Grokking: Generalization Beyond Overfitting on Small Algorithmic Datasets 小算法数据集上超越过度拟合的泛化
2022.6.6
代码地址- Sea-Snell
代码地址-teddykoker




Abstract
In this paper we propose to study generalization of neural networks on small algorithmically generated datasets. In this setting, questions about data efficiency, memorization, generalization, and speed of learning can be studied in great detail. In some situations we show that neural networks learn through a process of “grokking” a pattern in the data, improving generalization performance from random chance level to perfect generalization, and that this improvement in generalization can happen well past the point of overfitting. We also study generalization as a function of dataset size and find that smaller datasets require increasing amounts of optimization for generalization. We argue that these datasets provide a fertile ground for studying a poorly understood aspect of deep learning: generalization of overparametrized neural networks beyond memorization of the finite training dataset.
在本文中,我们提议在通过算法生成的小型数据集上研究神经网络的泛化。在这种情况下,有关数据效率、记忆、泛化和学习速度等问题都可以得到详细研究。
-
在某些情况下,我们发现神经网络可以通过 "摸索 "数据中的模式来学习,从而将泛化性能从随机概率水平提高到完美泛化水平,而且这种泛化性能的提高可以远远超过过度拟合的程度。
-
我们还研究了泛化与数据集大小的函数关系,发现较小的数据集需要越来越多的泛化优化。
我们认为,这些数据集为研究深度学习中一个鲜为人知的方面提供了肥沃的土壤:超参数化神经网络的泛化超越了对有限训练数据集的记忆。
Omnigrok: Grokking Beyond Algorithmic Data 算法数据之外的Grokking
ICLR 2023
Abstract
Grokking, the unusual phenomenon for algorithmic datasets where generalization happens long after overfitting the training data, has remained elusive. We aim to understand grokking by analyzing the loss landscapes of neural networks, identifying the mismatch between training and test losses as the cause for grokking. We refer to this as the “LU mechanism” because training and test losses (against model weight norm) typically resemble “L” and “U”, respectively. This simple mechanism can nicely explain many aspects of grokking: data size dependence, weight decay dependence, the emergence of representations, etc. Guided by the intuitive picture, we are able to induce grokking on tasks involving images, language and molecules. In the reverse direction, we are able to eliminate grokking for algorithmic datasets. We attribute the dramatic nature of grokking for algorithmic datasets to representation learning.
对于算法数据集来说,“摸索”(Grokking)是一种不寻常的现象,即在过度拟合训练数据后很长时间才出现泛化。
我们旨在通过分析神经网络的损失景观来理解 "摸索 "现象,并将训练和测试损失之间的不匹配确定为 "摸索 "的原因。
我们将其称为 “LU 机制”,因为训练和测试损失(与模型权重规范相对比)通常分别类似于 "L "和 “U”。这种简单的机制可以很好地解释摸索的许多方面:数据大小依赖性、权重衰减依赖性、表征的出现等。
-
在这一直观图景的指导下,我们能够在涉及图像、语言和分子的任务中诱导摸索。
-
反之,我们能够消除算法数据集的摸索。我们将算法数据集摸索的显著特征归因于表征学习。

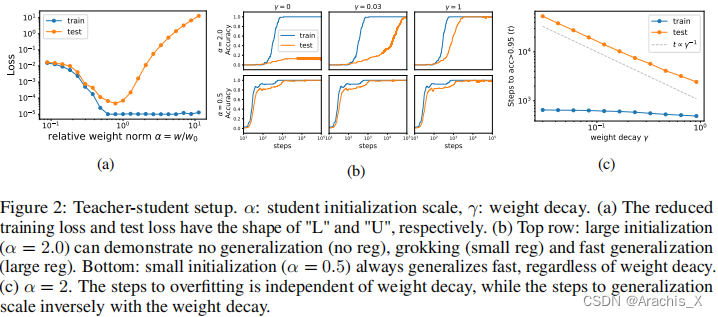



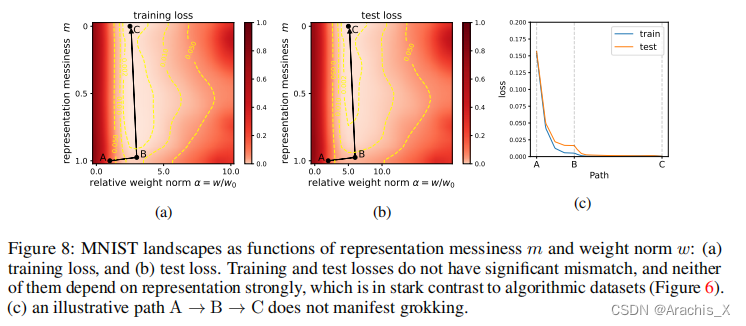








 两篇论文探讨了神经网络在小型算法生成数据集上的泛化行为,揭示了“Grokking”现象,即模型在过度拟合后仍能提升泛化性能。研究者通过分析损失景观和表征学习,揭示了数据大小、优化和模型行为之间的关系。
两篇论文探讨了神经网络在小型算法生成数据集上的泛化行为,揭示了“Grokking”现象,即模型在过度拟合后仍能提升泛化性能。研究者通过分析损失景观和表征学习,揭示了数据大小、优化和模型行为之间的关系。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








