面试结束复盘查漏补缺
每次面试都是检验自己知识与技术实力的一次机会,面试结束后建议大家及时总结复盘,查漏补缺,然后有针对性地进行学习,既能提高下一场面试的成功概率,还能增加自己的技术知识栈储备,可谓是一举两得。
以下最新总结的阿里P6资深Java必考题范围和答案,包含最全MySQL、Redis、Java并发编程等等面试题和答案,用于参考~
重要的事说三遍,关注+关注+关注!


更多笔记分享

import java.util.Arrays;
public class ShellSort {
/*
* 时间复杂度和增量有关系,所以无法得出准确的时间复杂度
* 但只需要记住:在一定的范围里,希尔排序的时间复杂度为 O(N^1.3 ~ N^1.5)
* 空间复杂度为 O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定
* 判断稳定性的技巧:如果在比较的过程中 发生了 跳跃式交换。那么,就是不稳定的排序。
* */
public static void shell(int[] array,int group){
for (int i = group; i < array.length; i += 1) {
int tmp = array[i];
int j = i-group;
for (; j >= 0; j-=group) {
if(tmp < array[j]){
array[j+group] = array[j];
}else{
break;
}
}
array[j+group] = tmp;
}
}
public static void shellSort(int[] array){
int group = array.length;
// 预排序
while(group > 1){
// 第一次分组委 数组的长度,即 头尾判断。
// 其后,每次分组个数,缩小一倍。
shell(array,group);
group /= 2;
}
// 最后调整
shell(array,1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array ={12,5,9,34,6,8,33,56,89,0,7,4,22,55,77};
shellSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

其实 希尔排序就是一个直接插入排序。
===================================================================

定义 一个 变量, 用来记录 此时的 i 后面最小值的下标。等 j 遍历完了,最小值的下标也就拿到了。此时,再进行交换。
这样就不必让上面那样,遇到比 i下标元素 小的,就交换。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectSort {
/*
* 稳定性: 不稳定 见附图
* 时间复杂度:O(N^2) 》》 外层循环 n -1,内层循环 n -1
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* */
public static void selectSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
int index = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < array.length; j++) {
if(array[index] > array[j]){
index = j;
}
}
int tmp = array[i];
array[i] = array[index];
array[index] = tmp;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,6,10,3,5};
selectSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

附图

==========================================================================
每一次从无序区间选出最小 + 最大的元素,存放在无序区间的最前和最后,直到全部待排序的数据元素排完 。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class SelectSortOP {
public static void selectSortOP(int[] array){
int low = 0;
int high = array.length - 1;
// [low,high] 表示整个无序区间
while(low < high){
int min = low;
int max = low;
for (int i = low+1; i <= high; i++) {
if(array[i] < array[min]){
min = i;
}
if(array[i] > array[max]){
max = i;
}
}
swap(array,min,low);
if(max == low){
max = min;
}
swap(array,max,high);
low++;
high--;
}
}
public static void swap(int[] array,int x,int y){
int tmp = array[x];
array[x] = array[y];
array[y] = tmp;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {9, 5, 2, 7, 3, 6, 8 };
selectSortOP(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

==================================================================
基本原理也是选择排序,只是不在使用遍历的方式查找无序区间的最大的数,而是通过堆来选择无序区间的最大的数。
注意: 排升序要建大堆;排降序要建小堆.
这个我就不讲,因为我在 堆/优先级中讲的很清楚!
有兴趣的,可以点击 链接关键字 ,跳转到该文章,该内容在 文章目录最后面。
这里我们就直接上代码。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class HeapSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,8,5,4,10,15};
creationHeap(array);// 建堆的时间复杂度:O(N)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
heapSort(array);// 堆排序的时间复杂度:O(N * log2 N)
// 空间复杂度:O(1)
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
// 创建一个大根堆
public static void creationHeap(int[] array){
for (int parent = (array.length-1-1)/2; parent >= 0; parent--) {
shiftDown(array,parent,array.length);
}
}
public static void heapSort(int[] array){
/*
* 时间复杂度:O(N * log2 N)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:不稳定
* */
int end = array.length - 1;
while(end>0){
int tmp = array[end];
array[end] = array[0];
array[0] = tmp;
shiftDown(array,0,end);
end--;
}
}
// 向下调整
public static void shiftDown(int[] array,int parent,int len){
int child = parent * 2 + 1;// 做孩纸
while(child < len){
// 获取左右子树最大值的下标
if(child+1 < len && (array[child] < array[child+1])){
child++;
}
if(array[child] > array[parent]){
int tmp = array[child];
array[child] = array[parent];
array[parent] = tmp;
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
}
}

