实验四 链队列各种操作的实现
一、实验目的
1.掌握队列的抽象数据类型。
2.掌握实现队列的各种操作的算法。
3.掌握队列的链式存储结构及基本操作,深入了解链队列的基本特性,以便在实际问题背景下灵活运用它们。
二、实验环境
1.硬件:每个学生需配备计算机一台。
2.软件:Windows操作系统+Visual C++。
三、实验要求
⒈用C描述每种操作在链队列上的实现。
2.将初始化队列、判断队列是否非空、入队列、出队列、十进制到二进制的转换分别定义为5个子函数,通过主函数实现对上述子函数的调用
四、实验内容
1.实现环形队列的各种基本运算
在实现环形队列各种基本运算的基础上,设计主程序,完成如下功能:
(1)初始化队列q。
(2)判断队列q是否为空。
(3)依次将6,8,10元素入队。
(4)出队一个元素,输出该元素。
(5)依次将20,30,24元素入队。
(6)输出队列序列。
(7)释放队列。
实现程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
#define MaxSize 100
typedef int ElemType;
//创建队列
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int front,rear;
}SqQueue;
//初始化队列
void InitQueue(SqQueue *&q)
{
q=(SqQueue *)malloc(sizeof(SqQueue));
q->front=q->rear=0;
}
//销毁队列
void DestroyQueue(SqQueue *&q)
{
free(q);
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(SqQueue *q)
{
return(q->front==q->rear);
}
//进队
bool enQueue(SqQueue *&q,ElemType e)
{
if((q->rear+1)%MaxSize==q->front)
return false;
q->rear=(q->rear+1)%MaxSize;
q->data[q->rear]=e;
return true;
}
//出队
bool deQueue(SqQueue *&q,ElemType &e)
{
if(q->front==q->rear)
return false;
q->front=(q->front+1)%MaxSize;
e=q->data[q->front];
return true;
}
//主函数
void main()
{
ElemType e;
SqQueue *q;
printf("环形队列基本运算如下:\n");
printf("(1)初始化队列q\n");
InitQueue(q);
printf("(2)判断队列q是否为空\t");
printf("%s\n",(QueueEmpty(q)?"空":"非空"));
printf("(3)依次6,8,10元素入队\n");
enQueue(q,6);
enQueue(q,8);
enQueue(q,10);
if(deQueue(q,e)==0)
printf("队空,不能出队");
else
printf("(4)出队一个元素,输出该元素%d\n",e);
printf("(5)依次将20,30,24元素入队\n");
enQueue(q,20);
enQueue(q,30);
enQueue(q,24);
printf("(6)输出队列序列");
while(!QueueEmpty(q))
{
deQueue(q,e);
printf("%d\t",e);
}
printf("\n");
printf("(7)释放队列\n");
DestroyQueue(q);
}
运行结果:
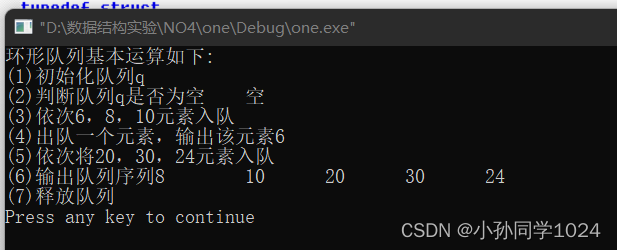
测试结果:
通过!
2.实现链队的各种基本运算
在实现链队各种基本运算的基础上,设计主程序,完成上题1的7个操作。
实现程序:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
typedef int ElemType;
//声明链队数据结点
typedef struct DataNode
{
ElemType data;
struct DataNode *next;
}DataNode;
//声明链队类型
typedef struct
{
DataNode *front;
DataNode *rear;
}LinkQuNode;
//初始化队列q
void InitQueue(LinkQuNode *&q)
{
q=(LinkQuNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkQuNode));
q->front=q->rear=NULL;
}
//销毁队列q
void DestoryQueue(LinkQuNode *&q)
{
DataNode *p=q->front,*r;
if(p!=-NULL)
{
r=p->next;
while(r!=NULL){
free(p);
p=r;
r=p->next;
}
}
free(p);
free(q);
}
//判断队列q是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(LinkQuNode *q)
{
return(q->rear==NULL);
}
//进队
void enQueue(LinkQuNode *&q,ElemType e)
{
DataNode *p;
p=(DataNode *)malloc(sizeof(DataNode));
p->data=e;
p->next=NULL;
if(q->rear==NULL)
q->front=q->rear=p;
else
{
q->rear->next=p;
q->rear=p;
}
}
//出队
bool deQueue(LinkQuNode *&q,ElemType &e)
{
DataNode *t;
if(q->rear==NULL)
return false;
t=q->front;
if(q->front==q->rear)
q->front=q->rear=NULL;
else
q->front=q->front->next;
