这是我的“理解非结构化数据”系列的第一部分。第二部分主要关注使用LangChain代理分析从非结构化文本中提取的结构化数据。
用例:使用LLMs提取非结构化竞争情报数据想象一下你是一个面包店,你已经派出你的糕点师情报团队去收集竞争对手的数据。他们报告了竞争对手的动态,并且他们有很多你想应用到你生意中的好主意。然而,这些数据是非结构化的!你如何分析这些数据以了解最常被要求的是什么,以及如何最好地优先安排你业务的下一步?
代码可在GitHub上获取:注意:代码根据使用的具体工具,被分割成两个文件:unstructured_extraction_chain.ipynb 和 unstructured_pydantic.ipynb。
https://github.com/ingridstevens/AI-projects/tree/main/unstructured_data?source=post_page-----71502addf52b--------------------------------
为了探索这个用例,我创建了一个玩具数据集。以下是数据集中的一个示例数据点:
在Velvet Frosting Cupcakes,我们的团队了解到了季节性糕点菜单的推出,该菜单每月更换。在我们的面包店引入使用“SeasonalJoy”订阅平台的轮换季节性菜单,并使用“FloralStamp”饼干印章为我们饼干添加特殊触感,可以使我们的产品保持新鲜和令人兴奋。
选项1:创建提取链我们可以先观察数据,通过这样做,我们可以识别出一个粗略的模式——或者说是结构——来进行提取。使用LangChain,我们可以创建一个提取链。

…接下来,我们定义一些测试输入:
# Inputs
in1 = """Sweet Delights Bakery introduced lavender-infused vanilla cupcakes with a honey buttercream frosting, using the "Frosting-Spreader-3000". This innovation could inspire our next cupcake creation"""
in2 = """Whisked Away Cupcakes introduced a dessert subscription service, ensuring regular customers receive fresh batches of various sweets. Exploring a similar subscription model using the "SweetSubs" program could boost customer loyalty."""
in3 = """At Velvet Frosting Cupcakes, our team learned about the unveiling of a seasonal pastry menu that changes monthly. Introducing a rotating seasonal menu at our bakery using the "SeasonalJoy" subscription platform and adding a special touch to our cookies with the "FloralStamp" cookie stamper could keep our offerings fresh and exciting for customers."""
inputs = [in1, in2, in3]
…并创建链