===================================================================

import java.util.Arrays;
/*
* 时间复杂度:O(N^2) 【无论是最好情况,还是最坏情况,时间复杂度都不变】
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:稳定【未发生跳跃式交换】
* */
public class BubbleSort {
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array){
// 比较的趟数 = 数组的长度 - 1 【 0 ~ 3 一共 4趟】
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
// 比较完一趟后,可以比较的元素个数减一。【因为靠后的数据已经有序】
// 内循环中,之所以要减一个 1,是因为防止 下面的if语句 发生 数组越界异常
for(int j = 0;j< array.length-1-i;j++){
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,6,10,3,5};
bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}


代码如下 - 优化
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort {
/*
* 时间复杂度:O(N^2)
* 最好情况【数组有序】可以达到 O(N)
* 空间复杂度:O(1)
* 稳定性:稳定【未发生跳跃式交换】
* */
public static void bubbleSort(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
for(int j = 0;j< array.length-1-i;j++){
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = tmp;
flag = false;// 表示这一趟比较,数组是无序的
}
}
// flag == true
if(flag){
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 前半段无序,后半段有序
int[] array = {2,3,1,4,5};
bubbleSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

public class BubbleSort {
// 优化
public static void bubbleSort2(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
boolean flag = true;
for(int j = 0;j< array.length-1-i;j++){
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = tmp;
flag = false;
}
}
// flag == true
if(flag){
break;
}
}
}
// 未优化
public static void bubbleSort1(int[] array){
for (int i = 0; i < array.length-1; i++) {
for(int j = 0;j< array.length-1-i;j++){
if(array[j] > array[j+1]){
int tmp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j+1];
array[j+1] = tmp;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = new int[10000];
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
array[i] = i;
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
bubbleSort2(array);// 优化
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);// 输出排序所需时间
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
bubbleSort1(array);// 未优化
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);//输出排序所需时间
}
}

========================================================================
1、从待排序区间选择一个数,作为基准值(pivot)
2、Partition(分割):遍历整个待排序区间,将比基准值小的(可以包含相等的)放到基准值的左边,将比基准值大的(可以包含相等的)放到基准值的右边。
3、采用分治思想,对左右两个小区间按照同样的方式处理,直到小区间的长度 == 1.代表已经有序,或者小区间的长度 == 0,代表没有数据。
快速排序,其实说白了 和 二叉树 很像,先根,再左,后右。利用递归去实现!
public class QuickSort {
public static void quickSort(int[] array){
quick(array,0, array.length);
}
public static void quick(int[] array,int start,int end){
if(start >= end){
return;
}
int pivot = partiton(array,start,end);
quick(array,start,pivot-1);// 递归左边
quick(array,pivot+1,end);// 递归右边
}
// 分割 - 找基准
private static int partiton(int[] array,int start,int end){
}
}
// 分割 - 找基准
private static int partiton(int[] array,int start,int end){
int tmp = array[start];
while(start < end){
while(start < end && array[end] >= tmp){
end--;
}
// 此时 end 下标 元素的值 是 小于 tmp的。
array[start] = array[end];
while(start<end && array[start] <= tmp){
start++;
}
//此时 start 下标元素的值 是 大于 tmp的。
array[end] = array[start];
}
// start 和 end 相遇了,将 tmp 赋予 它们相遇下标指向的空间
array[start] = tmp;
return start;
}

