这次博客我们来讲讲有关栈和队列的oj题目,虽然前两个题实际意义不大,但有助于提升我们的编程能力
先来看看第一个题目用栈实现队列

既然要实现队列的功能,那就得满足队列的特性先进先出,但我们用的是两个栈如何实现先进先出呢? 也不卖关子了,直接先说思路,既然是两个栈那就得通过栈来倒数据了,栈是先入后出,那我们需要先出的数据应当是栈底数据,所以我们只需要把一个栈中数据全部导入另一个栈,那么另一个栈的栈顶不正是我们出队的队头吗
废话不多说直接开写
首先需要自己写一个栈
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct {
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void ST_init(ST* pst);
void ST_destory(ST* pst);
void ST_push(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void ST_pop(ST* pst);
bool ST_empty(ST* pst);
STDataType ST_top(ST* pst);
int ST_size(ST* pst);
void ST_init(ST* pst)
{
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
void ST_destory(ST* pst)
{
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
bool ST_empty(ST* pst)
{
return pst->top == 0;
}
void ST_push(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
if (pst->capacity == pst->top)
{
int newcapacity= pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, newcapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc failed");
return;
}
else
{
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
pst->a[pst->top ] = x;
pst->top++;
}
void ST_pop(ST* pst)
{
assert(!ST_empty(pst));
pst->top--;
}
STDataType ST_top(ST* pst)
{
assert(!ST_empty(pst));
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
int ST_size(ST* pst)
{
return pst->top;
}
首先自然需要先有一个队列的结构体
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST popst;
} MyQueue;接下来便要初始化队列了
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
ST_init(&obj->pushst);
ST_init(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}入队便很简单了只需要往pushst栈中入数据
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
ST_push(&obj->pushst,x);
}出数据稍微复杂那么一点点但问题不大,简单来说就是popst栈中有数据便直接出栈,如果没有数据就将pushst栈中数据导入popst中再出数据,代码如下
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
if(ST_empty(&obj->popst))
{
while(!ST_empty(&obj->pushst))
{
ST_push(&obj->popst,ST_top(&obj->pushst));
ST_pop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
int top=ST_top(&obj->popst);
ST_pop(&obj->popst);
return top;
}返回开头元素呢就与出数据有异曲同工之处了,当婆婆st中有数据便直接返回栈顶元素,若无数据便如上一样导数据后再返回栈顶元素
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(!ST_empty(&obj->popst))
{
return ST_top(&obj->popst);
}else
{
while(!ST_empty(&obj->pushst))
{
ST_push(&obj->popst,ST_top(&obj->pushst));
ST_pop(&obj->pushst);
}
}
return ST_top(&obj->popst);
}判空和释放就很简单啦我就写到一起了,注意释放要把栈也给释放了哦
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return ST_empty(&obj->pushst)&&ST_empty(&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
ST_destory(&obj->pushst);
ST_destory(&obj->popst);
free(obj);
}再来看第二个题目队列实现栈,这题就与上一个题目又有区别了哦

