JAVA代码编写
491. 递增子序列
给你一个整数数组 nums ,找出并返回所有该数组中不同的递增子序列,递增子序列中 至少有两个元素 。你可以按 任意顺序 返回答案。
数组中可能含有重复元素,如出现两个整数相等,也可以视作递增序列的一种特殊情况。
示例 1:
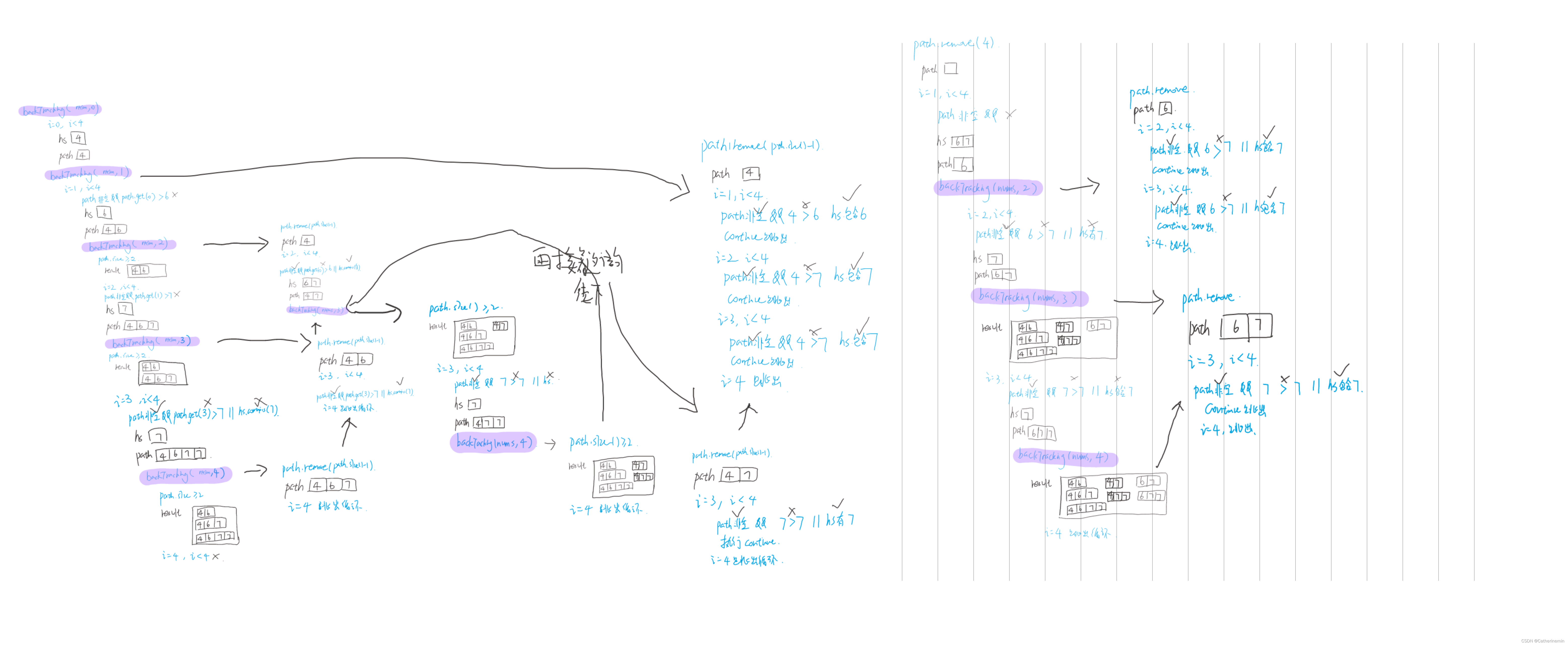
输入:nums = [4,6,7,7]
输出:[[4,6],[4,6,7],[4,6,7,7],[4,7],[4,7,7],[6,7],[6,7,7],[7,7]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [4,4,3,2,1]
输出:[[4,4]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 15-100 <= nums[i] <= 100
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0491.%E9%80%92%E5%A2%9E%E5%AD%90%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97.html
方法一:回溯
思路:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>(); // 结果
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();// 记录路径
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
backTracking(nums, 0);
return result;
}
private void backTracking(int[] nums, int startIndex){
if(path.size() >= 2)
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){
if(!path.isEmpty() && path.get(path.size() -1 ) > nums[i] || hs.contains(nums[i]))
continue;
hs.add(nums[i]);
path.add(nums[i]);
backTracking(nums, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.findSubsequences(new int[] {4,6,7,7});
}
}
46. 全排列
给定一个不含重复数字的数组 nums ,返回其 所有可能的全排列 。你可以 按任意顺序 返回答案。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,2,3]
输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]
示例 2:
输入:nums = [0,1]
输出:[[0,1],[1,0]]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1]
输出:[[1]]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 6-10 <= nums[i] <= 10nums中的所有整数 互不相同
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0046.%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97.html
方法一:回溯
思路:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();// 存放符合条件结果的集合
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();// 用来存放符合条件结果
boolean[] used;
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0){
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
permuteHelper(nums);
return result;
}
private void permuteHelper(int[] nums){
if (path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if (used[i]){
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
permuteHelper(nums);
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.permute(new int[] {1,2,3});
}
}
47. 全排列II
-
给定一个可包含重复数字的序列
nums,按任意顺序 返回所有不重复的全排列。示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,1,2] 输出: [[1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1]]示例 2:
输入:nums = [1,2,3] 输出:[[1,2,3],[1,3,2],[2,1,3],[2,3,1],[3,1,2],[3,2,1]]提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 8-10 <= nums[i] <= 10
教程:https://programmercarl.com/0047.%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97II.html
方法一:回溯
思路:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
class Solution {
//存放结果
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
//暂存结果
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
boolean[] used = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(used, false);
Arrays.sort(nums);
backTrack(nums, used);
return result;
}
private void backTrack(int[] nums, boolean[] used) {
if (path.size() == nums.length) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
// used[i - 1] == true,说明同⼀树⽀nums[i - 1]使⽤过
// used[i - 1] == false,说明同⼀树层nums[i - 1]使⽤过
// 如果同⼀树层nums[i - 1]使⽤过则直接跳过
if (i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) {
continue;
}
//如果同⼀树⽀nums[i]没使⽤过开始处理
if (used[i] == false) {
used[i] = true;//标记同⼀树⽀nums[i]使⽤过,防止同一树枝重复使用
path.add(nums[i]);
backTrack(nums, used);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);//回溯,说明同⼀树层nums[i]使⽤过,防止下一树层重复
used[i] = false;//回溯
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Solution solution = new Solution();
solution.permuteUnique(new int[] {1,2,3});
}
}


























 363
363

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










