该程序是基于我之前文章提到的BMP绘制实现的。
C语言实现BMP绘制:BMP详解及C语言实现BMP生成-CSDN博客
如有错误,欢迎指正,谢谢!
点阵字库(HZK16)
点阵字库就是基于点阵实现的字库,HZK16就是基于16*16的点阵形成的字库。
具体而言,就是在16*16的点格上,去绘制字,然后记录哪些点被绘制了,哪些没有,进而形成字库,从这里就可以发现,点阵字库中的每个字模对应的大小就为16*16bit,即32字节。
举个例子:
这是我利用程序输出出的"你“的点阵字模数据(16进制)
![]()
绘制后

简单讲述其原理,图中的每一格相当于1bit,一行就是两字节
![]() 这是第一行的字模数据,转换成二进制就是 00010001 00000000,而在图中的体现就是,绘制第一行的第4格和第八格。
这是第一行的字模数据,转换成二进制就是 00010001 00000000,而在图中的体现就是,绘制第一行的第4格和第八格。
HZK16是基于GB2312的,接下来简单介绍一下GB2312
GB2312
其共收录了 6763 个常用的汉字和字符,采取区位码的方式对应每一个字符,每个区含有 94 个字符,总共有 94 个区。每个字符对应两个字节,第一字节对应区号,第二字节字节对应位号。
GB2312编码表:GB2312 编码表 - 锤子在线工具
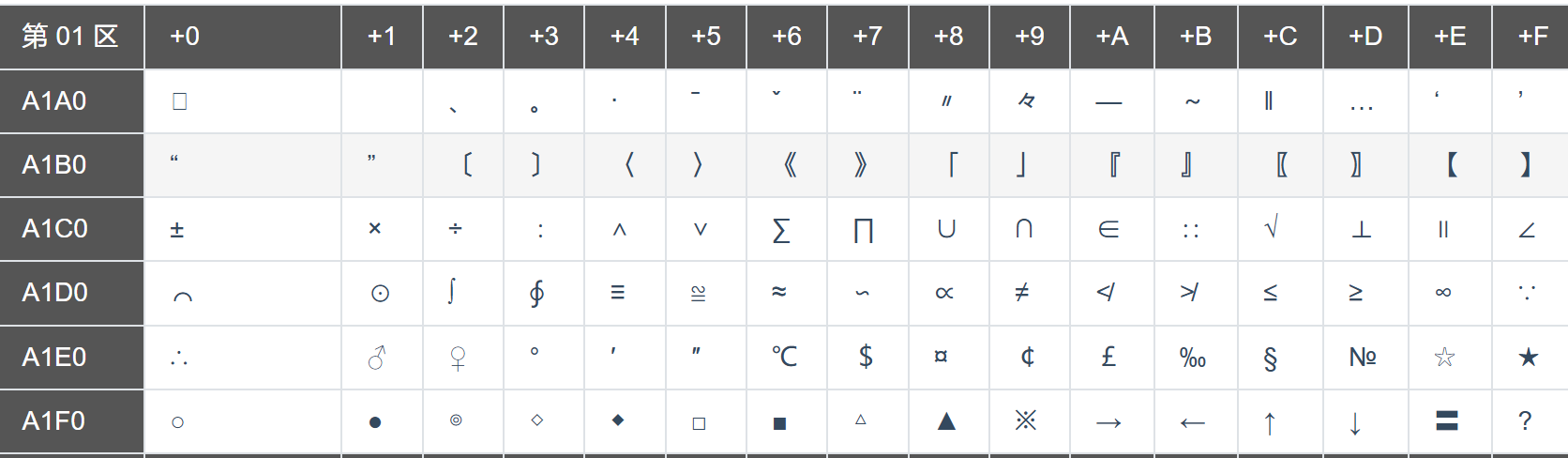
从图中可以看出,GB2312的区位码是从A1A0开始的。
![]()
C4 E3对应的就是"你"的区位码
HZK16字模定位
字模在HZK16中的偏移量=(94*(区号-0xA1)+(位号-0xA1))*32

简单解释一下,打开HZK16,可以看到前两行全为0,而第四行开始有了数据,这也就代表着第二个字模是有数据的,对照GB2312编码表,即可知:HZK16记录的字模数据是从区位码0xA1A1开始的。所以94*(区号-0xA1),是因为一个区有94个字符,最后*32是因为一个字的字模数据共32个字节。
注意
HZK16中的字模数据是包含英文的,但是其对应的是全角英文,所以其也是由两个字节组成,也有对应的区位码,即

