一 前期准备
1.设置GPU
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import torchvision
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
import os,PIL,pathlib
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
devicedevice(type='cpu')
2.导入数据
import os,PIL,random,pathlib
data_dir = './shoes/'
data_dir = pathlib.Path(data_dir)
data_paths = list(data_dir.glob('*'))
classeNames = [str(path).split("\\")[1] for path in data_paths]
classeNames熟悉一下这个案例的数据集结构:shoes文件夹下并没有直接的分类。如果是直接分类的话我们需要自行划分训练集和测试集,但此结构是shoes文件夹下有两个文件夹:train和test分别对应了训练集和测试集。每个文件夹下才是各种品牌运动鞋的分类。这也告诉我们当遇到自带的train和test文件如何处理
代码运行结果:['test', 'train']
- 第一步:使用
pathlib.Path()函数将字符串类型的文件夹路径转换为pathlib.Path对象。- 第二步:使用
glob()方法获取data_dir路径下的所有文件路径,并以列表形式存储在data_paths中。- 第三步:通过
split()函数对data_paths中的每个文件路径执行分割操作,获得各个文件所属的类别名称,并存储在classeNames中- 第四步:打印
classeNames列表,显示每个文件所属的类别名称。
# 关于transforms.Compose的更多介绍可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38251616/article/details/124878863
train_transforms = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
# transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(), # 随机水平翻转
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
test_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize([224, 224]), # 将输入图片resize成统一尺寸
transforms.ToTensor(), # 将PIL Image或numpy.ndarray转换为tensor,并归一化到[0,1]之间
transforms.Normalize( # 标准化处理-->转换为标准正太分布(高斯分布),使模型更容易收敛
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) # 其中 mean=[0.485,0.456,0.406]与std=[0.229,0.224,0.225] 从数据集中随机抽样计算得到的。
])
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder("./shoes/train/",transform=train_transforms)
test_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder("./shoes/test/",transform=test_transform)
train_dataset.class_to_idx{'adidas': 0, 'nike': 1}
3.设置参数
batch_size = 16
train_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
test_dl = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(test_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=1)
# 取一个批次查看数据格式
# 数据的shape为:[batch_size, channel, height, weight]
# 其中batch_size为自己设定,channel,height和weight分别是图片的通道数,高度和宽度。
imgs, labels = next(iter(train_dl))
imgs.shapeShape of X [N, C, H, W]: torch.Size([8, 3, 224, 224])
Shape of y: torch.Size([8]) torch.int64
4.展现图像数据
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
# 指定图像文件夹路径
image_folder = './shoes/train/nike'
# 获取文件夹中的所有图像文件
image_files = [f for f in os.listdir(image_folder) if f.endswith((".jpg", ".png", ".jpeg"))]
# 创建Matplotlib图像
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 8, figsize=(16, 6))
# 使用列表推导式加载和显示图像
for ax, img_file in zip(axes.flat, image_files):
img_path = os.path.join(image_folder, img_file)
img = Image.open(img_path)
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axis('off')
# 显示图像
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show() 
二 构建简单的CNN模型
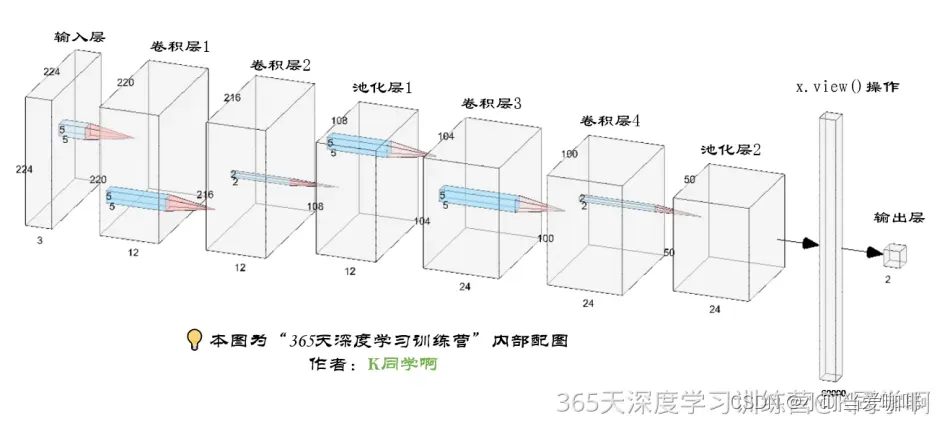
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.conv1=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 12, kernel_size=5, padding=0), # 12*220*220
nn.BatchNorm2d(12),
nn.ReLU())
self.conv2=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(12, 12, kernel_size=5, padding=0), # 12*216*216
nn.BatchNorm2d(12),
nn.ReLU())
self.pool3=nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(2)) # 12*108*108
self.conv4=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(12, 24, kernel_size=5, padding=0), # 24*104*104
nn.BatchNorm2d(24),
nn.ReLU())
