super");
string s2("man");
char str[] = "woman";
char ch = '!';
//string类 + string类
s = s1 + s2;
cout << s << endl; //superman
//string类 + 字符串
s = s1 + str;
cout << s << endl; //superwoman
//字符串 + string类
s = str + s1;
cout << s << endl; //womansuper
//string类 + 字符
s = s1 + ch;
cout << s << endl; //super!
//字符 + string类
s = ch + s1;
cout << s << endl; //!super
return 0;
}
4.sting类还支持cout<< cin>> 输入和输出运算符重载还要!= == < <= > >=等运算符重载


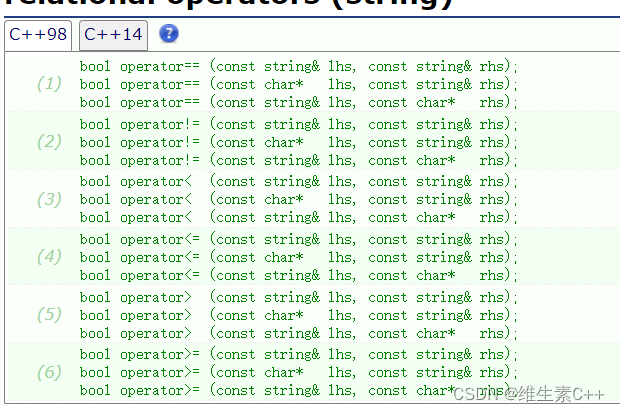
int main ()
{
std::string foo = "alpha";
std::string bar = "beta";
if (foo==bar) std::cout << "foo and bar are equal\n";
if (foo!=bar) std::cout << "foo and bar are not equal\n";
if (foo< bar) std::cout << "foo is less than bar\n";
if (foo> bar) std::cout << "foo is greater than bar\n";
if (foo<=bar) std::cout << "foo is less than or equal to bar\n";
if (foo>=bar) std::cout << "foo is greater than or equal to bar\n";
return 0;
十二、string中与迭代器相关的函数
1、与正向迭代器相关的函数
begin函数:
iterator begin();
const_iterator begin() const;
end函数:
iterator end();
const_iterator end() const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello string");
//正向迭代器
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end())
{
cout << *it;
it++;
}
cout << endl; //hello string
return 0;
}
2、与反向迭代器相关的函数
rbegin
reverse_iterator rbegin();
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const;
rend
reverse_iterator rend();
const_reverse_iterator rend() const;
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s("hello string");
//反向迭代器
string::reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit;
rit++;
}
cout << endl; //gnirts olleh
return 0;
}
十三、string与字符串之间的转换
1.将int,float,等转为string用to_string, 字符串转string前面已经讲了用构造

2、使用c_str或data将string转换为字符串, string转int等类型用stoi等

stoi例子:
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <string> // std::string, std::stoi
int main ()
{
std::string str_dec = "2001, A Space Odyssey";
std::string str_hex = "40c3";
std::string str_bin = "-10010110001";
std::string str_auto = "0x7f";
std::string::size_type sz; // alias of size_t
int i_dec = std::stoi (str_dec,&sz);
int i_hex = std::stoi (str_hex,nullptr,16);
int i_bin = std::stoi (str_bin,nullptr,2);
int i_auto = std::stoi (str_auto,nullptr,0);
std::cout << str_dec << ": " << i_dec << " and [" << str_dec.substr(sz) << "]\n";
std::cout << str_hex << ": " << i_hex << '\n';
std::cout << str_bin << ": " << i_bin << '\n';
std::cout << str_auto << ": " << i_auto << '\n';
return 0;
}

十四、string中子字符串的提取
1、使用substr函数提取string中的子字符串
// string::substr
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
std::string str="We think in generalities, but we live in details.";
// (quoting Alfred N. Whitehead)
std::string str2 = str.substr (3,5); // "think"
std::size_t pos = str.find("live"); // position of "live" in str
std::string str3 = str.substr (pos); // get from "live" to the end
std::cout << str2 << ' ' << str3 << '\n';
return 0;
}
2、使用copy函数将string的子字符串复制到字符数组中
// string::copy
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main ()
{
char buffer[20];
std::string str ("Test string...");
std::size_t length = str.copy(buffer,6,5);
buffer[length]='\0';
std::cout << "buffer contains: " << buffer << '\n';
return 0;
}
十五、string中的getline函数
我们知道,使用>>进行输入操作时,当>>读取到空格便会停止读取,基于此,我们将不能用>>将一串含有空格的字符串读入到string对象中。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s; //输入:hello CSDN
cout << s << endl; //输出:hello
return 0;
}
这时,我们就需要用getline函数完成一串含有空格的字符串的读取操作了。
用法一:
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);
getline函数将从is中提取到的字符存储到str中,直到读取到换行符’\n’为止。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin, s); //输入:hello CSDN
cout << s << endl; //输出:hello CSDN
return 0;
}
用法二:
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);
getline函数将从is中提取到的字符存储到str中,直到读取到分隔符delim或换行符’\n’为止。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin, s, 'D'); //输入:hello CSDN
cout << s << endl; //输出:hello CS
return 0;
}
十六、适用所有迭代器的reverse反转函数