既然要实现栈,那肯定就需要满足后进先出,但是队列的特性是先进先出,所以不同上个题目的是,将队列的数据全部导入另一个队列,数据的顺序不会改变,所以此时我们需要换一个思路,就是将其中一个队列的数据留下一个不导入另一个队列,这样出的最后一个数也就是最后入的数据,恰好满足了后入先出
接下来我来画个图帮助大家理解
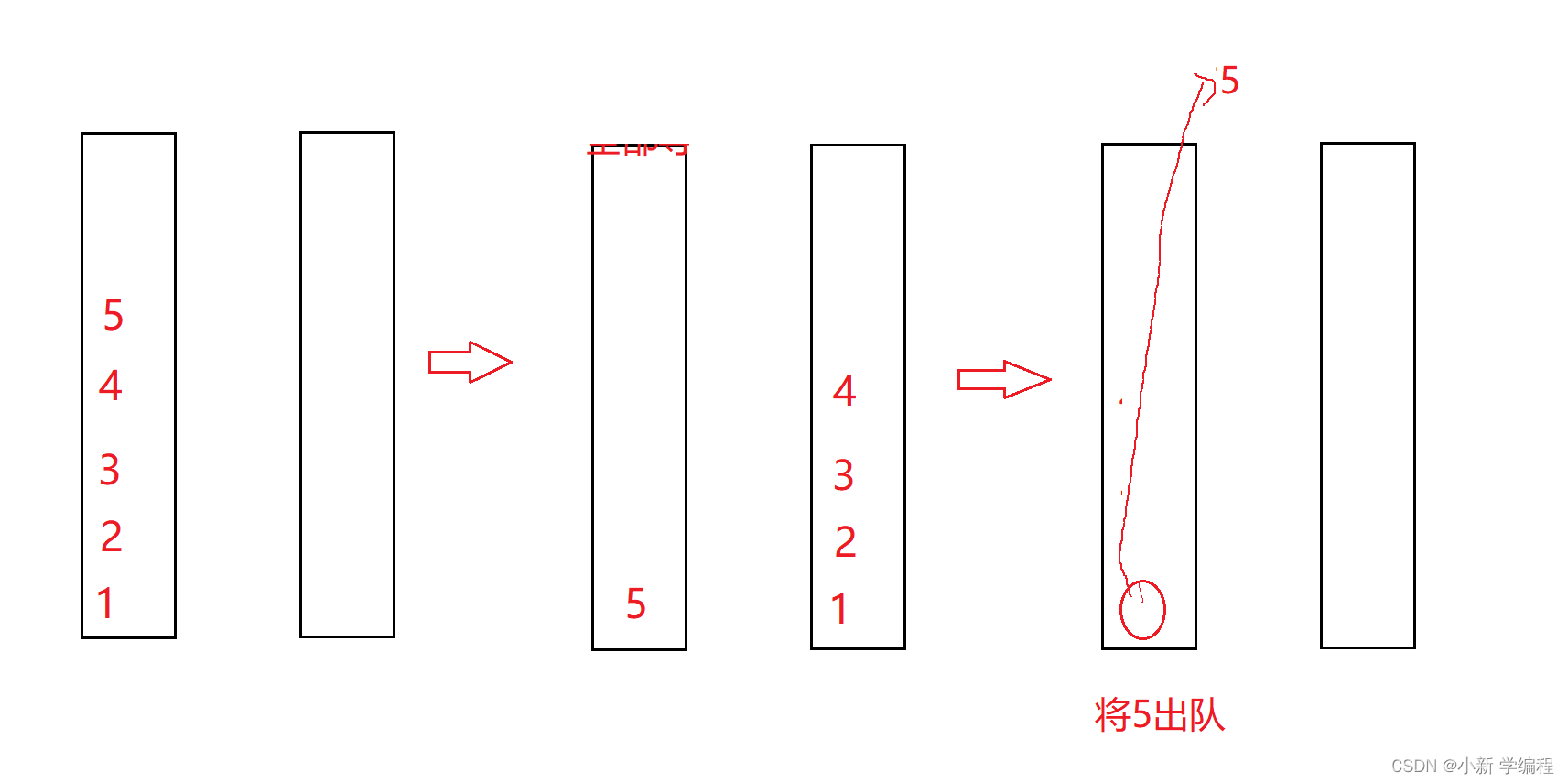
老样子首先需要自己先写个队列
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->phead = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Queue* pq)
{
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc failed");
return;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->phead == NULL)
{
assert(pq->ptail==NULL);
pq->phead = pq->ptail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->ptail ->next= newnode;
pq->ptail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->phead->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = pq->ptail=NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->phead->next;
pq->phead->next = NULL;
free(pq->phead);
pq->phead = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->phead->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->ptail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
return pq->size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
return pq->size == 0;
}
第一步当然还是需要一个结构体
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;第二步就是栈的初始化了
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* obj=(MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&obj->q1);
QueueInit(&obj->q2);
}入栈就很简单了,往空队中入就好了
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1,x);
}
else{
QueuePush(&obj->q2,x);
}
}出栈就如我上面方法所说的,导数据,代码如下
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* empty=&obj->q1;
Queue* noempty=&obj->q2;
if(QueueEmpty(&obj->q2))
{
empty=&obj->q2;
noempty=&obj->q1;
}
int top=QueueBack(noempty);
while(QueueSize(noempty)>1)
{
QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(noempty));
QueuePop(noempty);
}
QueuePop(noempty);
return top;
}找栈顶数据也很简单,只要返回有数据的队列中的队尾元素就好了
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}最后就是判空和释放了
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1)&&QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
QueueDestroy(&obj->q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}下一题循环队列稍微比前面复杂一点,但实际也并不难

