先自我介绍一下,小编浙江大学毕业,去过华为、字节跳动等大厂,目前阿里P7
深知大多数程序员,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长,但自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年最新Golang全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友。

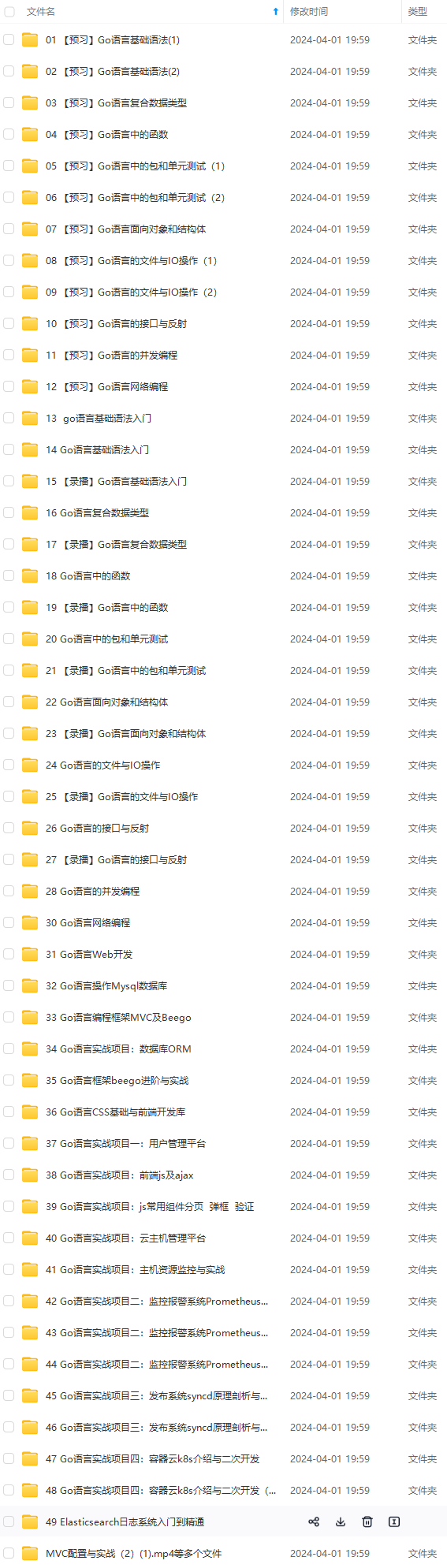
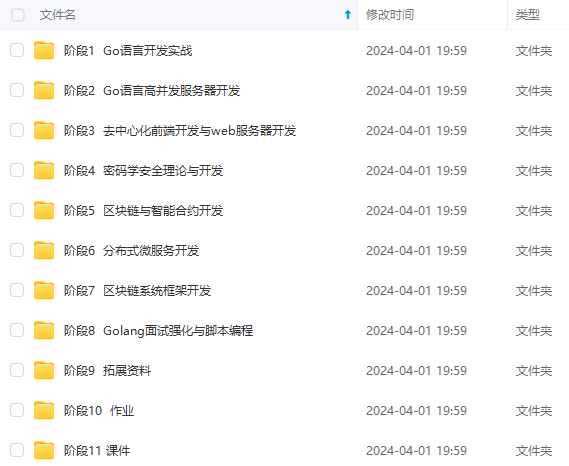
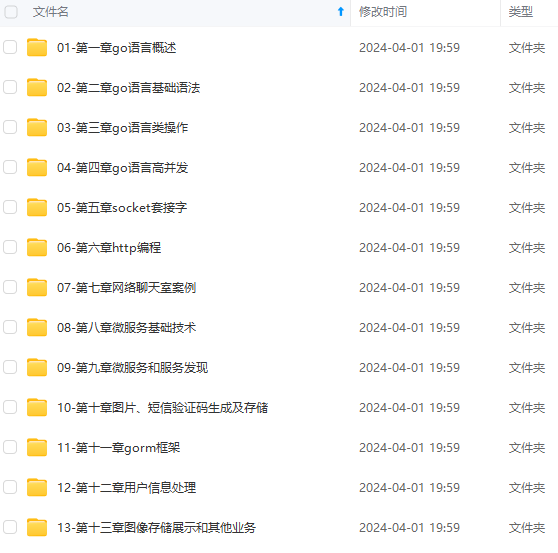
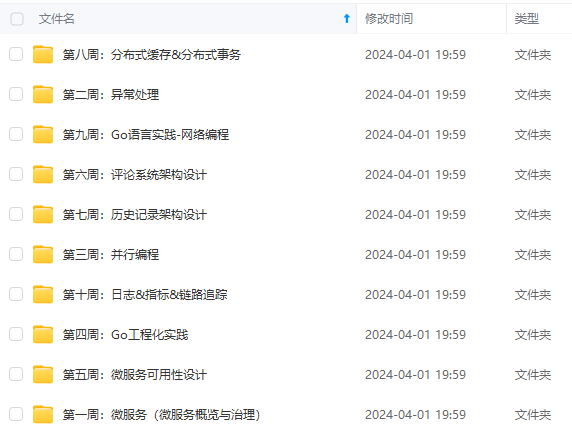
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,涵盖了95%以上Go语言开发知识点,真正体系化!
由于文件比较多,这里只是将部分目录截图出来,全套包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、大纲路线、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你需要这些资料,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注go)