代码细节部分

import java.util.Arrays;
public class QuickSort {
/*
* 时间复杂度:O(N^2) 【数据有序或者逆序的情况】
* 最好情况【每次可以均匀的分割待排序序列】:O(N * log2 N)
* 空间复杂度:O(N)[单分支的一棵树]
* 最好:log2 N
* 稳定性:不稳定
* */
public static void quickSort(int[] array){
quick(array,0, array.length-1);
}
public static void quick(int[] array,int start,int end){
if(start >= end){
return;
}
int pivot = partiton(array,start,end);
quick(array,start,pivot-1);// 递归左边
quick(array,pivot+1,end);// 递归右边
}
// 分割 - 找基准
private static int partiton(int[] array,int start,int end){
int tmp = array[start];
while(start < end){
while(start < end && array[end] >= tmp){
end--;
}
// 此时 end 下标 元素的值 是 小于 tmp的。
array[start] = array[end];
while(start<end && array[start] <= tmp){
start++;
}
array[end] = array[start];
}
array[start] = tmp;
return start;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {6,1,2,7,9,3,4,5,10,8};
quickSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

细心的朋友会发现 堆排序 和 快排 的 时间复杂度在最好情况下 都是N* log2 N。
那么,两者又有什么区别?
堆排序,无论最好还是最坏情况,时间复杂度都是N* log2 N。空间复杂度 O(1)
那么,又为什么快排 比 堆排序 要快?
其实再细一点说 :在两个排序的时间复杂度都为 N* log2 N时,其实连着前面还有 一个 k【K * N* log2 N 】,只不过快排前面的K要小一点。所以快排要快一点。
在对空间复杂度没有要求的情况: 快排
对空间复杂度有要求的情况,或者说对数据的序列也要要求: 堆排
if语句中 比较大小的代码中 等号是不能省略的
当 下面框选的代码 没有等号时,会造成死循环。
我就改了一下,末尾元素的值。
那么,问题来了:为什么没有等号就死循环了?
所以,在 写快排的时候,比较大小的代码,记住一定要加上等号!!!!!
目前版本的 快排代码 不支持 大量数据进行排序 - 会导致栈溢出。

这是因为 我们递归的太深了,1百万数据,4百万字节。
1TB等于1024GB;1GB等于1024MB;1MB等于1024KB;1KB等于1024Byte(字节);1Byte等于8bit(位);
有的朋友会说:这才多大啊?栈怎么会被挤爆?
这是因为在递归的时候,开辟的栈帧【函数的信息,参数等等等…都有】,所以,每次开辟的栈帧不止 4byte。故栈被挤爆了。
所以,我们要优化快排的 代码。【优化:数据有序的情况】
1、选择边上(左或者右) 【重点,上面使用的就是这种方法】
2、随机选择(针对 有序数据)【了解】
3、几数取中(常见的就是三数取中):array[left],array[mid] ,array[right]中 大小为 中间值的为基准值【优化的关键】
import java.util.Arrays;
public class QuickSort {
/*
* 时间复杂度:O(N^2) 【数据有序或者逆序的情况】
* 最好情况【每次可以均匀的分割待排序序列】:O(N * log2 N)
* 空间复杂度:O(N)[单分支情况]
* 最好:log2 N
* 稳定性:不稳定
* */
public static void quickSort(int[] array){
quick(array,0, array.length-1);
}
public static void quick(int[] array,int start,int end){
if(start >= end){
return;
}
// 在找基准之前,先确定 start 和 end 的 中间值。[三数取中法]
int midValIndex = findMidValIndex(array,start,end);
//将它 与 start 交换。这样后面的程序,就不用改动了。
swap(array,start,midValIndex);
int pivot = partiton(array,start,end);
quick(array,start,pivot-1);// 递归左边
quick(array,pivot+1,end);// 递归右边
}
// 确定基准值下标
private static int findMidValIndex(int[] array,int start,int end){
// 确定 start 和 end 的中间下标
int mid = start + ((end - start)>>>1);// == (start + end)/ 2
// 确定 mid、start、end 三个下标,谁指向的元素是三个元素中的中间值
if(array[end] > array[start]){
if(array[start] > array[mid]){
return start;
}else if(array[mid] > array[end]){
return end;
}else{
return mid;
}
}else{
// array[start] >= array[end]
if(array[end] > array[mid]){
return end;
}else if(array[mid] > array[start]){
return start;
}else {
return mid;
}
}
}
// 交换两个下标元素
private static void swap(int[] array,int x,int y){
int tmp = array[x];
array[x] = array[y];
array[y] = tmp;
}
// 分割 - 找基准
private static int partiton(int[] array,int start,int end){
int tmp = array[start];
while(start < end){
while(start < end && array[end] >= tmp){
end--;
}
// 此时 end 下标 元素的值 是 小于 tmp的。
array[start] = array[end];
while(start<end && array[start] <= tmp){
start++;
}
array[end] = array[start];
}
array[start] = tmp;
return start;
}
// 有序
public static void test1(int capacity){
int[] array = new int[capacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
array[i] = i;
}
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
quickSort(array);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end - start);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1(100_0000);
int[] array = {6,1,2,7,9,3,4,5,10,6};
quickSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

