最后
小编的一位同事在校期间连续三年参加ACM-ICPC竞赛。从参赛开始,原计划每天刷一道算法题,实际上每天有时候不止一题,一年最终完成了 600+:
凭借三年刷题经验,他在校招中很快拿到了各大公司的offer。
入职前,他把他的刷题经验总结成1121页PDF书籍,作为礼物赠送给他的学弟学妹,希望同学们都能在最短时间内掌握校招常见的算法及解题思路。

整本书,我仔细看了一遍,作者非常细心地将常见核心算法题和汇总题拆分为4个章节。

开源分享:【大厂前端面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+真实项目实战+最新讲解视频】
而对于有时间的同学,作者还给出了他结合众多数据结构算法书籍,挑选出的一千多道题的解题思路和方法,以供有需要的同学慢慢研究。

TypeScript 里的类型保护机制让它成为了现实。 类型保护就是一些表达式,它们会在运行时检查以确保在某个作用域里的类型。定义一个类型保护,我们只要简单地定义一个函数,它的返回值是一个类型谓词:
function isFish(pet: Fish | Bird): pet is Fish {
return (pet as Fish).swim !== undefined
}
在这个例子里,pet is Fish 就是类型谓词。谓词为 parameterName is Type 这种形式, parameterName 必须是来自于当前函数签名里的一个参数名。
每当使用一些变量调用 isFish 时,TypeScript 会将变量缩减为那个具体的类型。
if (isFish(pet)) {
pet.swim()
}
else {
pet.fly()
}
注意 TypeScript 不仅知道在 if 分支里 pet 是 Fish 类型;它还清楚在 else 分支里,一定不是 Fish类型而是 Bird 类型。
typeof 类型保护
现在我们回过头来看看怎么使用联合类型书写 padLeft 代码。我们可以像下面这样利用类型断言来写:
function isNumber (x: any):x is string {
return typeof x === 'number'
}
function isString (x: any): x is string {
return typeof x === 'string'
}
function padLeft (value: string, padding: string | number) {
if (isNumber(padding)) {
return Array(padding + 1).join(' ') + value
}
if (isString(padding)) {
return padding + value
}
throw new Error(`Expected string or number, got '${padding}'.`)
}
然而,你必须要定义一个函数来判断类型是否是原始类型,但这并不必要。其实我们不必将 typeof x === 'number'抽象成一个函数,因为 TypeScript 可以将它识别为一个类型保护。 也就是说我们可以直接在代码里检查类型了。
function padLeft (value: string, padding: string | number) {
if (typeof padding === 'number') {
return Array(padding + 1).join(' ') + value
}
if (typeof padding === 'string') {
return padding + value
}
throw new Error(`Expected string or number, got '${padding}'.`)
}
这些 typeof 类型保护只有两种形式能被识别:typeof v === "typename" 和 typeof v !== "typename", "typename"必须是 "number", "string","boolean" 或 "symbol"的基本类型。 但是 TypeScript 并不会阻止你与其它字符串比较,只是 TypeScript 不会把那些表达式识别为类型保护。