全角字符:A
半角字符:A
还是能够看出来有些差别的吧(大概)
代码实现
头文件部分
#ifndef BMP_H
#define BMP_H
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#pragma pack(1)
#define PER_BYTE 3
#define COLOR_DATA(x, y, z) color_data[x*width*3 + y*3 + z]
typedef struct {
unsigned char bfType[2];
unsigned int bfSize;
unsigned short int bfReserved1;
unsigned short int bfReserved2;
unsigned int bfOffBits;
}BMP_FILE_HEADER;
typedef struct {
unsigned int biSize;
int biWidth;
int biHeight;
unsigned short int biPlane;
unsigned short int biBitCount;
unsigned int biCompression;
unsigned int biSizeImage;
int biXPelsPerMeter;
int biYPelsPerMeter;
unsigned int biClrUsed;
unsigned int biClrImportant;
}BMP_INFO_HEADER;
int bmp_generate(const char* file, unsigned char* color_data, int width, int height);
#endifBMP生成
// 生成BMP
// file为输出文件名
// color_data为位图数据(但是以倒向、单像素以RGB形式而非BGR,便于理解,不完全等同于位图数据)
int bmp_generate(const char* file, unsigned char* color_data, int width, int height)
{
FILE* fp;
int image_size; // 图像大小,对应biSizeImage
unsigned char* bmp_data; // 对应位图数据
int i;
int j;
int k;
int pixel_pointer; // 用于去指向单个像素首字节
int byte_count; // 单像素中byte计数
int supplement; // 每一行补充字节数
int offset; // 位图数据偏移量
fp = fopen(file, "wb+");
if (fp == NULL) {
printf("open file error\n");
return -1;
}
if (width <= 0) {
printf("width error\n");
return -2;
}
offset = 64;
// 计算每一行需要补充多少字节
supplement = 0;
while ((width * PER_BYTE + supplement) % 4 != 0) {
supplement++;
}
// 计算位图数据大小
image_size = width * fabs(height) * PER_BYTE + supplement * fabs(height);
bmp_data = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(char)*image_size);
// 定义文件头、信息头
BMP_FILE_HEADER file_header;
BMP_INFO_HEADER info_header;
file_header.bfType[0] = 'B';
file_header.bfType[1] = 'M';
file_header.bfSize = image_size + offset;
file_header.bfReserved1 = 0;
file_header.bfReserved2 = 0;
file_header.bfOffBits = 64;
info_header.biSize = 40;
info_header.biWidth = width;
info_header.biHeight = height;
info_header.biPlane = 1;
info_header.biBitCount = 24;
info_header.biCompression = 0;
info_header.biSizeImage = image_size;
info_header.biXPelsPerMeter = 0;
info_header.biYPelsPerMeter = 0;
info_header.biClrUsed = 0;
info_header.biClrImportant = 0;
// 将头部信息写入
fwrite(&file_header, sizeof(BMP_FILE_HEADER), 1, fp);
fwrite(&info_header, sizeof(BMP_INFO_HEADER), 1, fp);
// 将color_data处理为真实的位图数据
// 正向
if (height < 0) {
for (i = 0, j = 0 , pixel_pointer = 0, byte_count = PER_BYTE - 1; i < image_size;) {
bmp_data[i] = color_data[pixel_pointer + byte_count];
i++;
byte_count--;
// 处理完一个像素,重置bit_count,增加pixel_count
if (byte_count < 0) {
byte_count = PER_BYTE - 1;
pixel_pointer += PER_BYTE;
}
// 当一行数据写完后,后续是填充数据,直接跳过不写
if (++j == width * PER_BYTE) {
j = 0;
i += supplement;
}
}
}
// 倒向
else {
for (i = 0, j = 0, k = height - 1, pixel_pointer = k * width * 3, byte_count = PER_BYTE - 1; i < image_size;) {
bmp_data[i++] = color_data[pixel_pointer + byte_count];
if (--byte_count < 0) {
byte_count = PER_BYTE - 1;
pixel_pointer += PER_BYTE;
}
if (++j == width * PER_BYTE) {
j = 0;
i += supplement;
k--;
pixel_pointer = k * width * 3;
}
}
}
// 定位文件读写处
fseek(fp, offset, SEEK_SET);
// 写入位图数据