优化总结
1、选择基准值很重要,通常使用几数取中法
2、partition 过程中把和基准值相等的数也选择出来
3、待排序区间小于一个阈(yù)值【临界值】
随着不断的划分基准,数组逐渐趋于有序,而区间随着递归也在减小。所以,利用 直接插入排序的特性【越有序越快】,来进一步优化 快排。
非递归实现快速排序的思维

代码如下
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Stack;
public class QuickSortNonRecursion {
public static void quickSort(int[] array){
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int left = 0;
int right = array.length-1;
int pivot = partiton(array,left,right);
if(pivot > left+1){
stack.push(left);
stack.push(pivot-1);
}
if(pivot < right -1){
stack.push(pivot+1);
stack.push(right);
}
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
right = stack.pop();
left = stack.pop();
pivot = partiton(array,left,right);
if(pivot>left+1){
stack.push(left);
stack.push(pivot-1);
}
if (pivot<right-1){
stack.push(pivot+1);
stack.push(right);
}
}
}
public static int partiton(int[] array,int start,int end){
int tmp = array[start];
while(start<end){
while(start<end && array[end] >=tmp){
end--;
}
array[start] = array[end];
while (start<end && array[start] <= tmp){
start++;
}
array[end] = array[start];
}
array[start] = tmp;
return start;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,8,1,10,15};
quickSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

========================================================================
将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。【简单说就是 将两个有序数组合并为一个有序数组,称为二路合并】
二路合并的代码如下
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
/*
* array1 已有序
* array2 已有序
* */
public static int[] mergeArrays(int[] array1,int[] array2){
if(array1 == null || array2 == null){
return array1 == null ? array2: array1;
}
int[] arr = new int[array1.length + array2.length];
int i = 0;// arr 的 遍历变量
int s1 = 0;//array1 的 遍历变量
int s2 = 0;//array2 的 遍历变量
while(s1 < array1.length && s2 < array2.length){
if(array1[s1] > array2[s2]){
arr[i++] = array2[s2++];
// s2++;
// i++;
}else{
arr[i++] = array1[s1++];
// s1++;
// i++;
}
}
// 循环结束,有一个数组的元素已经全部存入
// 接下来就是将另一个数组的元素放入 arr 中
while (s1 < array1.length){
arr[i++] = array1[s1++];
// i++;
// s1++;
}
while (s2 < array2.length){
arr[i++] = array2[s2++];
// i++;
// s2++;
}
return arr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array1 = {1,6,7,10};
int[] array2 = {2,3,4,9};
int[] mergeArray = mergeArrays(array1,array2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(mergeArray));
}
}

归并排序(MERGE - SORT)是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Divide and Conquer)的一个非常典型的应用。将已有序的子序列合并,得到完全有序的序列;即先使每个子序列有序,再使子序列段间有序。若将两个有序表合并成一个有序表,称为二路归并。
难点1 - 如何将一个数组拆分成一个个单独数组【每个数组里只包含一个元素】。


