# 程序文件 ti5_7.py
import cvxpy as cp
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 修正导入库
# 定义优化变量
x = cp.Variable(3, pos=True)
# 定义约束条件
constraints = [x[0] >= 0, sum(x[:2]) >= 100, sum(x) == 180]
# 定义第一个优化问题
obj0 = cp.Minimize(0.2 * sum(x ** 2) + 50 * sum(x) + 4 * (2 * x[0] + x[1] - 140))
prob0 = cp.Problem(obj0, constraints)
prob0.solve()
print('最优值为:', prob0.value)
print('最优解为:\n', x.value)
# 初始化绘图数据
plt.subplots_adjust(wspace=0.5)
V1 = []
for a in np.arange(40, 61, 2):
# 定义第二个优化问题(改变线性项的系数)
obj1 = cp.Minimize(0.2 * sum(x ** 2) + a * sum(x) + 4 * (2 * x[0] + x[1] - 140))
prob1 = cp.Problem(obj1, constraints)
prob1.solve()
V1.append(prob1.value)
# 绘制第一个图
plt.subplot(131)
plt.plot(np.arange(40, 61, 2), V1)
plt.title('Varying linear coefficient a')
V2 = []
for b in np.arange(0.15, 0.26, 0.01):
# 定义第三个优化问题(改变二次项的系数)
obj2 = cp.Minimize(b * sum(x ** 2) + 50 * sum(x) + 4 * (2 * x[0] + x[1] - 140))
prob2 = cp.Problem(obj2, constraints)
prob2.solve()
V2.append(prob2.value)
# 绘制第二个图
plt.subplot(132)
plt.plot(np.arange(0.15, 0.26, 0.01), V2)
plt.title('Varying quadratic coefficient b')
V3 = []
for c in np.arange(3, 5.1, 0.1):
# 定义第四个优化问题(改变某个特定线性组合的系数)
obj3 = cp.Minimize(0.2 * sum(x ** 2) + 50 * sum(x) + c * (2 * x[0] + x[1] - 140))
prob3 = cp.Problem(obj3, constraints)
prob3.solve()
V3.append(prob3.value)
# 绘制第三个图
plt.subplot(133)
plt.plot(np.arange(3, 5.1, 0.1), V3)
plt.title('Varying specific linear combination coefficient c')
# 显示图形
plt.show()
# 程序文件 ti6_1.py
import networkx as nx
import pylab as plt
L1=[(1,2),(1,3),(1,4),(2,3),(2,6),(3,4),(4,5),(5,6)]
G1= nx.Graph ();G1.add_nodes_from ( range (1,7))
G1.add_edges_from(L1);pos1=nx.shell_layout(G1)
plt.subplot (131)
nx.draw(G1,pos1,with_labels=True,font_weight='bold')
L2=[(1,2,7),(1,3,3),(1,4,12),(2,3,1),(2,6,1),(3,4,8),(4,5,9),(5,6,3)]
G2= nx.Graph();G2.add_nodes_from(range(1,7))
G2.add_weighted_edges_from(L2);pos2=nx.shell_layout(G2)
plt.subplot(132)
nx.draw(G2,pos2,with_labels=True,font_weight='bold')
w2=nx.get_edge_attributes(G2,'weight ')
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G2,pos2,edge_labels =w2)
L3=[(1,3,3),(2,1,7),(2,3,1),(3,4,8),(4,1,12),(5,4,9),(5,6,3),(6,2,1)]
G3=nx.DiGraph();G3.add_nodes_from(range(1,7))
G3.add_weighted_edges_from(L3);pos3=nx.shell_layout(G3)
plt.subplot(133)
nx.draw(G3,pos3,with_labels=True,font_weight='bold')
w3= nx.get_edge_attributes(G3,' weight ')
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(G3,pos3,edge_labels =w3)
plt.show ()

# 程序文件 ti6_3.py
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # 导入绘图库
L = [(1, 2, 20), (1, 5, 15), (2, 3, 20), (2, 4, 60), (2, 5, 25),
(3, 4, 30), (3, 5, 18), (4, 5, 35), (4, 6, 10), (5, 6, 15)]
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_nodes_from(range(1, 7))
G.add_weighted_edges_from(L)
T = nx.minimum_spanning_tree(G)
w = nx.get_edge_attributes(T, 'weight')
TL = sum(w.values())
print('最小生成树的长度:', TL)
pos = nx.shell_layout(G)
s = ['v' + str(i) for i in range(1, 7)]
s = dict(zip(range(1, 7), s)) # 这一步其实是多余的,因为可以直接在draw中使用labels参数
# 绘制最小生成树
nx.draw(T, pos, labels=s, with_labels=True, node_color='lightblue', node_size=500, font_weight='bold')
nx.draw_networkx_edge_labels(T, pos, edge_labels=w)
plt.show()

# 程序文件 ti6_4.py
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
import pylab as plt
a = np . zeros ((5,5))
a[0,1:]=[0.8,2,3.8,6]
a[1,2:]=[0.9,2.1,3.9]
a[2,3:]=[1.1,2.3]; a [3,4]=1.4
G=nx.DiGraph ( a )
p=nx.shortest_path(G,0,4, weight =' weight ')
d =nx.shortest_path_length( G ,0,4, weight =' weight ')
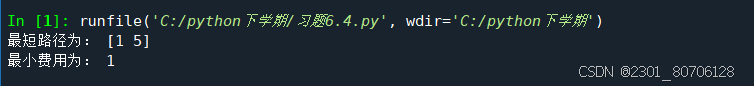
print ('最短路径为:', np . array ( p )+1)
print ('最小费用为:', d )
# 程序文件 ti6_5.py
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n = 6
node = ['v' + str(i) for i in range(1, n + 1)]
A = np.zeros((n, n))
A[0, [1, 2]] = [2, 7]
A[1, 2:5] = [4, 6, 8]
A[2, [3, 4]] = [1, 3]
A[3, [4, 5]] = [1, 6]
A[4, 5] = 3
G = nx.Graph(A)
d = nx.floyd_warshall_numpy(G)
dm1 = np.max(d, axis=0)
print('d= \n', d)
print('逐列最大值为:', dm1)
f = pd.ExcelWriter('ti6_5.xlsx')
dd = pd.DataFrame(d)
dd.to_excel(f, 'Sheet1', index=False)
num = np.array([[50, 40, 60, 20, 70, 90]]).T
D = num * d
DD = pd.DataFrame(D)
DD.to_excel(f, 'Sheet2', index=False)
sd = np.sum(D, axis=0)
sdm = np.min(sd)
ind = np.argmin(sd)
f.close()
print('最小值为:', sdm)
print('达到最小值的地点为:', node[ind])
























 1816
1816

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