fwrite(bmp_data, 1, image_size, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}字模提取函数
// pixel_color 用于指定绘制的字的颜色
// file 表示配置文件,为txt文件,文件中存放需要绘制的内容
// width 为BMP的宽度
int get_color_data(unsigned char* color_data, unsigned char pixel_color[3], char* file, int width)
{
unsigned char buffer_typeface[32];
int i;
int j;
int k;
int a;
int count_height; // 用于记录绘制第几行
int offset; // 表示字模数据的偏移量
int row; // 表示txt配置文件中,有几行数据
FILE* fp_config; // 配置文件fp
FILE* fp_hzk; // HZK16文件fp
unsigned char** buffer_txt; // 存放待绘制的字符
char* buffer_test; // 用于测试配置文件行数
int judge; // 用于判断
count_height = 0;
offset = 0;
row = 0;
fp_config = fopen(file, "r");
if (fp_config == NULL) {
printf("open file error\n");
return -1;
}
fp_hzk = fopen("HZK16", "r");
if (fp_hzk == NULL) {
printf("open hzk error\n");
return -2;
}
buffer_test = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 1024);
// 计算txt文件行数
while (fgets(buffer_test, 1024, fp_config)) {
row++;
}
// 初始化空间
buffer_txt = (unsigned char**)malloc(sizeof(char*) * row);
for (i = 0; i < row; i++) {
buffer_txt[i] = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 1024);
}
// 重定位文件指针
fseek(fp_config, 0, SEEK_SET);
while (fgets((char*)buffer_txt[count_height], 1024, fp_config)) { //提取一行
for (a = 0; a < strlen((const char*)buffer_txt[count_height]) - 1; a += 2) { //提取单个字,注意汉字是两个字节
// 这表示读取到了HZK16中不包含的字符,直接跳过那一个字符,
if (buffer_txt[count_height][a] < 0xA0) {
a--;
continue;
}
// 获取字模
offset = (94 * (buffer_txt[count_height][a] - 0xA1) + (buffer_txt[count_height][a + 1] - 0xA1)) * 32;
fseek(fp_hzk, offset, SEEK_SET);
fread(buffer_typeface, 1, 32, fp_hzk);
// write
for (k = 0; k < 16; k++) { // k代表行数
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++) { // j代表列数
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) { // 代表位数
judge = buffer_typeface[k * 2 + j] & ((int)pow(2,7-i));
if (judge) {
COLOR_DATA((k + count_height * 16), (i + j * 8 + a * 16), 0) = pixel_color[0];
COLOR_DATA((k + count_height * 16), (i + j * 8 + a * 16), 1) = pixel_color[1];
COLOR_DATA((k + count_height * 16), (i + j * 8 + a * 16), 2) = pixel_color[2];
}
}
}
}
}
count_height++;
}
fclose(fp_config);
fclose(fp_hzk);
return 0;
}
测试函数
int main()
{
char* outfile; // 输出的BMP文件
char* infile; //作为配置输入的txt文件
unsigned char pixel_color[3] = { 0,0xFF,0xFF }; // 指定颜色
int width;
int height;
unsigned char* color_data;
// 初始化
width = 500;
height = 500;
outfile = (char*)"12.bmp";
infile = (char*)"12.txt";
color_data = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * width * height * PER_BYTE);
// 设置背景色
for (int i = 0; i < width; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < height; j++){
COLOR_DATA(i, j, 0) = 0x00;
COLOR_DATA(i, j, 1) = 0x66;
COLOR_DATA(i, j, 2) = 0x00;
}
}
get_color_data(color_data, pixel_color, infile, width);
bmp_generate(outfile, (unsigned char*)color_data, width, -height);
return 0;
}附加
12.txt(不知道怎么打全角英文,还是一个个复制出来的)
你 好,世 界!
Hello,World!

12.bmp

需要注意的是,利用txt作为配置文件时,一定要注意其编码形式,HZK16是基于GB2312的,所以选择的编码格式一定要是GB系列的(更高版本向下兼容)。我这里的ANSI代表系统自动选择编码,既然成功了,那就代表其自动选择的就是GB系列编码。























 3938
3938

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