正文
g.set_titles(“”)
g.set(yticks=[])
g.despine(bottom=True, left=True)

“”"
FacetGrid with custom projection
“”"
sns.set()
Generate an example radial datast
r = np.linspace(0, 10, num=100)
df = pd.DataFrame({‘r’: r, ‘slow’: r, ‘medium’: 2 * r, ‘fast’: 4 * r})
Convert the dataframe to long-form or “tidy” format
df = pd.melt(df, id_vars=[‘r’], var_name=‘speed’, value_name=‘theta’)
Set up a grid of axes with a polar projection
g = sns.FacetGrid(df, col=“speed”, hue=“speed”,
subplot_kws=dict(projection=‘polar’), height=4.5,
sharex=False, sharey=False, despine=False)
Draw a scatterplot onto each axes in the grid
g.map(sns.scatterplot, “theta”, “r”)

“”"
Facetting histograms by subsets of data
“”"
sns.set(style=“darkgrid”)
tips = sns.load_dataset(“tips”)
g = sns.FacetGrid(tips, row=“sex”, col=“time”, margin_titles=True)
bins = np.linspace(0, 60, 13)
g.map(plt.hist, “total_bill”, color=“steelblue”, bins=bins)

“”"
Plotting on a large number of facets
“”"
sns.set(style=“ticks”)
Create a dataset with many short random walks
rs = np.random.RandomState(4)
pos = rs.randint(-1, 2, (20, 5)).cumsum(axis=1)
pos -= pos[:, 0, np.newaxis]
step = np.tile(range(5), 20)
walk = np.repeat(range(20), 5)
df = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[pos.flat, step, walk],
columns=[“position”, “step”, “walk”])
Initialize a grid of plots with an Axes for each walk
grid = sns.FacetGrid(df, col=“walk”, hue=“walk”, palette=“tab20c”,
col_wrap=4, height=1.5)
Draw a horizontal line to show the starting point
grid.map(plt.axhline, y=0, ls=“:”, c=“.5”)
Draw a line plot to show the trajectory of each random walk
grid.map(plt.plot, “step”, “position”, marker=“o”)
Adjust the tick positions and labels
grid.set(xticks=np.arange(5), yticks=[-3, 3],
xlim=(-.5, 4.5), ylim=(-3.5, 3.5))
Adjust the arrangement of the plots
grid.fig.tight_layout(w_pad=1)

distplot(单变量分布直方图)
在seaborn中想要对单变量分布进行快速了解最方便的就是使用distplot()函数,默认情况下它将绘制一个直方图,并且可以同时画出核密度估计(KDE)。
“”"
Distribution plot options
“”"
sns.set(style=“white”, palette=“muted”, color_codes=True)
rs = np.random.RandomState(10)
Set up the matplotlib figure
f, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(7, 7), sharex=True)
sns.despine(left=True)
Generate a random univariate dataset
d = rs.normal(size=100)
Plot a simple histogram with binsize determined automatically
sns.distplot(d, kde=False, color=“b”, ax=axes[0, 0])
Plot a kernel density estimate and rug plot
sns.distplot(d, hist=False, rug=True, color=“r”, ax=axes[0, 1])
Plot a filled kernel density estimate
sns.distplot(d, hist=False, color=“g”, kde_kws={“shade”: True}, ax=axes[1, 0])
Plot a historgram and kernel density estimate
sns.distplot(d, color=“m”, ax=axes[1, 1])
plt.setp(axes, yticks=[])
plt.tight_layout()

lineplot
绘制线段
seaborn里的lineplot函数所传数据必须为一个pandas数组,这一点跟matplotlib里有较大区别,并且一开始使用较为复杂,sns.lineplot里有几个参数值得注意。
x: plot图的x轴label
y: plot图的y轴label
ci: 与估计器聚合时绘制的置信区间的大小
data: 所传入的pandas数组
“”"
Timeseries plot with error bands
“”"
sns.set(style=“darkgrid”)
Load an example dataset with long-form data
fmri = sns.load_dataset(“fmri”)
Plot the responses for different events and regions
sns.lineplot(x=“timepoint”, y=“signal”,
hue=“region”, style=“event”,
data=fmri)