直接来说我的方法吧,这题我用的数组来存数据,但是注意这里我是会多开一个空间,方便判断队空和队满
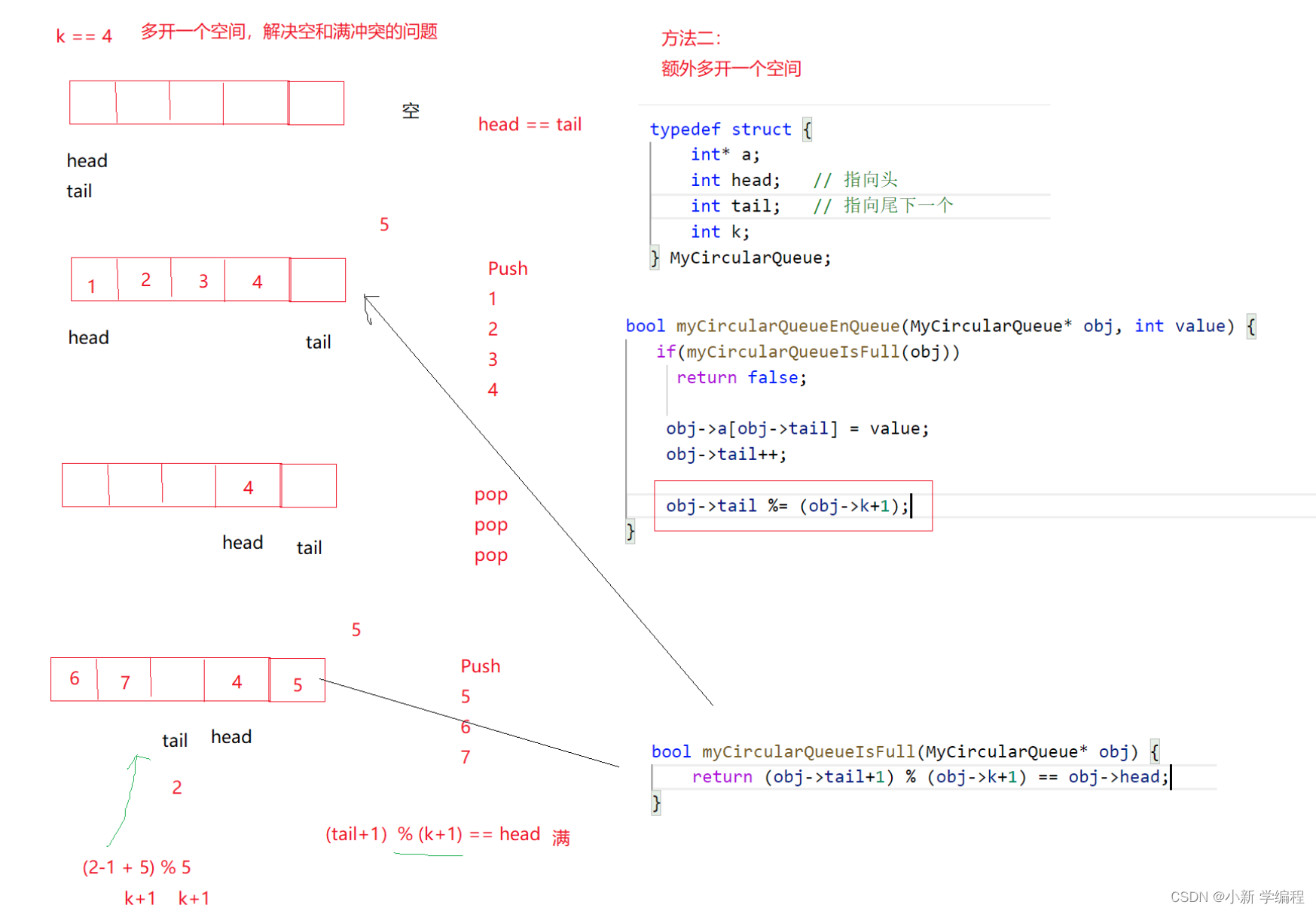

完整代码如下
typedef struct {
int front;
int tail;
int* a;
int k;
} MyCircularQueue;
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj=(MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->front=obj->tail=0;
obj->k=k;
return obj;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return obj->front==obj->tail;
}
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
return (obj->tail+1)%(obj->k+1)==obj->front;
}
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value) {
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
return false;
obj->a[obj->tail]=value;
obj->tail=(obj->tail+1)%(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return false;
obj->front=(obj->front+1)%(obj->k+1);
return true;
}
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
return obj->a[(obj->tail-1+obj->k+1)%(obj->k+1)];
}
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj) {
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}
这次博客到这里也就结束了,写的不是很好请大家多多包涵,谢谢啦!






















 717
717

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








