DELL: Generating Reactions and Explanations for LLM-Based Misinformation Detection 为基于 LLM 的错误信息检测 生成回应和解释
论文地址
代码地址暂无

Abstract
Large language models are limited by challenges in factuality and hallucinations to be directly employed off-the-shelf for judging the veracity of news articles, where factual accuracy is paramount. In this work, we propose DELL that identifies three key stages in misinformation detection where LLMs could be incorporated as part of the pipeline: 1) LLMs could generate news reactions to represent diverse perspectives and simulate user-news interaction networks; 2) LLMs could generate explanations for proxy tasks (e.g., sentiment, stance) to enrich the contexts of news articles and produce experts specializing in various aspects of news understanding; 3) LLMs could merge task-specific experts and provide an overall prediction by incorporating the predictions and confidence scores of varying experts. Extensive experiments on seven datasets with three LLMs demonstrate that DELL outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by up to 16.8% in macro f1-score. Further analysis reveals that the generated reactions and explanations are greatly helpful in misinformation detection, while our proposed LLM-guided expert merging helps produce better-calibrated predictions.
大型语言模型受限于事实性和幻觉方面的挑战,无法直接用于判断新闻文章的真实性,而事实准确性是最重要的。在这项工作中,我们提出了 DELL方案,该方案确定了误报检测的三个关键阶段,其中 LLM 可以作为pipeline的一部分:
- LLM 可以生成新闻反应,以代表不同的观点,并模拟用户与新闻的交互网络;
- LLM 可以生成代理任务(如情感、立场)的解释,以丰富新闻文章的上下文,并产生专门从事新闻理解各个方面的专家;
- LLM 可以合并特定任务的专家,并通过合并不同专家的预测和置信度分数来提供整体预测。
使用三个 LLM 在七个数据集上进行的广泛实验表明,DELL 在宏观 f1 分数上比最先进的基线高出 16.8%。进一步的分析表明,生成的反应和解释对错误信息检测大有帮助,而我们提出的由 LLM 引导的专家合并则有助于产生更好的校准预测。
Results


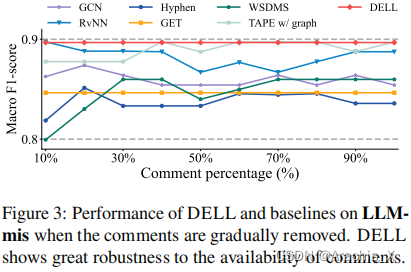
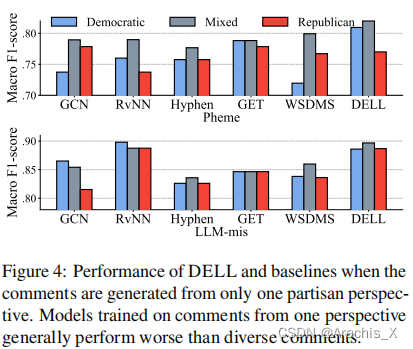
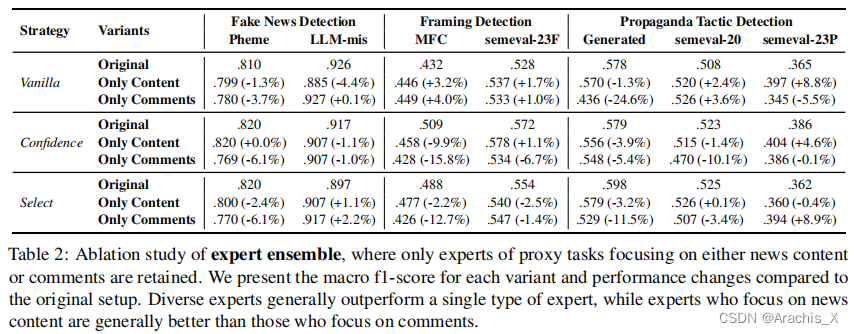











 研究提出DELL方法,利用大型语言模型在新闻真实性判断中生成反应、解释和专家预测,通过模拟交互、丰富上下文和融合专家提升性能,实验显示优于现有方法16.8%的F1得分。
研究提出DELL方法,利用大型语言模型在新闻真实性判断中生成反应、解释和专家预测,通过模拟交互、丰富上下文和融合专家提升性能,实验显示优于现有方法16.8%的F1得分。
















 474
474

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








