####(二)生成构造函数
主要是createBindingConstructor 方法,主要是对成员变量赋值,以及设置监听事件。先看下javapoet提供的几个方法或类:
1.MethodSpec:生成方法的辅助类
这里主要是生成构造函数,当然也可以生成其它的普通方法,构造函数也是方法的一种吗。
通过constructorBuilder构造出一个方法,通过addAnnotation添加注解,通过addModifiers添加修饰符。
MethodSpec.Builder constructor =
MethodSpec.constructorBuilder()
.addAnnotation(UI_THREAD)
.addModifiers(PUBLIC);
通过如下方法添加参数targetType为参数类型,”target”为参数的变量名
constructor.addParameter(targetType, “target”);
通过如下方法添加代码语句
第一参数是String类型,可以有占位符S(字符串类型),S(字符串类型),T(类型)等
第二个参数Object… args,类型,多参数不固定。
就像你平时使用String.format()方法一样的意思.
constructor.addStatement(“this.target = target”);
2.构造函数中变量的赋值
这里主要是对使用了如下的代码进行一个赋值操作。
@BindView(R2.id.title) TextView title;
@OnClick(R2.id.hello) void sayHello() {}
这里我们主要看一下关键方法,因为都是类似的拼接代码字符串。
我们看一下变量的赋值:
private void addViewBindings(MethodSpec.Builder result, ViewBindings bindings) {
if (bindings.isSingleFieldBinding()) {
// Optimize the common case where there’s a single binding directly to a field.
FieldViewBinding fieldBinding = bindings.getFieldBinding();
CodeBlock.Builder builder = CodeBlock.builder()
.add("target.$L = ", fieldBinding.getName());
boolean requiresCast = requiresCast(fieldBinding.getType());
if (!requiresCast && !fieldBinding.isRequired()) {
builder.add(“source.findViewById(KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 30: …getId().code); }̲ else { builder…T.find”, UTILS);
builder.add(fieldBinding.isRequired() ? “RequiredView” : “OptionalView”);
if (requiresCast) {
builder.add(“AsType”);
}
builder.add(“(source, $L”, bindings.getId().code);
if (fieldBinding.isRequired() || requiresCast) {
builder.add(“, $S”, asHumanDescription(singletonList(fieldBinding)));
}
if (requiresCast) {
builder.add(“, KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 39: …getRawType()); }̲ builder.add(")…L”, builder.build());
return;
}
List requiredViewBindings = bindings.getRequiredBindings();
if (requiredViewBindings.isEmpty()) {
result.addStatement(“view = source.findViewById($L)”, bindings.getId().code);
} else if (!bindings.isBoundToRoot()) {
result.addStatement(“view = $T.findRequiredView(source, $L, $S)”, UTILS,
bindings.getId().code, asHumanDescription(requiredViewBindings));
}
addFieldBindings(result, bindings);
addMethodBindings(result, bindings);
}
主要是调用系统的findViewById 方法,但是你看到了findRequiredViewAsType,findRequiredView方法和castView方法,findRequiredView,findRequiredViewAsType是作者为乐代码的书写方便对findViewById的一层封装,你可以看一下源码,最后都会调用的findRequiredView方法的findViewById方法。
public static View findRequiredView(View source, @IdRes int id, String who) {
View view = source.findViewById(id);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
String name = getResourceEntryName(source, id);
throw new IllegalStateException(“Required view '”
- name
- "’ with ID "
- id
- " for "
- who
- " was not found. If this view is optional add ‘@Nullable’ (fields) or ‘@Optional’"
- " (methods) annotation.");
}
这个castView是什么方法呢?是Class类的方法,直接转换为指定的类型
public static T castView(View view, @IdRes int id, String who, Class cls) {
try {
return cls.cast(view);
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
String name = getResourceEntryName(view, id);
throw new IllegalStateException(“View '”
- name
- "’ with ID "
- id
- " for "
- who
- " was of the wrong type. See cause for more info.", e);
}
}
说白了都是调用系统的方法。
好了到这里成员变量的赋值算是完了。
注意一点target.title target就是我们的activity或者view ;也验证了为什么是使用了类似BindView注解不能是private修饰符的另一个原因了。
接下来是方法的监听 private void addMethodBindings(MethodSpec.Builder result, ViewBindings bindings) {}方法,李 main 也是通过循环添加方法借助我们上文提到的
MethodSpec.methodBuilder构造器
for (ListenerMethod method : getListenerMethods(listener)) {
MethodSpec.Builder callbackMethod = MethodSpec.methodBuilder(method.name())
.addAnnotation(Override.class)
.addModifiers(PUBLIC)
