
🌻个人主页:相洋同学
🥇学习在于行动、总结和坚持,共勉!
目录
#刷题记录#
今天来解决三道二叉树的求路径问题
分别对应力扣
1.二叉树所有路径:
2.路径总和
3.路径总和II
1.二叉树的所有路径
给你一个二叉树的根节点root,按任意顺序,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径(叶子节点指的是没有子节点的节点)
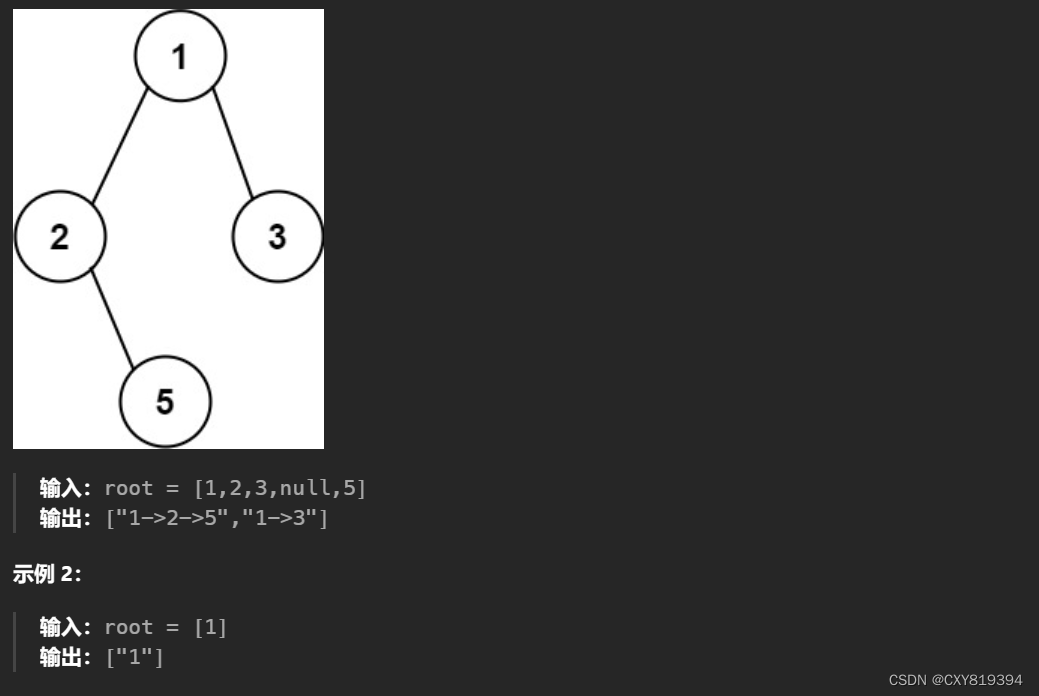
这道题上来会想到前序遍历,因为要求的输出也是前序,我们用递归来解决:
(1).确定输入和输出:
输入为二叉树根节点root,输出为路径列表resuult -> List[str];
result = []
path = []
def traval(self,cur,path,result)(2).确定终止条件:
自然地想到当节点的左右节点为空时,返回
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
.....
return中间的省略号还要执行其他步骤,因为当遍历到跟节点时也意味着当前路径结束,可以将其放入结果中,这里我们后面再写。
(3).确定中间过程:
应为采取了前序遍历,我们采取中左右的写法,中为处理当前节点的语句,值得注意的是,我们在遍历的过程中要加入回溯的操作,因为遍历完当前节点,需要弹出,对其他路径进行遍历。
# 中间过程
path.append(cur.val)
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
...