“”"
Lineplot from a wide-form dataset
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
rs = np.random.RandomState(365)
values = rs.randn(365, 4).cumsum(axis=0)
dates = pd.date_range(“1 1 2016”, periods=365, freq=“D”)
data = pd.DataFrame(values, dates, columns=[“A”, “B”, “C”, “D”])
data = data.rolling(7).mean()
sns.lineplot(data=data, palette=“tab10”, linewidth=2.5)

relplot
这是一个图形级别的函数,它用散点图和线图两种常用的手段来表现统计关系。
“”"
Line plots on multiple facets
“”"
sns.set(style=“ticks”)
dots = sns.load_dataset(“dots”)
Define a palette to ensure that colors will be
shared across the facets
palette = dict(zip(dots.coherence.unique(),
sns.color_palette(“rocket_r”, 6)))
Plot the lines on two facets
sns.relplot(x=“time”, y=“firing_rate”,
hue=“coherence”, size=“choice”, col=“align”,
size_order=[“T1”, “T2”], palette=palette,
height=5, aspect=.75, facet_kws=dict(sharex=False),
kind=“line”, legend=“full”, data=dots)

boxplot
箱形图(Box-plot)又称为盒须图、盒式图或箱线图,是一种用作显示一组数据分散情况资料的统计图。它能显示出一组数据的最大值、最小值、中位数及上下四分位数。
“”"
Grouped boxplots
“”"
sns.set(style=“ticks”, palette=“pastel”)
Load the example tips dataset
tips = sns.load_dataset(“tips”)
Draw a nested boxplot to show bills by day and time
sns.boxplot(x=“day”, y=“total_bill”,
hue=“smoker”, palette=[“m”, “g”],
data=tips)
sns.despine(offset=10, trim=True)

violinplot
violinplot与boxplot扮演类似的角色,它显示了定量数据在一个(或多个)分类变量的多个层次上的分布,这些分布可以进行比较。不像箱形图中所有绘图组件都对应于实际数据点,小提琴绘图以基础分布的核密度估计为特征。
“”"
Violinplots with observations
“”"
sns.set()
Create a random dataset across several variables
rs = np.random.RandomState(0)
n, p = 40, 8
d = rs.normal(0, 2, (n, p))
d += np.log(np.arange(1, p + 1)) * -5 + 10
Use cubehelix to get a custom sequential palette
pal = sns.cubehelix_palette(p, rot=-.5, dark=.3)
Show each distribution with both violins and points
sns.violinplot(data=d, palette=pal, inner=“points”)

“”"
Grouped violinplots with split violins
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”, palette=“pastel”, color_codes=True)
Load the example tips dataset
tips = sns.load_dataset(“tips”)
Draw a nested violinplot and split the violins for easier comparison
sns.violinplot(x=“day”, y=“total_bill”, hue=“smoker”,
split=True, inner=“quart”,
palette={“Yes”: “y”, “No”: “b”},
data=tips)
sns.despine(left=True)

“”"
Violinplot from a wide-form dataset
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
Load the example dataset of brain network correlations
df = sns.load_dataset(“brain_networks”, header=[0, 1, 2], index_col=0)
Pull out a specific subset of networks
used_networks = [1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 11, 12, 13, 16, 17]
used_columns = (df.columns.get_level_values(“network”)
.astype(int)
.isin(used_networks))
df = df.loc[:, used_columns]
Compute the correlation matrix and average over networks
corr_df = df.corr().groupby(level=“network”).mean()
corr_df.index = corr_df.index.astype(int)
corr_df = corr_df.sort_index().T
Set up the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(11, 6))
Draw a violinplot with a narrower bandwidth than the default
sns.violinplot(data=corr_df, palette=“Set3”, bw=.2, cut=1, linewidth=1)
Finalize the figure
ax.set(ylim=(-.7, 1.05))
sns.despine(left=True, bottom=True)

heatmap热力图
利用热力图可以看数据表里多个特征两两的相似度。
“”"
Annotated heatmaps
“”"
sns.set()
Load the example flights dataset and conver to long-form
flights_long = sns.load_dataset(“flights”)
flights = flights_long.pivot(“month”, “year”, “passengers”)
Draw a heatmap with the numeric values in each cell
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(9, 6))
sns.heatmap(flights, annot=True, fmt=“d”, linewidths=.5, ax=ax)