归并排序的程序框架
public class MergeSort {
// 归并排序的调用“接口”
public static int[] mergeSort(int[] array){
if(array == null){
return array;
}
mergeSortFunc(array,0,array.length-1);
return array;
}
// 归并排序实现
private static void mergeSortFunc(int[] array,int low,int high){
if(low >= high){
return;
}
// 递归分解
// int mid = (high + low) >>> 1
int mid = low + ((high - low) >>> 1);
mergeSortFunc(array,low,mid);// 左边
mergeSortFunc(array,mid+1,high);// 右边
// 合并
merge(array,low,mid,high);
}
private static void merge(int[] array,int low,int mid,int high){
}
}
合并程序的完善
其实这个并不难,跟我前面做的知识铺垫的思路是一样的。
需要注意的是:
1、我们的参数中 只有一个数组
2、数组 arr ,只是一个临时数组,用来存储 合并之后的结果。
3、在将 arr 数组 存储的结果,转移到 原本数组的时候,注意赋值的位置!
private static void merge(int[] array,int low,int mid,int high){
// 获取 区间之内的元素个数,加一 是因为 零下标元素也算一个元素。
int[] arr = new int[high - low +1];
// 左边 区间 【你可以理解为 有序数组 array1的起始与结束下标位置】
int start1 = low;
int end1 = mid;
// 右边 区间【你可以理解为 有序数组 array2的起始与结束下标位置】
int start2 = mid+1;
int end2 = high;
int i = 0;
while (start1 <= end1 && start2 <= end2){
if(array[start1] > array[start2]){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}else{
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
}
while(start1 <= end1){
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
while(start2 <= end2){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}
// 将 arr 存储的 合并数据,转换到原本数组上。
// 注意 array 数组中括号的下标的位置。
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
array[low++] = arr[j];
}
}
附图

import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSort {
/*
* 时间复杂度:N * log2 N
* 空间复杂丢:O(N)
* 稳定性:稳定
* */
public static int[] mergeSort(int[] array){
if(array == null){
return array;
}
mergeSortFunc(array,0,array.length-1);
return array;
}
private static void mergeSortFunc(int[] array,int low,int high){
if(low >= high){
return;
}
// int mid = (high + low) >>> 1
int mid = low + ((high - low) >>> 1);
mergeSortFunc(array,low,mid);// 左边
mergeSortFunc(array,mid+1,high);// 右边
merge(array,low,mid,high);
}
private static void merge(int[] array,int low,int mid,int high){
int[] arr = new int[high - low +1];
int start1 = low;
int end1 = mid;
int start2 = mid+1;
int end2 = high;
int i = 0;
while (start1 <= end1 && start2 <= end2){
if(array[start1] > array[start2]){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}else{
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
}
while(start1 <= end1){
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
while(start2 <= end2){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
array[low++] = arr[j];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1,6,7,10,2,3,4,9};
mergeSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}