.returns(bestGuess(method.returnType()));
String[] parameterTypes = method.parameters();
for (int i = 0, count = parameterTypes.length; i < count; i++) {
callbackMethod.addParameter(bestGuess(parameterTypes[i]), “p” + i);
//…
}
感兴趣的可以根据生成的代码来对照这查看,这里就不多说了。
最后生成的如下所示的代码。
@UiThread
public SimpleActivity_ViewBinding(final T target, View source) {
this.target = target;
View view;
target.title = Utils.findRequiredViewAsType(source, R.id.title, “field ‘title’”, TextView.class);
target.subtitle = Utils.findRequiredViewAsType(source, R.id.subtitle, “field ‘subtitle’”, TextView.class);
view = Utils.findRequiredView(source, R.id.hello, “field ‘hello’, method ‘sayHello’, and method ‘sayGetOffMe’”);
target.hello = Utils.castView(view, R.id.hello, “field ‘hello’”, Button.class);
view2130968578 = view;
view.setOnClickListener(new DebouncingOnClickListener() {
@Override
public void doClick(View p0) {
target.sayHello();
}
});
view.setOnLongClickListener(new View.OnLongClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onLongClick(View p0) {
return target.sayGetOffMe();
}
});
view = Utils.findRequiredView(source, R.id.list_of_things, “field ‘listOfThings’ and method ‘onItemClick’”);
target.listOfThings = Utils.castView(view, R.id.list_of_things, “field ‘listOfThings’”, ListView.class);
view2130968579 = view;
((AdapterView<?>) view).setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() { @Override public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> p0, View p1, int p2, long p3) {
target.onItemClick(p2);
}
});
target.footer = Utils.findRequiredViewAsType(source, R.id.footer, “field ‘footer’”, TextView.class);
target.headerViews = Utils.listOf(
Utils.findRequiredView(source, R.id.title, “field ‘headerViews’”),
Utils.findRequiredView(source, R.id.subtitle, “field ‘headerViews’”),
Utils.findRequiredView(source, R.id.hello, “field ‘headerViews’”));
}
####(三)生成unbind方法
createBindingUnbindMethod方法主要是把的成员变量啦,Listener等 置为空,比如setOnClickListener(null)。
private MethodSpec createBindingUnbindMethod(TypeSpec.Builder bindingClass,
TypeName targetType) {
MethodSpec.Builder result = MethodSpec.methodBuilder(“unbind”)
.addAnnotation(Override.class)
.addModifiers(PUBLIC);
if (!isFinal && !hasParentBinding()) {
result.addAnnotation(CALL_SUPER);
}
boolean rootBindingWithFields = !hasParentBinding() && hasFieldBindings();
if (hasFieldBindings() || rootBindingWithFields) {
result.addStatement(“KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 39: …, targetType); }̲ if (!hasParent…N == null) throw new
T
(
T(
T(S)”, target, IllegalStateException.class,
“Bindings already cleared.”);
} else {
result.addStatement(“super.unbind()”);
}
if (hasFieldBindings()) {
result.addCode(“\n”);
for (ViewBindings bindings : viewIdMap.values()) {
if (bindings.getFieldBinding() != null) {
result.addStatement(“target.KaTeX parse error: Expected 'EOF', got '}' at position 51: …().getName()); }̲ } for (FieldCo…L = null”, fieldCollectionBinding.getName());
}
}
if (hasMethodBindings()) {
result.addCode(“\n”);
for (ViewBindings bindings : viewIdMap.values()) {
addFieldAndUnbindStatement(bindingClass, result, bindings);
}
}
if (!hasParentBinding()) {
result.addCode(“\n”);
result.addStatement(“this.target = null”);
}
return result.build();
}
主要就是addStatement方法,上文已经说了,该方法的意思就是生成一句代码,
第一参数是String类型,可以有占位符S(字符串类型),S(字符串类型),T(类型)等
第二个参数Object… args,类型,多参数不固定。
就像你平时使用String.format()方法一样的意思.
比较简单,最后生成的方法类似:
@Override
public void unbind() {
SimpleAdapter.ViewHolder target = this.target;
if (target == null) throw new IllegalStateException(“Bindings already cleared.”);
target.word = null;
target.length = null;
target.position = null;
this.target = null;
}
最后我们看下对外提供的API。
bind 方法
那么还差一步,什么时候都要我们生成的java文件呢?