“”"
Plotting a diagonal correlation matrix
“”"
from string import ascii_letters
sns.set(style=“white”)
Generate a large random dataset
rs = np.random.RandomState(33)
d = pd.DataFrame(data=rs.normal(size=(100, 26)),
columns=list(ascii_letters[26:]))
Compute the correlation matrix
corr = d.corr()
Generate a mask for the upper triangle
mask = np.zeros_like(corr, dtype=np.bool)
mask[np.triu_indices_from(mask)] = True
Set up the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(11, 9))
Generate a custom diverging colormap
cmap = sns.diverging_palette(220, 10, as_cmap=True)
Draw the heatmap with the mask and correct aspect ratio
sns.heatmap(corr, mask=mask, cmap=cmap, vmax=.3, center=0,
square=True, linewidths=.5, cbar_kws={“shrink”: .5})

jointplot
用于2个变量的画图
“”"
Joint kernel density estimate
“”"
sns.set(style=“white”)
Generate a random correlated bivariate dataset
rs = np.random.RandomState(5)
mean = [0, 0]
cov = [(1, .5), (.5, 1)]
x1, x2 = rs.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 500).T
x1 = pd.Series(x1, name=“
X
_
1
X\_1
X_1”)
x2 = pd.Series(x2, name=“
X
_
2
X\_2
X_2”)
Show the joint distribution using kernel density estimation
g = sns.jointplot(x1, x2, kind=“kde”, height=7, space=0)

pos_id=img-FBBVohhM-1694680791085)
HexBin图
直方图的双变量类似物被称为“hexbin”图,因为它显示了落在六边形仓内的观测数。该图适用于较大的数据集。
“”"
Hexbin plot with marginal distributions
“”"
sns.set(style=“ticks”)
rs = np.random.RandomState(11)
x = rs.gamma(2, size=1000)
y = -.5 * x + rs.normal(size=1000)
sns.jointplot(x, y, kind=“hex”, color=“#4CB391”)

“”"
Linear regression with marginal distributions
“”"
sns.set(style=“darkgrid”)
tips = sns.load_dataset(“tips”)
g = sns.jointplot(“total_bill”, “tip”, data=tips, kind=“reg”,
xlim=(0, 60), ylim=(0, 12), color=“m”, height=7)

barplot(条形图)
条形图表示数值变量与每个矩形高度的中心趋势的估计值,并使用误差线提供关于该估计值附近的不确定性的一些指示。
“”"
Horizontal bar plots
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
Load the example car crash dataset
crashes = sns.load_dataset(“car_crashes”).sort_values(“total”, ascending=False)
Initialize the matplotlib figure
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 15))
Plot the total crashes
sns.set_color_codes(“pastel”)
sns.barplot(x=“total”, y=“abbrev”, data=crashes,
label=“Total”, color=“b”)
Plot the crashes where alcohol was involved
sns.set_color_codes(“muted”)
sns.barplot(x=“alcohol”, y=“abbrev”, data=crashes,
label=“Alcohol-involved”, color=“b”)
Add a legend and informative axis label
ax.legend(ncol=2, loc=“lower right”, frameon=True)
ax.set(xlim=(0, 24), ylabel=“”,
xlabel=“Automobile collisions per billion miles”)
sns.despine(left=True, bottom=True)

catplot
分类图表的接口,通过指定kind参数可以画出下面的八种图
stripplot() 分类散点图
swarmplot() 能够显示分布密度的分类散点图
boxplot() 箱图
violinplot() 小提琴图
boxenplot() 增强箱图
pointplot() 点图
barplot() 条形图
countplot() 计数图
“”"
Grouped barplots
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
Load the example Titanic dataset
titanic = sns.load_dataset(“titanic”)
Draw a nested barplot to show survival for class and sex
g = sns.catplot(x=“class”, y=“survived”, hue=“sex”, data=titanic,
height=6, kind=“bar”, palette=“muted”)
g.despine(left=True)
g.set_ylabels(“survival probability”)