代码如下
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MergeSortNonRecursion {
public static void mergeSort(int[] array){
//归并排序非递归实现
int groupNum = 1;// 每组的数据个数
while(groupNum < array.length){
// 无论数组含有几个元素, 数组每次都需要从下标 0位置,开始遍历。
for(int i = 0;i<array.length;i+= groupNum * 2){
int low = i;
int mid = low + groupNum -1;
// 防止越界【每组的元素个数,超过了数组的长度】
if(mid >= array.length){
mid = array.length-1;
}
int high = mid + groupNum;
// 防止越界【超过了数组的长度】
if(high >= array.length){
high = array.length-1;
}
merge(array,low,mid,high);
}
groupNum *= 2;//每组的元素个数扩大到原先的两倍。
}
}
public static void merge(int[] array,int low,int mid,int high){
// high 与 mid 相遇,说明 此时数组分组只有一组,也就说没有另一组的数组与其合并
// 即数组已经有序了,程序不用再往下走。
if(high == mid){
return;
}
int[] arr = new int[high -low + 1];
int start1 = low;
int end1 = mid;
int start2 = mid+1;
int end2 = high;
int i = 0;
while(start1 <= end1 && start2 <= end2){
if(array[start1]>array[start2]){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}else{
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
}
while (start1 <= end1){
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
while(start2 <= end2){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
array[low++] = arr[j];
}
}
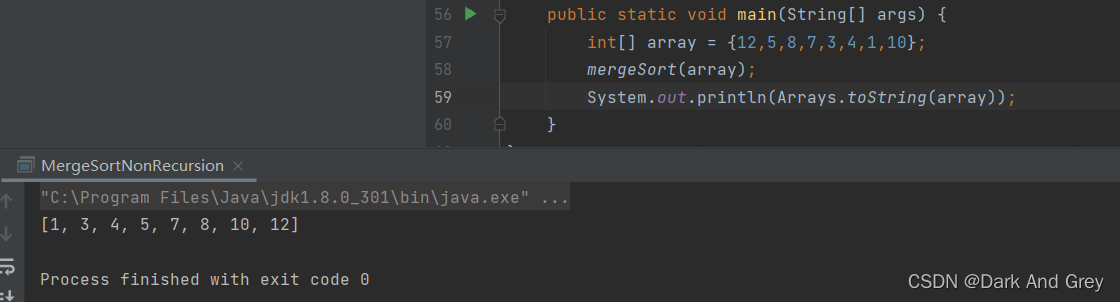
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,8,7,3,4,1,10};
mergeSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}
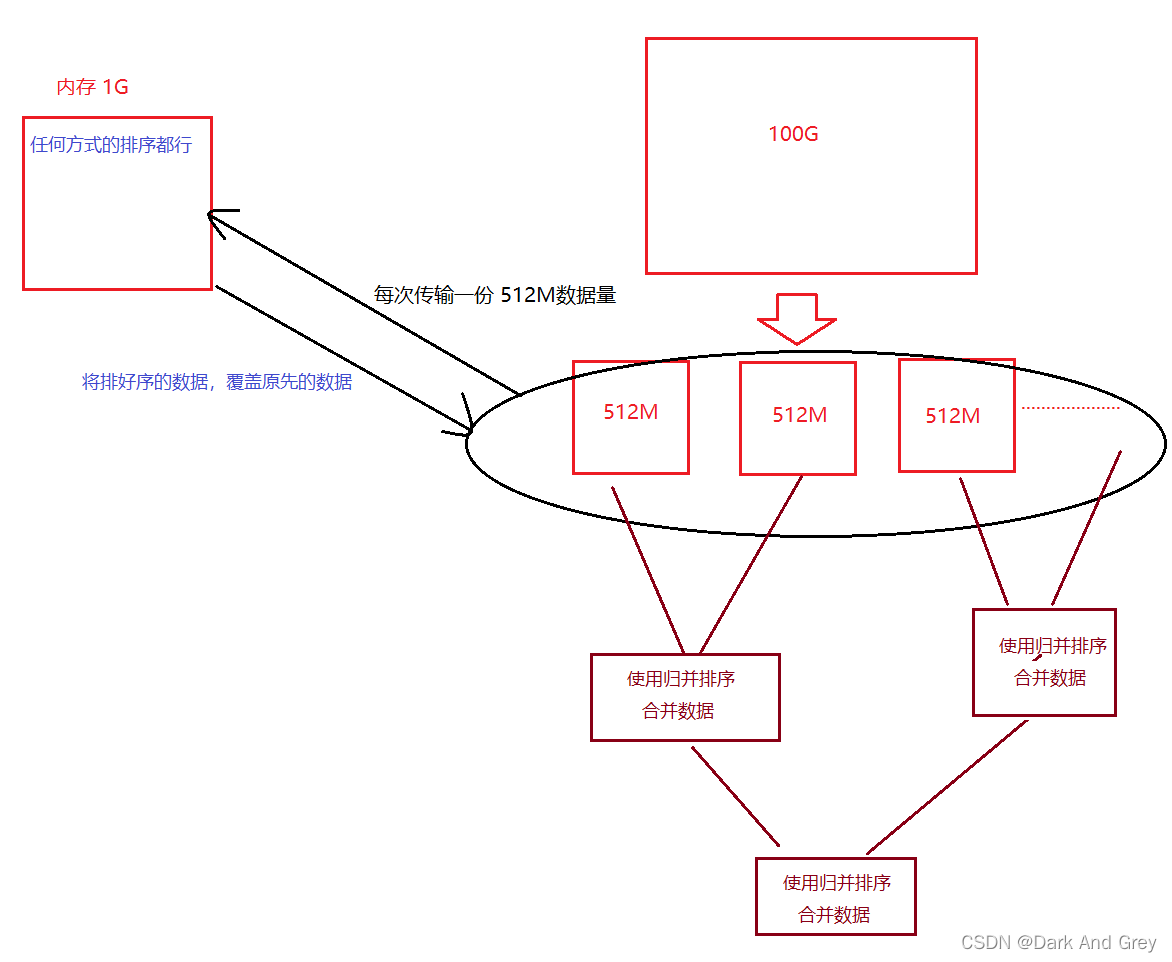
外部排序:排序过程需要在磁盘等外部存储进行的排序
【内部排序:排序过程需要在 内存上进行排序】
前提:内存只有 1G,需要排序的数据有 100G
因为内存中无法把所有数据全部放下,所以需要外部排序,而归并排序是最常用的外部排序。
1、先把文件切分成 200 份,每个512M
2、分别对 512M 的数据量 进行排序,因为 内存已经被分割了,512M < 1G 内存放得下。所以任何排序方式都可以,
3、进行 200 路归并,同时对 200 份有序文件做归并过程,最终结果就有序了
==================================================================
目前,我们讲了八种排序:直接插入排序、希尔排序、直接选择排序,双向选择排序、冒泡排序,堆排序、快速排序,归并排序。
其中稳定的排序:插入排序,冒泡排序,归并排序,一共三种。
另外,堆排序、归并排序、快速排序的时间复杂度都是 N * log2 N。
如果,你想速度快,就用快排。
如果,你想稳定,就用归并。
如果,你想空间复杂度低,就用堆排。
惊喜
最后还准备了一套上面资料对应的面试题(有答案哦)和面试时的高频面试算法题(如果面试准备时间不够,那么集中把这些算法题做完即可,命中率高达85%+)