答案是: ButterKnife.bind(this);方法。
我们看一下ButterKnife对外提供的API
/**
- BindView annotated fields and methods in the specified {@link Activity}. The current content
- view is used as the view root.
- @param target Target activity for view binding.
*/
@NonNull @UiThread
public static Unbinder bind(@NonNull Activity target) {
View sourceView = target.getWindow().getDecorView();
return createBinding(target, sourceView);
}
/**
- BindView annotated fields and methods in the specified {@link View}. The view and its children
- are used as the view root.
- @param target Target view for view binding.
*/
@NonNull @UiThread
public static Unbinder bind(@NonNull View target) {
return createBinding(target, target);
}
/**
- BindView annotated fields and methods in the specified {@link Dialog}. The current content
- view is used as the view root.
- @param target Target dialog for view binding.
*/
@NonNull @UiThread
public static Unbinder bind(@NonNull Dialog target) {
View sourceView = target.getWindow().getDecorView();
return createBinding(target, sourceView);
}
/**
- BindView annotated fields and methods in the specified {@code target} using the {@code source}
- {@link Activity} as the view root.
- @param target Target class for view binding.
- @param source Activity on which IDs will be looked up.
*/
@NonNull @UiThread
public static Unbinder bind(@NonNull Object target, @NonNull Activity source) {
View sourceView = source.getWindow().getDecorView();
return createBinding(target, sourceView);
}
/**
- BindView annotated fields and methods in the specified {@code target} using the {@code source}
- {@link View} as the view root.
- @param target Target class for view binding.
- @param source View root on which IDs will be looked up.
*/
@NonNull @UiThread
public static Unbinder bind(@NonNull Object target, @NonNull View source) {
return createBinding(target, source);
}
/**
- BindView annotated fields and methods in the specified {@code target} using the {@code source}
- {@link Dialog} as the view root.
- @param target Target class for view binding.
- @param source Dialog on which IDs will be looked up.
*/
@NonNull @UiThread
public static Unbinder bind(@NonNull Object target, @NonNull Dialog source) {
View sourceView = source.getWindow().getDecorView();
return createBinding(target, sourceView);
}
private static Unbinder createBinding(@NonNull Object target, @NonNull View source) {
Class<?> targetClass = target.getClass();
if (debug) Log.d(TAG, "Looking up binding for " + targetClass.getName());
Constructor<? extends Unbinder> constructor = findBindingConstructorForClass(targetClass);
if (constructor == null) {
return Unbinder.EMPTY;
}
//noinspection TryWithIdenticalCatches Resolves to API 19+ only type.
try {
return constructor.newInstance(target, source);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to invoke " + constructor, e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to invoke " + constructor, e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
}
if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(“Unable to create binding instance.”, cause);
}
}
我们看到bind的一系列方法都会调用createBinding方法
private static Unbinder createBinding(@NonNull Object target, @NonNull View source) {
Class<?> targetClass = target.getClass();
if (debug) Log.d(TAG, "Looking up binding for " + targetClass.getName());
Constructor<? extends Unbinder> constructor = findBindingConstructorForClass(targetClass);
if (constructor == null) {
return Unbinder.EMPTY;
}
//noinspection TryWithIdenticalCatches Resolves to API 19+ only type.