instanceof 类型保护
如果你已经阅读了 typeof 类型保护并且对 JavaScript 里的 instanceof 操作符熟悉的话,你可能已经猜到了这节要讲的内容。
instanceof 类型保护是通过构造函数来细化类型的一种方式。我们把之前的例子做一个小小的改造:
class Bird {
fly () {
console.log('bird fly')
}
layEggs () {
console.log('bird lay eggs')
}
}
class Fish {
swim () {
console.log('fish swim')
}
layEggs () {
console.log('fish lay eggs')
}
}
function getRandomPet () {
return Math.random() > 0.5 ? new Bird() : new Fish()
}
let pet = getRandomPet()
// 如果是类,可以直接通过instanceof来获取类的构造函数名
if (pet instanceof Bird) {
pet.fly()
}
if (pet instanceof Fish) {
pet.swim()
}
可以为 null 的类型
TypeScript 具有两种特殊的类型,null 和 undefined,它们分别具有值 null 和 undefined。我们在基础类型一节里已经做过简要说明。 默认情况下,类型检查器认为 null 与 undefined 可以赋值给任何类型。 null 与 undefined 是所有其它类型的一个有效值。 这也意味着,你阻止不了将它们赋值给其它类型,就算是你想要阻止这种情况也不行。null的发明者,Tony Hoare,称它为价值亿万美金的错误。
--strictNullChecks 标记可以解决此错误:当你声明一个变量时,它不会自动地包含 null 或 undefined。 你可以使用联合类型明确的包含它们:
let s = 'foo'
s = null // 错误, 'null'不能赋值给'string'
let sn: string | null = 'bar'
sn = null // 可以
sn = undefined // error, 'undefined'不能赋值给'string | null'
注意,按照 JavaScript 的语义,TypeScript 会把 null 和 undefined 区别对待。string | null,string | undefined 和 string | undefined | null 是不同的类型。
可选参数和可选属性
使用了 --strictNullChecks,可选参数会被自动地加上 | undefined:
function f(x: number, y?: number) {
return x + (y || 0)
}
f(1, 2)
f(1)
f(1, undefined)
f(1, null) // error, 'null' 不能赋值给 'number | undefined'
可选属性也会有同样的处理:
class C {
a: number
b?: number
}
let c = new C()
c.a = 12
c.a = undefined // error, 'undefined' 不能赋值给 'number'
c.b = 13
c.b = undefined // ok
c.b = null // error, 'null' 不能赋值给 'number | undefined'
类型保护和类型断言
由于可以为 null 的类型能和其它类型定义为联合类型,那么你需要使用类型保护来去除 null。幸运地是这与在 JavaScript 里写的代码一致:
function f(sn: string | null): string {
if (sn === null) {
return 'default'
} else {
return sn
}
}
这里很明显地去除了 null,你也可以使用短路运算符:
function f(sn: string | null): string {
return sn || 'default'