0;
while(start1 <= end1 && start2 <= end2){
if(array[start1]>array[start2]){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}else{
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
}
while (start1 <= end1){
arr[i++] = array[start1++];
}
while(start2 <= end2){
arr[i++] = array[start2++];
}
for (int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
array[low++] = arr[j];
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {12,5,8,7,3,4,1,10};
mergeSort(array);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(array));
}
}

* * *
[]( )海量数据的排序问题
------------------------------------------------------------------------
> 外部排序:排序过程需要在磁盘等外部存储进行的排序
> 【内部排序:排序过程需要在 内存上进行排序】
> 前提:内存只有 1G,需要排序的数据有 100G
> 因为内存中无法把所有数据全部放下,所以需要外部排序,而归并排序是最常用的外部排序。
> 1、先把文件切分成 200 份,每个512M
> 
> 2、分别对 512M 的数据量 进行排序,因为 内存已经被分割了,512M < 1G 内存放得下。所以任何排序方式都可以,
> 3、进行 200 路归并,同时对 200 份有序文件做归并过程,最终结果就有序了
> 
* * *
[]( )小总结
==================================================================
> 目前,我们讲了八种排序:直接插入排序、希尔排序、直接选择排序,双向选择排序、冒泡排序,堆排序、快速排序,归并排序。
> 其中稳定的排序:插入排序,冒泡排序,归并排序,一共三种。
>
> 另外,堆排序、归并排序、快速排序的时间复杂度都是 N \* log2 N。
> 如果,你想速度快,就用快排。
> 如果,你想稳定,就用归并。
> 如果,你想空间复杂度低,就用堆排。
# 惊喜
最后还准备了一套上面资料对应的面试题(有答案哦)和面试时的高频面试算法题(如果面试准备时间不够,那么集中把这些算法题做完即可,命中率高达85%+)
[外链图片转存中...(img-3QdwoEH8-1715822920837)]
[外链图片转存中...(img-2v5IXpIl-1715822920838)]
> **本文已被[CODING开源项目:【一线大厂Java面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+最新讲解视频+实战项目源码】](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618154847)收录**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618154847)**





































 774
774

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