…最后,运行链在示例上

现在我们有了作为Python列表的结构化输出:
[{'company': 'Sweet Delights Bakery', 'offering': 'lavender-infused vanilla cupcakes', 'advantage': 'inspiring next cupcake creation', 'products_and_services': 'Frosting-Spreader-3000'}]
[{'company': 'Whisked Away Cupcakes', 'offering': 'dessert subscription service', 'advantage': 'ensuring regular customers receive fresh batches of various sweets', 'products_and_services': '', 'additional_details': ''}, {'company': '', 'offering': 'subscription model using the "SweetSubs" program', 'advantage': 'boost customer loyalty', 'products_and_services': '', 'additional_details': ''}]
[{'company': 'Velvet Frosting Cupcakes', 'offering': 'rotating seasonal menu', 'advantage': 'fresh and exciting offerings', 'products_and_services': 'SeasonalJoy subscription platform, FloralStamp cookie stamper'}]
让我们使用附加参数更新我们的原始数据这是一个不错的开始,看起来它正在运行。然而,最佳工作流程涉及导入包含竞争情报的CSV文件,将其应用到提取链进行解析和结构化,然后将解析后的信息无缝地整合回原始数据集。下面的Python代码正是这样做的:
import pandas as pd
from langchain.chains import create_extraction_chain
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
# Load in the data.csv (semicolon separated) file
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv", sep=';')
# Define Schema based on your data
schema = {
"properties": {
"company": {"type": "string"},
"offering": {"type": "string"},
"advantage": {"type": "string"},
"products_and_services": {"type": "string"},
"additional_details": {"type": "string"},
}
}
# Create extraction chain
llm = ChatOpenAI(temperature=0, model="gpt-3.5-turbo")
chain = create_extraction_chain(schema, llm)
# ----------
# Add the data to a data frame
# ----------
# Extract information and create a DataFrame from the list of dictionaries
extracted_data = df['INTEL'].apply(lambda x: chain.run(x)[0]).apply(pd.Series)
# Replace missing values with NaN
extracted_data.replace('', np.nan, inplace=True)# Concatenate the extracted_data DataFrame with the original dfdf = pd.concat([df, extracted_data], axis=1)
# display the data frame
df.head()
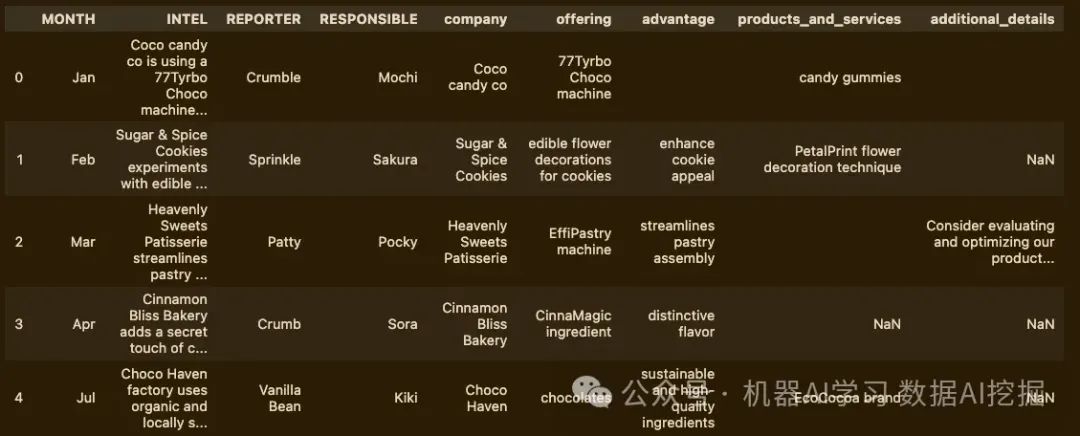
这次运行花了大约15秒,但它还没有找到我们请求的所有信息。让我们尝试另一种方法。
选项2:Pydantic在下面的代码中,Pydantic被用来定义表示竞争情报信息结构的数据模型。Pydantic是Python的一个数据验证和解析库,允许你使用Python数据类型定义简单或复杂的数据结构。在这种情况下,我们使用Pydantic模型(Competitor和Company)来定义竞争情报数据的结构。
import pandas as pd
from typing import Optional, Sequence
from langchain.llms import OpenAI
from langchain.output_parsers import PydanticOutputParser
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from pydantic import BaseModel
# Load data from CSV
df = pd.read_csv("data.csv", sep=';')
# Pydantic models for competitive intelligence
class Competitor(BaseModel):
company: str
offering: str
advantage: str
products_and_services: str
additional_details: str
class Company(BaseModel):
"""Identifying information about all competitive intelligence in a text."""
company: Sequence[Competitor]
# Set up a Pydantic parser and prompt template
parser = PydanticOutputParser(pydantic_object=Company)
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template="Answer the user query.\n{format_instructions}\n{query}\n",
input_variables=["query"],
partial_variables={"format_instructions": parser.get_format_instructions()},
)
# Function to process each row and extract information
def process_row(row):
_input = prompt.format_prompt(query=row['INTEL'])
model = OpenAI(temperature=0)
output = model(_input.to_string())
result = parser.parse(output)
# Convert Pydantic result to a dictionary
competitor_data = result.model_dump()
# Flatten the nested structure for DataFrame creation
flat_data = {'INTEL': [], 'company': [], 'offering': [], 'advantage': [], 'products_and_services': [], 'additional_details': []}
for entry in competitor_data['company']:
flat_data['INTEL'].append(row['INTEL'])
flat_data['company'].append(entry['company'])
flat_data['offering'].append(entry['offering'])
flat_data['advantage'].append(entry['advantage'])
flat_data['products_and_services'].append(entry['products_and_services'])
flat_data['additional_details'].append(entry['additional_details'])
# Create a DataFrame from the flattened data
df_cake = pd.DataFrame(flat_data)
return df_cake
# Apply the function to each row and concatenate the results
intel_df = pd.concat(df.apply(process_row, axis=1).tolist(), ignore_index=True)
# Display the resulting DataFrame
intel_df.head()
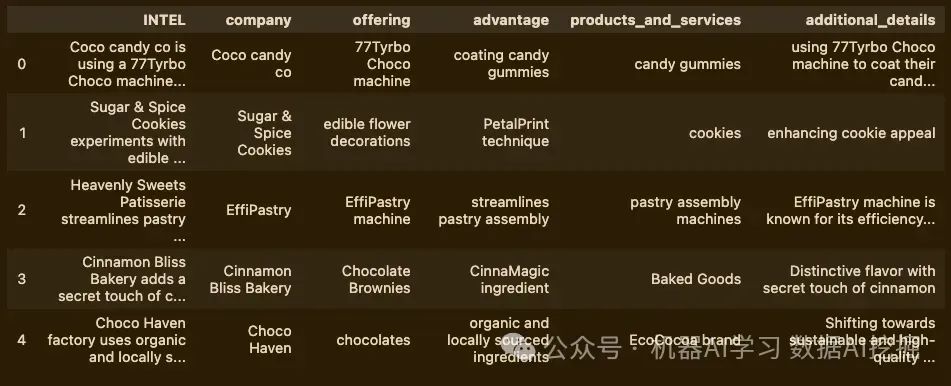
这真的很快!而且它找到了所有条目的细节,不像create_extraction_chain尝试那样。
如何学习AI大模型?
我在一线互联网企业工作十余年里,指导过不少同行后辈。帮助很多人得到了学习和成长。
我意识到有很多经验和知识值得分享给大家,也可以通过我们的能力和经验解答大家在人工智能学习中的很多困惑,所以在工作繁忙的情况下还是坚持各种整理和分享。但苦于知识传播途径有限,很多互联网行业朋友无法获得正确的资料得到学习提升,故此将并将重要的AI大模型资料包括AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频免费分享出来。