“”"
Plotting a three-way ANOVA
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
Load the example exercise dataset
df = sns.load_dataset(“exercise”)
Draw a pointplot to show pulse as a function of three categorical factors
g = sns.catplot(x=“time”, y=“pulse”, hue=“kind”, col=“diet”,
capsize=.2, palette=“YlGnBu_d”, height=6, aspect=.75,
kind=“point”, data=df)
g.despine(left=True)

pointplot
点图代表散点图位置的数值变量的中心趋势估计,并使用误差线提供关于该估计的不确定性的一些指示。点图可能比条形图更有用于聚焦一个或多个分类变量的不同级别之间的比较。他们尤其善于表现交互作用:一个分类变量的层次之间的关系如何在第二个分类变量的层次之间变化。连接来自相同色调等级的每个点的线允许交互作用通过斜率的差异进行判断,这比对几组点或条的高度比较容易。
“”"
Conditional means with observations
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
iris = sns.load_dataset(“iris”)
“Melt” the dataset to “long-form” or “tidy” representation
iris = pd.melt(iris, “species”, var_name=“measurement”)
Initialize the figure
f, ax = plt.subplots()
sns.despine(bottom=True, left=True)
Show each observation with a scatterplot
sns.stripplot(x=“value”, y=“measurement”, hue=“species”,
data=iris, dodge=True, jitter=True,
alpha=.25, zorder=1)
Show the conditional means
sns.pointplot(x=“value”, y=“measurement”, hue=“species”,
data=iris, dodge=.532, join=False, palette=“dark”,
markers=“d”, scale=.75, ci=None)
Improve the legend
handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
ax.legend(handles[3:], labels[3:], title=“species”,
handletextpad=0, columnspacing=1,
loc=“lower right”, ncol=3, frameon=True)

scatterplot(散点图)
“”"
Scatterplot with categorical and numerical semantics
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
Load the example iris dataset
diamonds = sns.load_dataset(“diamonds”)
Draw a scatter plot while assigning point colors and sizes to different
variables in the dataset
f, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6.5, 6.5))
sns.despine(f, left=True, bottom=True)
clarity_ranking = [“I1”, “SI2”, “SI1”, “VS2”, “VS1”, “VVS2”, “VVS1”, “IF”]
sns.scatterplot(x=“carat”, y=“price”,
hue=“clarity”, size=“depth”,
palette=“ch:r=-.2,d=.3_r”,
hue_order=clarity_ranking,
sizes=(1, 8), linewidth=0,
data=diamonds, ax=ax)

boxenplot(增强箱图)
“”"
Plotting large distributions
“”"
sns.set(style=“whitegrid”)
diamonds = sns.load_dataset(“diamonds”)
clarity_ranking = [“I1”, “SI2”, “SI1”, “VS2”, “VS1”, “VVS2”, “VVS1”, “IF”]
sns.boxenplot(x=“clarity”, y=“carat”,
color=“b”, order=clarity_ranking,
scale=“linear”, data=diamonds)

Scatterplot(散点图)
“”"
Scatterplot with continuous hues and sizes
“”"
sns.set()
Load the example iris dataset
planets = sns.load_dataset(“planets”)
cmap = sns.cubehelix_palette(rot=-.2, as_cmap=True)
ax = sns.scatterplot(x=“distance”, y=“orbital_period”,
hue=“year”, size=“mass”,
palette=cmap, sizes=(10, 200),
data=planets)

“”"
Scatterplot with marginal ticks
“”"
sns.set(style=“white”, color_codes=True)
Generate a random bivariate dataset
rs = np.random.RandomState(9)
mean = [0, 0]
cov = [(1, 0), (0, 2)]
x, y = rs.multivariate_normal(mean, cov, 100).T
Use JointGrid directly to draw a custom plot
grid = sns.JointGrid(x, y, space=0, height=6, ratio=50)
grid.plot_joint(plt.scatter, color=“g”)
grid.plot_marginals(sns.rugplot, height=1, color=“g”)

PairGrid
用于绘制数据集中成对关系的子图网格。
“”"
Paired density and scatterplot matrix
“”"
sns.set(style=“white”)
df = sns.load_dataset(“iris”)
g = sns.PairGrid(df, diag_sharey=False)
g.map_lower(sns.kdeplot)
g.map_upper(sns.scatterplot)
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注Go)

一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
to draw a custom plot
grid = sns.JointGrid(x, y, space=0, height=6, ratio=50)
grid.plot_joint(plt.scatter, color=“g”)
grid.plot_marginals(sns.rugplot, height=1, color=“g”)

PairGrid
用于绘制数据集中成对关系的子图网格。
“”"
Paired density and scatterplot matrix
“”"
sns.set(style=“white”)
df = sns.load_dataset(“iris”)
g = sns.PairGrid(df, diag_sharey=False)
g.map_lower(sns.kdeplot)
g.map_upper(sns.scatterplot)
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以添加V获取:vip1024b (备注Go)
[外链图片转存中…(img-lyw9TV2J-1713442591528)]
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 3621
3621

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