}
如果编译器不能够去除 null 或 undefined,你可以使用类型断言手动去除。语法是添加 ! 后缀: identifier! 从 identifier 的类型里去除了 null 和 undefined:
function broken(name: string | null): string {
function postfix(epithet: string) {
return name.charAt(0) + '. the ' + epithet // error, 'name' 可能为 null
}
name = name || 'Bob'
return postfix('great')
}
function fixed(name: string | null): string {
function postfix(epithet: string) {
return name!.charAt(0) + '. the ' + epithet // ok
}
name = name || 'Bob'
return postfix('great')
}
broken(null)
本例使用了嵌套函数,因为编译器无法去除嵌套函数的 null(除非是立即调用的函数表达式)。因为它无法跟踪所有对嵌套函数的调用,尤其是你将内层函数做为外层函数的返回值。如果无法知道函数在哪里被调用,就无法知道调用时 name 的类型。
字符串字面量类型
字符串字面量类型允许你指定字符串必须具有的确切值。在实际应用中,字符串字面量类型可以与联合类型,类型保护很好的配合。通过结合使用这些特性,你可以实现类似枚举类型的字符串。
type Easing = 'ease-in' | 'ease-out' | 'ease-in-out'
class UIElement {
animate (dx: number, dy: number, easing: Easing) {
if (easing === 'ease-in') {
// ...
} else if (easing === 'ease-out') {
} else if (easing === 'ease-in-out') {
} else {
// error! 不能传入 null 或者 undefined.
}
}
}
let button = new UIElement()
button.animate(0, 0, 'ease-in')
button.animate(0, 0, 'uneasy') // error
你只能从三种允许的字符中选择其一来做为参数传递,传入其它值则会产生错误。
Argument of type '"uneasy"' is not assignable to parameter of type '"ease-in" | "ease-out" | "ease-in-out"'
### 计算机网络
* HTTP 缓存
* 你知道 302 状态码是什么嘛?你平时浏览网页的过程中遇到过哪些 302 的场景?
* HTTP 常用的请求方式,区别和用途?
* HTTPS 是什么?具体流程
* 三次握手和四次挥手
* 你对 TCP 滑动窗口有了解嘛?
* WebSocket与Ajax的区别
* 了解 WebSocket 嘛?
* HTTP 如何实现长连接?在什么时候会超时?
* TCP 如何保证有效传输及拥塞控制原理。
* TCP 协议怎么保证可靠的,UDP 为什么不可靠?
**[开源分享:【大厂前端面试题解析+核心总结学习笔记+真实项目实战+最新讲解视频】](https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/4304bb5a486d4c3ab8389e65ecb71ac0)**
### 算法
* 链表
* 字符串
* 数组问题
* 二叉树
* 排序算法
* 二分查找
* 动态规划
* BFS
* 栈
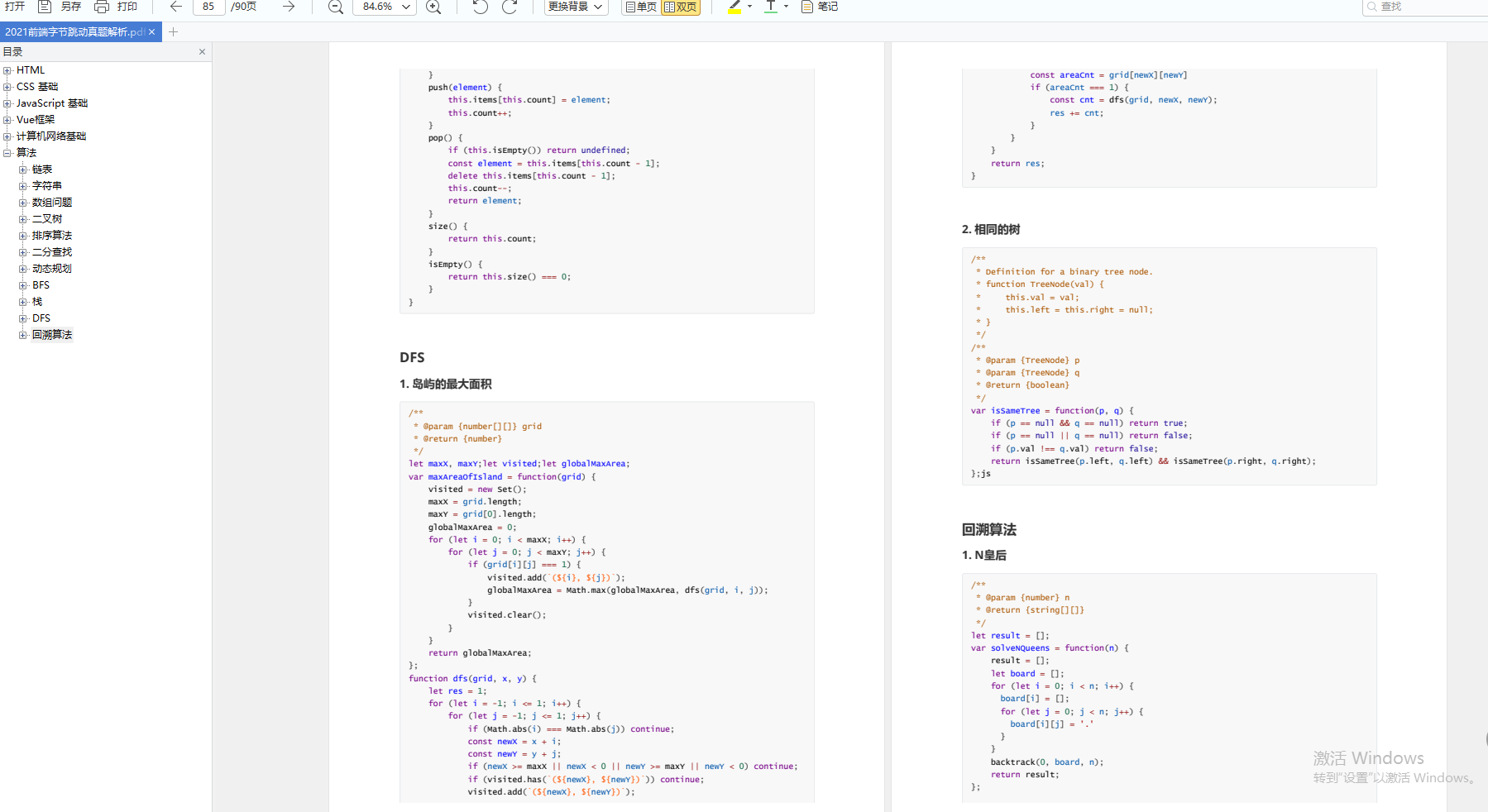
* DFS
* 回溯算法
























 962
962

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