self.conv5=nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(24, 24, kernel_size=5, padding=0), # 24*100*100
nn.BatchNorm2d(24),
nn.ReLU())
self.pool6=nn.Sequential(
nn.MaxPool2d(2)) # 24*50*50
self.dropout = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(0.2))
self.fc=nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(24*50*50, len(classeNames)))
def forward(self, x):
batch_size = x.size(0)
x = self.conv1(x) # 卷积-BN-激活
x = self.conv2(x) # 卷积-BN-激活
x = self.pool3(x) # 池化
x = self.conv4(x) # 卷积-BN-激活
x = self.conv5(x) # 卷积-BN-激活
x = self.pool6(x) # 池化
x = self.dropout(x)
x = x.view(batch_size, -1) # flatten 变成全连接网络需要的输入 (batch, 24*50*50) ==> (batch, -1), -1 此处自动算出的是24*50*50
x = self.fc(x)
return x
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
print("Using {} device".format(device))
model = Model().to(device)
model
Using cuda device
Model(
(conv1): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 12, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(12, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
(conv2): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(12, 12, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(12, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
(pool3): Sequential(
(0): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(conv4): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(12, 24, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
(conv5): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(24, 24, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1))
(1): BatchNorm2d(24, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(2): ReLU()
)
(pool6): Sequential(
(0): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(dropout): Sequential(
(0): Dropout(p=0.2, inplace=False)
)
(fc): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=60000, out_features=2, bias=True)
)
)
三 训练模型
1.编写训练函数
# 训练循环
def train(dataloader, model, loss_fn, optimizer):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 训练集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
train_loss, train_acc = 0, 0 # 初始化训练损失和正确率
for X, y in dataloader: # 获取图片及其标签
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
# 计算预测误差
pred = model(X) # 网络输出
loss = loss_fn(pred, y) # 计算网络输出和真实值之间的差距,targets为真实值,计算二者差值即为损失
# 反向传播
optimizer.zero_grad() # grad属性归零
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 每一步自动更新
# 记录acc与loss
train_acc += (pred.argmax(1) == y).type(torch.float).sum().item()
train_loss += loss.item()
train_acc /= size
train_loss /= num_batches
return train_acc, train_loss2.编写测试函数
def test (dataloader, model, loss_fn):
size = len(dataloader.dataset) # 测试集的大小
num_batches = len(dataloader) # 批次数目, (size/batch_size,向上取整)
test_loss, test_acc = 0, 0
# 当不进行训练时,停止梯度更新,节省计算内存消耗
with torch.no_grad():
for imgs, target in dataloader:
imgs, target = imgs.to(device), target.to(device)
# 计算loss
target_pred = model(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(target_pred, target)
test_loss += loss.item()
test_acc += (target_pred.argmax(1) == target).type(torch.float).sum().item()
test_acc /= size
test_loss /= num_batches
return test_acc, test_loss3.设置动态学习率
# 调用官方动态学习率接口时使用
learn_rate = 1e-4 # 初始学习率
lambda1 = lambda epoch: (0.92 ** (epoch // 2))
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learn_rate)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=lambda1) #选定调整方法4.正式训练
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss() # 创建损失函数
epochs = 40
train_loss = []
train_acc = []
test_loss = []