return
# 当左节点不为空
if cur.left:
self.traval(cur.left,path,result)
path.pop()
if cur.left:
self.traval(cur.right,path,result)
path.pop()接下来我们将路径path加入result,就是按照要求输出:
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
# 创建一个空字符串
s = ''
for i in range(len(path)-1):
s += str(path[i]) + '->'
# 将最后一位加入字符串
s += path[-1]
result.append(s)(4)汇总:
上面我们分步骤写了traval遍历函数,为了达到题目要求输入root,输出result,我们需要对主函数进行构造,结果如下:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def binaryTreePaths(self, root):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:rtype: List[str]
"""
path = []
result = []
if not root:
return []
self.traval(root,path,result)
return result
def traval(self,root,path,result):
path.append(root.val)
if root.left is None and root.right is None:
s = ''
for i in range(len(path)-1):
s += str(path[i]) + '->'
s += str(path[-1])
result.append(s)
if root.left:
self.traval(root.left,path,result)
path.pop()
if root.right:
self.traval(root.right,path,result)
path.pop()上面就是本道题的解法,值得注意的几个地方有,1.中间过程应当写到判断结束的前面,并且要对左右节点是否为空进行判断;2.输出时,注意结尾是没有->的。所以我们要单独拿出来处理。
这道题用到了回溯的思想,后面几道题同理。
2.路径总和
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点 的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
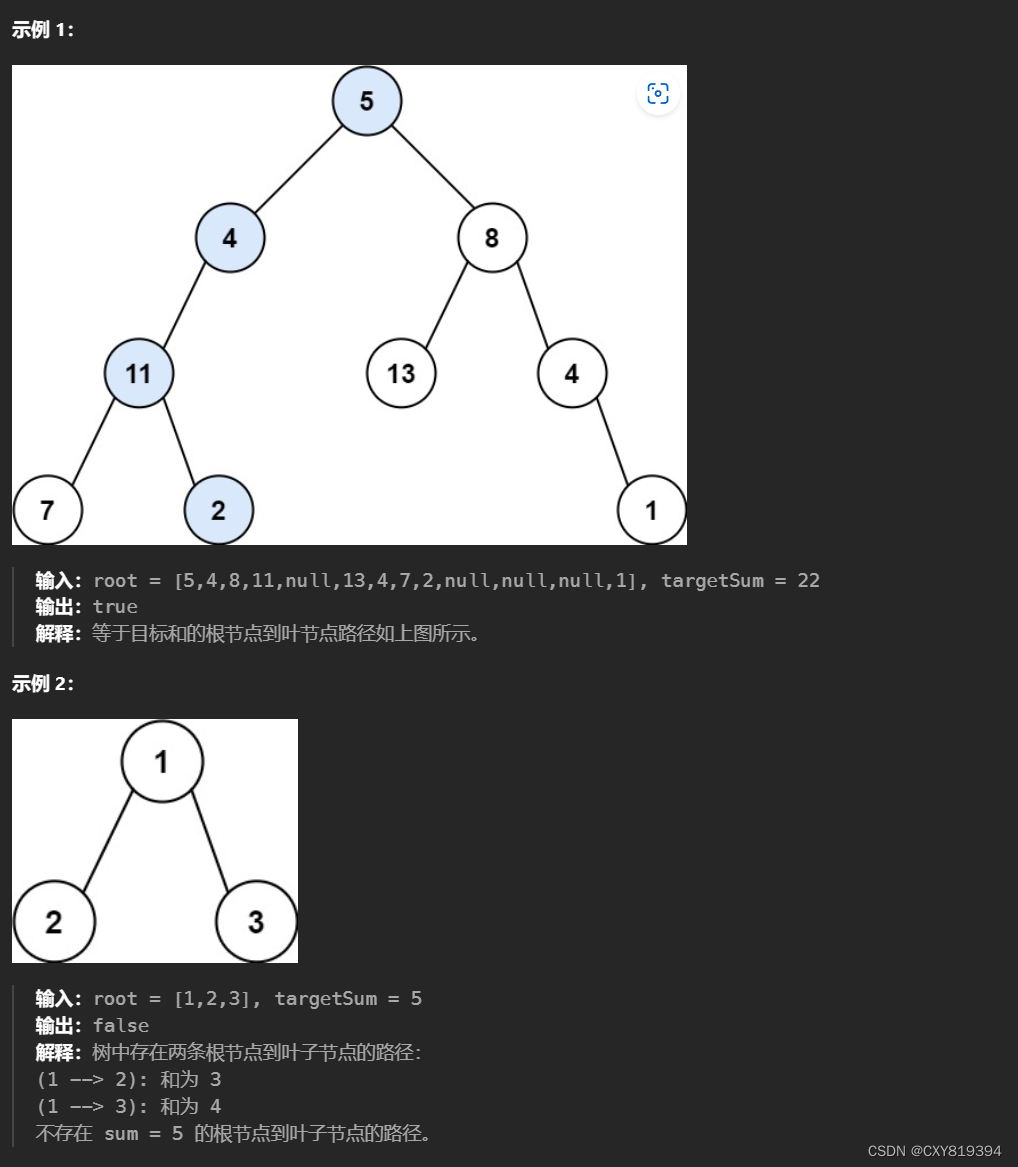
做完第一道题之后,我们的第一想法是:直接把所有路径列表存放在结果里,然后进行暴力搜索。我们先来看看这样的写法:
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, targetSum):
path = []
result = []
if not root:
return False
self.traval(root,path,result)
# 暴力判断
for path in result:
if sum(path) == targetSum:
return True
return False
def traval(self, cur, path,result):
path.append(cur.val)
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
# 这里注意是添加list(path)否则会报错,因为添加的path会动态变化
result.append(list(path))
if cur.left:
self.traval(cur.left,path,result)
path.pop()
if cur.right:
self.traval(cur.right,path,result)
path.pop()我们是否可以将判断纳入搜索的过程中呢,这样会更加'优雅'
我们可以设定一个count,让其等于目标值,当其遍历到某一节点时,就减去该节点,如果遍历到叶子节点,能够出现count == 0 的情况,就证明有路径能够满足目标和。
在这个过程中回溯由count来体现
(1)确定输入和输出值
输出值为bool类型
(2)确定终止条件:
当遍历到叶子节点且count==0就表明找到了目标路径
if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0:
return True
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
return False(3)确定中间过程
中间过程同1 ,但不一样的地方是回溯用count来体现,但是当返回值为True时,也就是找到路径时,就可以不用再接着遍历了,直接return True即可
if cur.left:
count -= cur.left.val
if self.traval(cur.left,count):
return True
count += cur.left.val
if cur.right:
count -= cur.right.val
if self.traval(cur.left,count):
return True
count += cur.left.val(4)汇总
最后我们将代码整合:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, targetSum):
