问题及代码:
/*
*Copyright(c)2016,烟台大学计算机与控制工程学院
*All right reserved.
*文件名称:77.cpp
*作 者:董凯琦
*完成日期:2016年5月25日
*版 本 号:v1.0
*
*问题描述:(1)实现分数类中的运算符重载,在分数类中可以完成分数的加减乘除(运算后再化简)、比较(6种关系)的运算。
class CFraction
{
private:
int nume; // 分子
int deno; // 分母
public:
//构造函数及运算符重载的函数声明
};
//重载函数的实现及用于测试的main()函数
(2)在(1)的基础上,实现分数类中的对象和整型数的四则运算。分数类中的对象可以和整型数进行四则运算,且运算符合交换律。例如:CFraction a(1,3),b; int i=2; 可以完成b=a+i;。同样,可以完成i+a, 45+a, a*27, 5/a等各种运算。
(3)定义分数的一目运算+和-,分别代表分数取正和求反,将“按位取反运算符”~重载为分数的求倒数运算。
(4)定义分数类中<<和>>运算符重载,实现分数的输入输出,改造原程序中对运算结果显示方式,使程序读起来更自然。
*输入描述:
*程序输出:
*/
#include <iostream>
#include<Cmath>
using namespace std;
class CFraction
{
private:
int nume;
int deno;
public:
CFraction(int nu=0,int de=1):nume(nu),deno(de){}
void simplify();
friend istream &operator>>(istream &in,CFraction &x);
friend ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,CFraction x);//输入输出的重载
CFraction operator+(const CFraction &c);
CFraction operator-(const CFraction &c);
CFraction operator*(const CFraction &c);
CFraction operator/(const CFraction &c);
CFraction operator+(); //取正一目运算
CFraction operator-(); //取反一目运算
CFraction operator~(); //取倒数一目运算
bool operator>(const CFraction &c);
bool operator<(const CFraction &c);
bool operator==(const CFraction &c);
bool operator!=(const CFraction &c);
bool operator>=(const CFraction &c);
bool operator<=(const CFraction &c);
};
void CFraction::simplify()
{
int a,b,r;
a=fabs(deno);
b=fabs(nume);
while(r=b%a)
{
b=a;
a=r;
}
deno/=a;
nume/=b;
if(deno<0)
{
deno=-deno;
nume=-nume;
}
}
// 重载输入运算符>>
istream &operator>>(istream &in,CFraction &x)
{
char ch;
while(1)
{
cin>>x.nume>>ch>>x.deno;
if (x.deno==0)
cerr<<"分母为0, 请重新输入\n";
else if(ch!='/')
cerr<<"格式错误(形如m/n)! 请重新输入\n";
else
break;
}
return cin;
}
// 重载输出运算符<<
ostream &operator<<(ostream &out,CFraction x)
{
cout<<x.nume<<'/'<<x.deno;
return cout;
}
// 分数相加
CFraction CFraction::operator+(const CFraction &c)
{
CFraction t;
t.nume=nume*c.deno+c.nume*deno;
t.deno=deno*c.deno;
t.simplify();
return t;
}
// 分数相减
CFraction CFraction:: operator-(const CFraction &c)
{
CFraction t;
t.nume=nume*c.deno-c.nume*deno;
t.deno=deno*c.deno;
t.simplify();
return t;
}
// 分数相乘
CFraction CFraction:: operator*(const CFraction &c)
{
CFraction t;
t.nume=nume*c.nume;
t.deno=deno*c.deno;
t.simplify();
return t;
}
// 分数相除
CFraction CFraction:: operator/(const CFraction &c)
{
CFraction t;
t.nume=nume*c.deno;
t.deno=deno*c.nume;
t.simplify();
return t;
}
// 分数取正号
CFraction CFraction:: operator+()
{
return *this;
}
// 分数取负号
CFraction CFraction:: operator-()
{
CFraction x;
x.nume=-nume;
x.deno=deno;
return x;
}
// 分数取倒数
CFraction CFraction:: operator~()
{
CFraction x;
x.nume=deno;
x.deno=nume; //未对原分子为0的情况进行处理
if(x.deno<0) //保证负分数的负号在分子上
{
x.deno=-x.deno;
x.nume=-x.nume;
}
return x;
}
// 分数比较大小
bool CFraction::operator>(const CFraction &c)
{
int this_nume,c_nume,common_deno;
this_nume=nume*c.deno; // 计算分数通分后的分子,同分母为deno*c.deno
c_nume=c.nume*deno;
common_deno=deno*c.deno;
if ((this_nume-c_nume)*common_deno>0) return true;
return false;
}
// 分数比较大小
bool CFraction::operator<(const CFraction &c)
{
int this_nume,c_nume,common_deno;
this_nume=nume*c.deno;
c_nume=c.nume*deno;
common_deno=deno*c.deno;
if ((this_nume-c_nume)*common_deno<0) return true;
return false;
}
// 分数比较大小
bool CFraction::operator==(const CFraction &c)
{
if (*this!=c) return false;
return true;
}
// 分数比较大小
bool CFraction::operator!=(const CFraction &c)
{
if (*this>c || *this<c) return true;
return false;
}
// 分数比较大小
bool CFraction::operator>=(const CFraction &c)
{
if (*this<c) return false;
return true;
}
// 分数比较大小
bool CFraction::operator<=(const CFraction &c)
{
if (*this>c) return false;
return true;
}
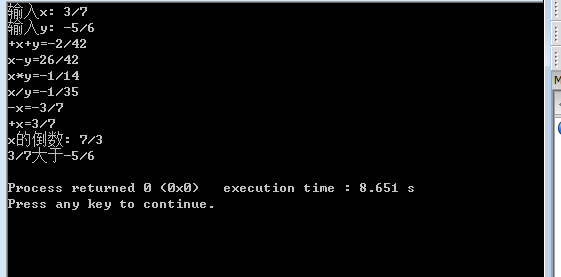
int main()
{
CFraction x,y,s;
cout<<"输入x: ";
cin>>x;
cout<<"输入y: ";
cin>>y;
s=+x+y;
cout<<"+x+y="<<s<<endl;
s=x-y;
cout<<"x-y="<<s<<endl;
s=x*y;
cout<<"x*y="<<s<<endl;
s=x/y;
cout<<"x/y="<<s<<endl;
cout<<"-x="<<-x<<endl;
cout<<"+x="<<+x<<endl;
cout<<"x的倒数: "<<~x<<endl;
cout<<x;
if (x>y) cout<<"大于";
if (x<y) cout<<"小于";
if (x==y) cout<<"等于";
cout<<y<<endl;
return 0;
}
知识点总结:
从这个程序中,我们可以熟悉运算符重载的知识点。
在分数类中的运算符重载中要注意化简函数的实现。
学习心得:
要注意考虑到方方面面!





















 1161
1161

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