try {
return constructor.newInstance(target, source);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to invoke " + constructor, e);
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to invoke " + constructor, e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable cause = e.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
}
if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(“Unable to create binding instance.”, cause);
}
}
Class<?> (?是转义字符csdn要不支持)targetClass = target.getClass();获取类的实例,最后获取构造函数,最后constructor.newInstance方法来调用该类的构造函数。
而该类的构造函数是通过findBindingConstructorForClass方法,我可没来看下此方法:
@Nullable @CheckResult @UiThread
private static Constructor<? extends Unbinder> findBindingConstructorForClass(Class<?> cls) {
//缓存中查找,找到直接返回
Constructor<? extends Unbinder> bindingCtor = BINDINGS.get(cls);
if (bindingCtor != null) {
if (debug) Log.d(TAG, “HIT: Cached in binding map.”);
return bindingCtor;
}
//检查合法性
String clsName = cls.getName();
if (clsName.startsWith(“android.”) || clsName.startsWith(“java.”)) {
if (debug) Log.d(TAG, “MISS: Reached framework class. Abandoning search.”);
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数同学面临毕业设计项目选题时,很多人都会感到无从下手,尤其是对于计算机专业的学生来说,选择一个合适的题目尤为重要。因为毕业设计不仅是我们在大学四年学习的一个总结,更是展示自己能力的重要机会。
因此收集整理了一份《2024年计算机毕业设计项目大全》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助提高效率,同时减轻大家的负担。
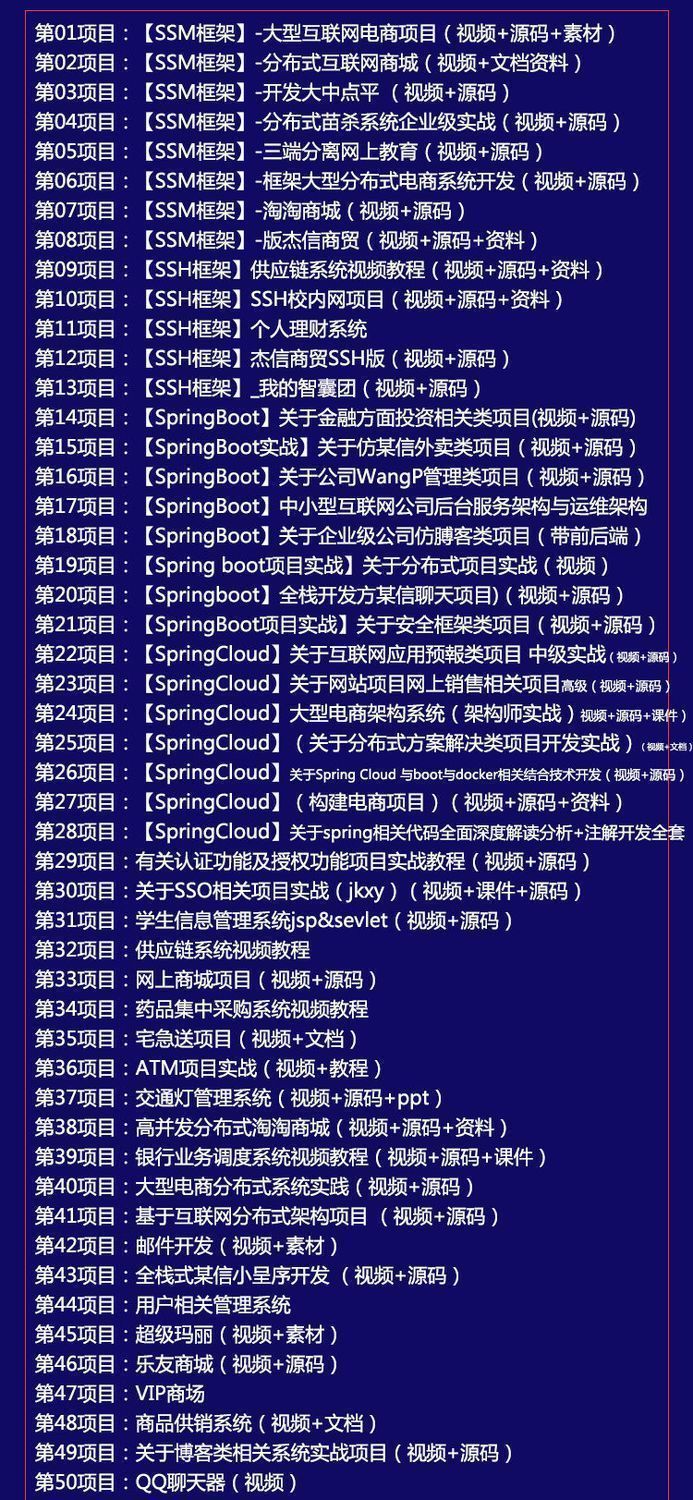
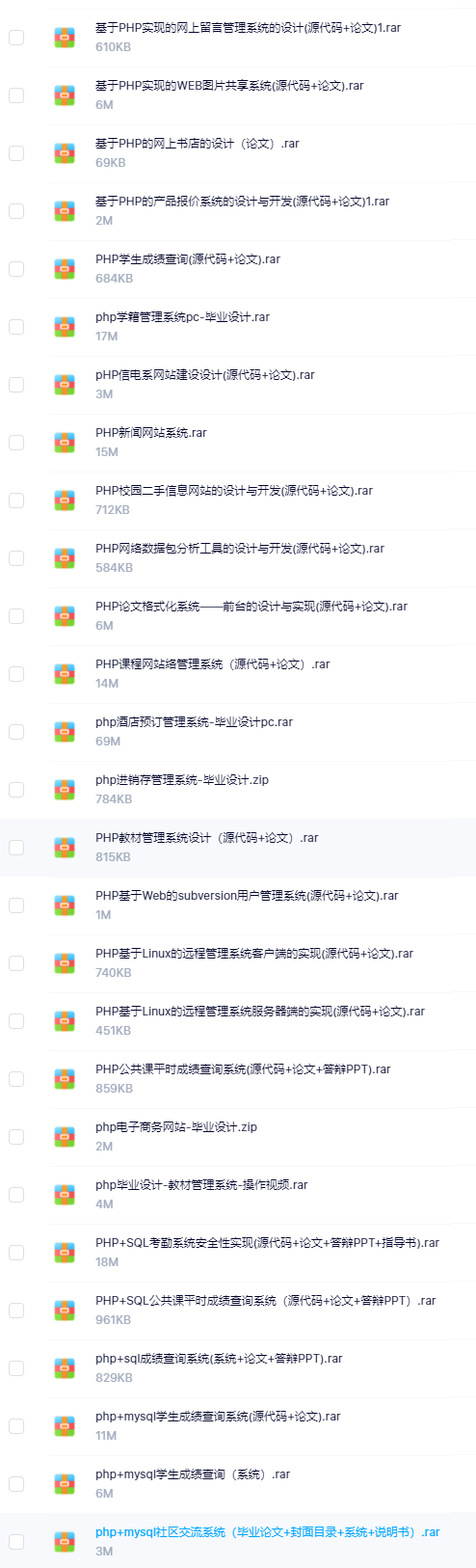
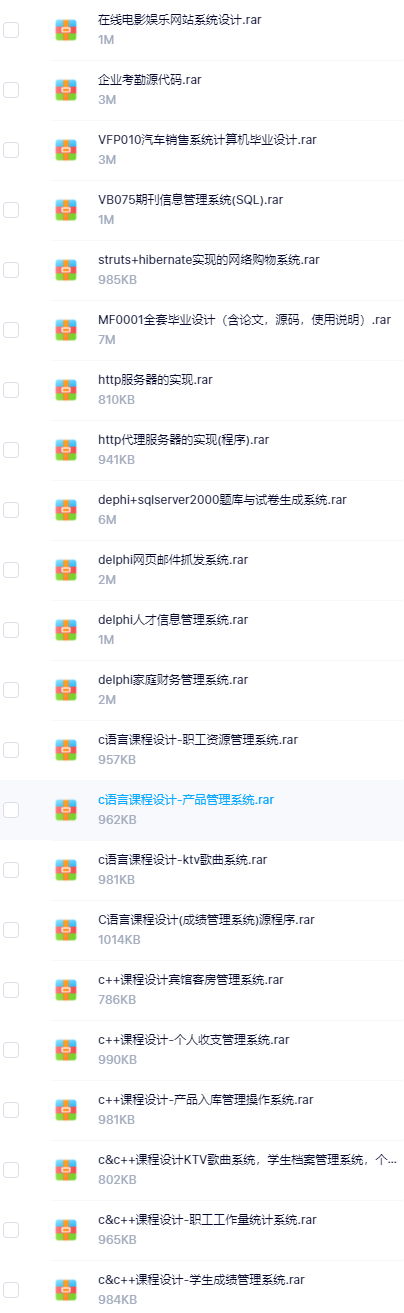
既有Java、Web、PHP、也有C、小程序、Python等项目供你选择,真正体系化!
由于项目比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含素材文档、项目源码、讲解视频
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加VX:vip1024c (备注项目大全获取)

,更是展示自己能力的重要机会。**
因此收集整理了一份《2024年计算机毕业设计项目大全》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助提高效率,同时减轻大家的负担。
[外链图片转存中…(img-FOLrvsww-1712521146062)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-bdNebTO5-1712521146063)]
[外链图片转存中…(img-KYRiNCx3-1712521146063)]
既有Java、Web、PHP、也有C、小程序、Python等项目供你选择,真正体系化!
由于项目比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,每个节点里面都包含素材文档、项目源码、讲解视频
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加VX:vip1024c (备注项目大全获取)
[外链图片转存中…(img-NXxEbpRk-1712521146063)]





















 412
412











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