"""
检查树中是否存在根到叶的路径,其节点值之和等于targetSum。
:type root: TreeNode
:type targetSum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return False
# 调用traval函数开始递归检查
return self.traval(root, targetSum - root.val)
def traval(self, cur, count):
"""
递归函数,用于遍历树并检查路径和。
:type cur: TreeNode
:type count: int
:rtype: bool
"""
# 到达叶节点,且计数为0,表示找到了符合条件的路径
if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0:
return True
# 到达叶节点但计数不为0,返回False
if not cur.left and not cur.right:
return False
# 递归遍历左子树
if cur.left:
# 更新计数并递归调用
count -= cur.left.val
if self.traval(cur.left, count):
return True
# 回溯时恢复计数
count += cur.left.val
# 递归遍历右子树
if cur.right:
# 更新计数并递归调用
count -= cur.right.val
if self.traval(cur.right, count):
return True
# 回溯时恢复计数
count += cur.right.val
return False3.路径总和II
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
不难看出这道题是前两道题的结合,万变不离其宗,我们还是用前序递归加回溯来解决,只不过回溯的逻辑稍显复杂。
(1)确定输入和输出:
输入为root 输出为二维列表
(2)确定递归终止条件
递归终止的条件是遍历到叶子节点,或者遍历到叶子节点的同时找到对应路径
if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0:
result.append(list(path))
return
if not cur.left and not cur.right and count == 0:
return(3) 确定中间过程
值得注意的是,中间处理过程写到了两个分支中,对于root根节点的处理,我们写到了主函数中。
if root.left:
path.append(root.left.val)
count -= root.left.val
self.traval(root.left,path,result,count)
count += root.left.val
path.pop()
if root.right;
path.append(root.right.val)
count -= root.right.val
self.traval(root.right,path,result,count)
count += root.right.val
path.pop()(4)汇总
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode(object):
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution(object):
def pathSum(self, root, targetSum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type targetSum: int
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
if not root:
return []
path = [root.val,]
result = []
self.traval(root,path,result,targetSum-root.val)
return result
def traval(self,root,path,result,count):
if root.left is None and root.right is None and count == 0:
result.append(list(path))
return
if not root.left and not root.right:
return
if root.left:
path.append(root.left.val)
count -= root.left.val
self.traval(root.left,path,result,count)
count += root.left.val
path.pop()
if root.right:
path.append(root.right.val)
count -= root.right.val
self.traval(root.right,path,result,count)
count += root.right.val
path.pop()以上就是二叉树的学习记录,学习重在总结和坚持。共勉。























 167
167











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