注意所有的迭代区间都是左闭右开的,函数功能反转该迭代区间的元素
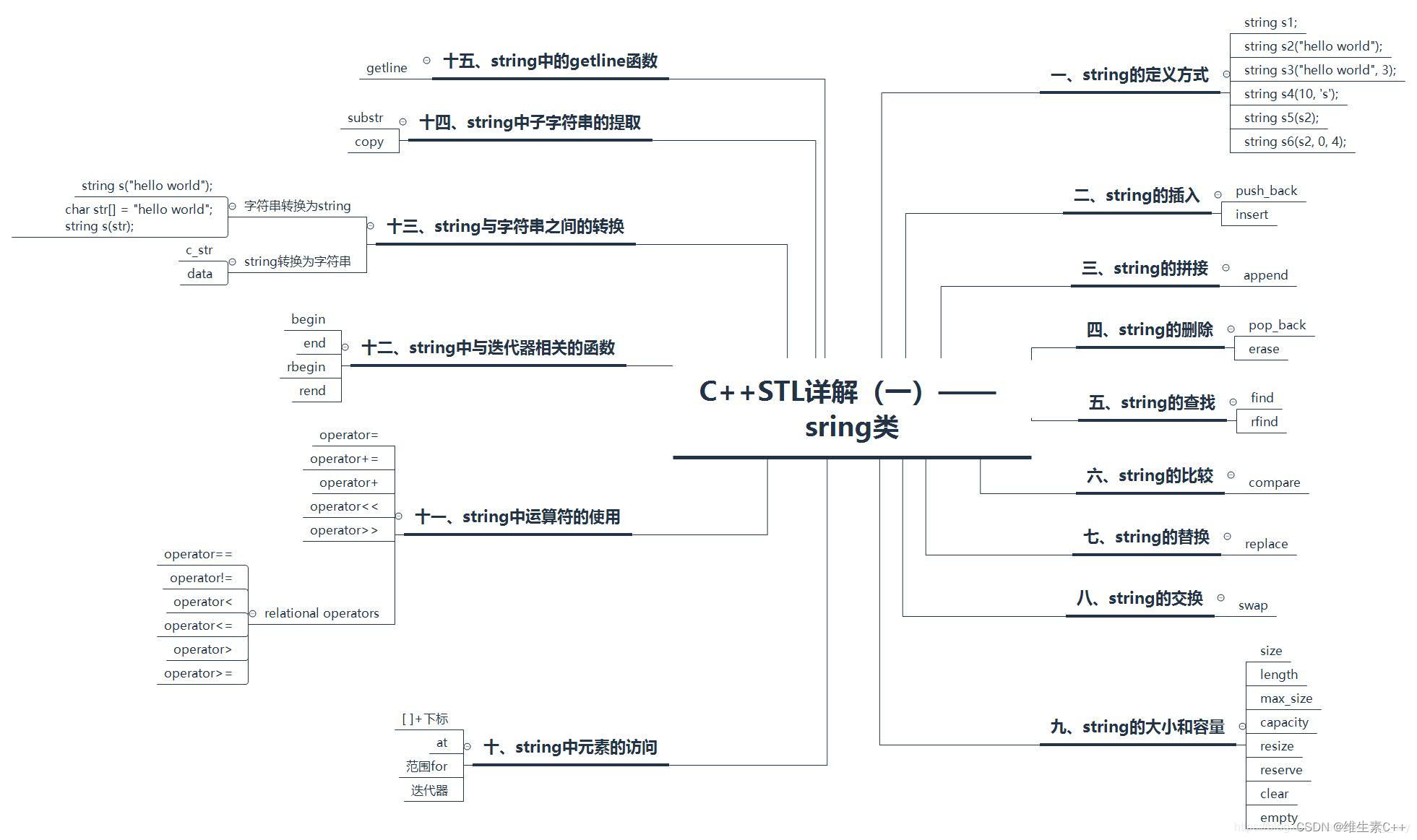
献上完整思维导图:
感谢老铁的支持!























 3445
3445











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