e=t->data;
free(t);
return true;
}
//主函数
void main()
{
ElemType e;
LinkQuNode *q;
printf("链队的基本运算如下:\n");
printf("(1)初始化队列q\n");
InitQueue(q);
printf("(2)判断队列q是否为空\t");
printf("%s\n",(QueueEmpty(q)?"空":"非空"));
printf("(3)依次将6,8,10元素入队\n");
enQueue(q,6);
enQueue(q,8);
enQueue(q,10);
if(deQueue(q,e)==0)
printf("\t队空,不能出队");
else
printf("(4)出队一个元素,输出该元素\n");
printf("(5)依次将20,30,24元素入队\n");
enQueue(q,20);
enQueue(q,30);
enQueue(q,24);
printf("(6)输出队列序列");
while(!QueueEmpty(q))
{
deQueue(q,e);
printf("%d",e);
}
printf("\n");
printf("(7)释放队列\n");
DestoryQueue(q);
}
运行结果:
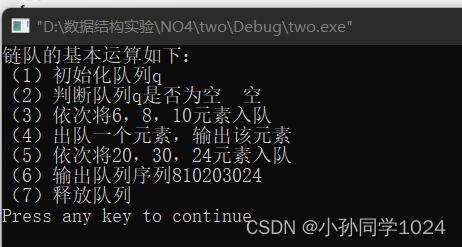
测试结果:
通过!
3.队列的应用
设计算法,利用队列将一个十进制数转换为二进制数。
实现程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#define M 100
typedef long ElemType;
// 栈
typedef struct
{
ElemType data[M];
int top;
} Stack;
// 队列
typedef struct QNode
{
ElemType data;
struct QNode * next;
} QNode, *QueuePtr;
//定义队列结构
typedef struct
{
QueuePtr front;
QueuePtr rear;
} LinkQueue;
//初始化栈;
void InitStack(Stack *s)
{
s->top=-1;
}
int Push(Stack *s,ElemType e)
{
if(s->top==M-1)
{
printf("栈满\n");
return 0;
}
s->top++;
s->data[s->top]=e;
return 1;
}
bool Pop(Stack *&s, ElemType &e)
{
if(s->top==-1)
return false;
e=s->data[s->top];
s->top--;
return true;
}
//判断是否为空
bool StackEmpty(Stack * s)
{
return(s->top==-1);
}
//栈的大小
int StackSize(Stack * s)
{
return(s->top + 1);
}
// 初始化队列
void initQueue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
Q->front = Q->rear = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!Q->front) exit(OVERFLOW);
Q->front->next = NULL;
}
// 销毁队列
void destroyQueue(LinkQueue *Q)
{
while (Q->front)
{
Q->rear = Q->front->next;
free(Q->front);
Q->front = Q->rear;
}
}
// 入队
void enQueue(LinkQueue *Q, ElemType e)
{
QueuePtr p = (QueuePtr)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if(!p) exit(OVERFLOW);
//插入数据
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
Q->rear->next = p;
Q->rear = p;
}
// 出队
void deQueue(LinkQueue *Q, ElemType &e)
{
if(Q->front == Q->rear) return;
QueuePtr p = Q->front->next;
e = p->data;
Q->front->next = p->next;
if(Q->rear == p)
Q->rear = Q->front = NULL;
free(p);
}
// 队列是否空
bool isQueueEmpty(LinkQueue *Q) {
return Q->front->next == NULL;
}
// 整数部分十进制转二进制
void convertIntegerToBinary(ElemType N)
{
ElemType e;
Stack *s=(Stack *)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
InitStack(s);
while(N)
{
Push(s,N%2);
N=N/2;
}
while(! StackEmpty(s))
{
Pop(s,e);
printf("%d",e);
}
}
//主函数
void main() {
int digital;
printf("请输入待转的十进制数:\n");
scanf("%d", &digital);
printf("转换为二进制值为:\n");
convertIntegerToBinary(digital);
}
运行结果:

测试结果:
通过!
六、实验总结
通过本次实验学习了队的应用,对链队和环形队进队出队等基本操作和队与栈的结合应用。论进制转换实验而言,栈方便与队,但与队功能不同。
























 149
149











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