第一阶段: 从大模型系统设计入手,讲解大模型的主要方法;
第二阶段: 在通过大模型提示词工程从Prompts角度入手更好发挥模型的作用;
第三阶段: 大模型平台应用开发借助阿里云PAI平台构建电商领域虚拟试衣系统;
第四阶段: 大模型知识库应用开发以LangChain框架为例,构建物流行业咨询智能问答系统;
第五阶段: 大模型微调开发借助以大健康、新零售、新媒体领域构建适合当前领域大模型;
第六阶段: 以SD多模态大模型为主,搭建了文生图小程序案例;
第七阶段: 以大模型平台应用与开发为主,通过星火大模型,文心大模型等成熟大模型构建大模型行业应用。

👉学会后的收获:👈
• 基于大模型全栈工程实现(前端、后端、产品经理、设计、数据分析等),通过这门课可获得不同能力;
• 能够利用大模型解决相关实际项目需求: 大数据时代,越来越多的企业和机构需要处理海量数据,利用大模型技术可以更好地处理这些数据,提高数据分析和决策的准确性。因此,掌握大模型应用开发技能,可以让程序员更好地应对实际项目需求;
• 基于大模型和企业数据AI应用开发,实现大模型理论、掌握GPU算力、硬件、LangChain开发框架和项目实战技能, 学会Fine-tuning垂直训练大模型(数据准备、数据蒸馏、大模型部署)一站式掌握;
• 能够完成时下热门大模型垂直领域模型训练能力,提高程序员的编码能力: 大模型应用开发需要掌握机器学习算法、深度学习框架等技术,这些技术的掌握可以提高程序员的编码能力和分析能力,让程序员更加熟练地编写高质量的代码。

1.AI大模型学习路线图
2.100套AI大模型商业化落地方案
3.100集大模型视频教程
4.200本大模型PDF书籍
5.LLM面试题合集
6.AI产品经理资源合集
👉获取方式:
😝有需要的小伙伴,可以保存图片到wx扫描二v码免费领取【保证100%免费】🆓

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