test_acc = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
model.train()
epoch_train_acc, epoch_train_loss = train(train_dl, model, loss_fn, optimizer)
# scheduler.step() # 更新学习率(调用官方动态学习率接口时使用)
model.eval()
epoch_test_acc, epoch_test_loss = test(test_dl, model, loss_fn)
train_acc.append(epoch_train_acc)
train_loss.append(epoch_train_loss)
test_acc.append(epoch_test_acc)
test_loss.append(epoch_test_loss)
# 获取当前的学习率
lr = optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr']
template = ('Epoch:{:2d}, Train_acc:{:.1f}%, Train_loss:{:.3f}, Test_acc:{:.1f}%, Test_loss:{:.3f}, Lr:{:.2E}')
print(template.format(epoch+1, epoch_train_acc*100, epoch_train_loss,
epoch_test_acc*100, epoch_test_loss, lr))
print('Done')
Epoch: 1, Train_acc:55.4%, Train_loss:0.770, Test_acc:61.8%, Test_loss:0.632, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 2, Train_acc:68.5%, Train_loss:0.634, Test_acc:63.2%, Test_loss:0.666, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 3, Train_acc:68.1%, Train_loss:0.577, Test_acc:59.2%, Test_loss:0.653, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 4, Train_acc:74.9%, Train_loss:0.512, Test_acc:64.5%, Test_loss:0.623, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 5, Train_acc:79.1%, Train_loss:0.458, Test_acc:76.3%, Test_loss:0.533, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 6, Train_acc:83.1%, Train_loss:0.409, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.508, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 7, Train_acc:86.3%, Train_loss:0.375, Test_acc:77.6%, Test_loss:0.446, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 8, Train_acc:88.6%, Train_loss:0.334, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.497, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch: 9, Train_acc:89.8%, Train_loss:0.309, Test_acc:69.7%, Test_loss:0.506, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:10, Train_acc:93.6%, Train_loss:0.289, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.421, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:11, Train_acc:90.6%, Train_loss:0.289, Test_acc:81.6%, Test_loss:0.436, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:12, Train_acc:93.2%, Train_loss:0.265, Test_acc:81.6%, Test_loss:0.418, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:13, Train_acc:95.2%, Train_loss:0.238, Test_acc:78.9%, Test_loss:0.420, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:14, Train_acc:95.0%, Train_loss:0.230, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.407, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:15, Train_acc:96.0%, Train_loss:0.216, Test_acc:81.6%, Test_loss:0.435, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:16, Train_acc:95.8%, Train_loss:0.208, Test_acc:78.9%, Test_loss:0.398, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:17, Train_acc:97.6%, Train_loss:0.183, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.381, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:18, Train_acc:98.8%, Train_loss:0.175, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.489, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:19, Train_acc:96.2%, Train_loss:0.194, Test_acc:81.6%, Test_loss:0.400, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:20, Train_acc:99.0%, Train_loss:0.166, Test_acc:82.9%, Test_loss:0.381, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:21, Train_acc:98.2%, Train_loss:0.158, Test_acc:81.6%, Test_loss:0.388, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:22, Train_acc:98.4%, Train_loss:0.152, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.361, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:23, Train_acc:98.8%, Train_loss:0.141, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.389, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:24, Train_acc:98.4%, Train_loss:0.136, Test_acc:82.9%, Test_loss:0.376, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:25, Train_acc:98.6%, Train_loss:0.141, Test_acc:85.5%, Test_loss:0.424, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:26, Train_acc:98.2%, Train_loss:0.143, Test_acc:78.9%, Test_loss:0.397, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:27, Train_acc:99.4%, Train_loss:0.121, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.365, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:28, Train_acc:99.2%, Train_loss:0.122, Test_acc:77.6%, Test_loss:0.377, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:29, Train_acc:99.8%, Train_loss:0.113, Test_acc:84.2%, Test_loss:0.379, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:30, Train_acc:99.6%, Train_loss:0.110, Test_acc:84.2%, Test_loss:0.382, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:31, Train_acc:99.2%, Train_loss:0.111, Test_acc:77.6%, Test_loss:0.370, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:32, Train_acc:99.0%, Train_loss:0.109, Test_acc:81.6%, Test_loss:0.372, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:33, Train_acc:99.6%, Train_loss:0.103, Test_acc:80.3%, Test_loss:0.366, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:34, Train_acc:99.6%, Train_loss:0.104, Test_acc:78.9%, Test_loss:0.366, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:35, Train_acc:99.4%, Train_loss:0.103, Test_acc:78.9%, Test_loss:0.346, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:36, Train_acc:100.0%, Train_loss:0.093, Test_acc:76.3%, Test_loss:0.352, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:37, Train_acc:99.8%, Train_loss:0.090, Test_acc:78.9%, Test_loss:0.355, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:38, Train_acc:99.8%, Train_loss:0.084, Test_acc:84.2%, Test_loss:0.367, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:39, Train_acc:100.0%, Train_loss:0.084, Test_acc:84.2%, Test_loss:0.355, Lr:1.00E-04 Epoch:40, Train_acc:99.4%, Train_loss:0.082, Test_acc:82.9%, Test_loss:0.341, Lr:1.00E-04 Done
四 结果可视化
1.loss和Accuary图
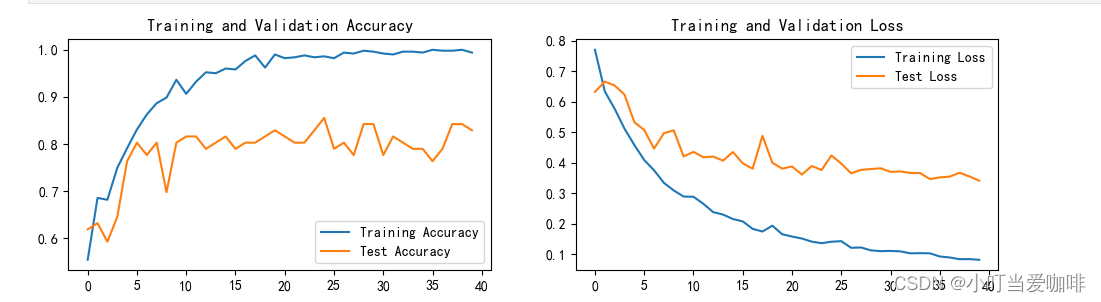
2.指定图片预测
⭐torch.squeeze()详解
对数据的维度进行压缩,去掉维数为1的的维度函数原型:
torch.squeeze(input, dim=None, *, out=None)关键参数说明:
● input (Tensor):输入Tensor
● dim (int, optional):如果给定,输入将只在这个维度上被压缩
from PIL import Image
classes = list(train_dataset.class_to_idx)
def predict_one_image(image_path, model, transform, classes):
test_img = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
# plt.imshow(test_img) # 展示预测的图片
test_img = transform(test_img)
img = test_img.to(device).unsqueeze(0)
model.eval()
output = model(img)
_,pred = torch.max(output,1)
pred_class = classes[pred]
print(f'预测结果是:{pred_class}')
# 预测训练集中的某张照片
predict_one_image(image_path='./shoes/test/adidas/1.jpg',
model=model,
transform=train_transforms,
classes=classes)预测结果是:adidas
五 保存模型
# 模型保存
PATH = './model.pth' # 保存的参数文件名
torch.save(model.state_dict(), PATH)
# 将参数加载到model当中
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(PATH, map_location=device))





















 353
353

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








