几乎所有的iOS app都至少使用了一些UIKit框架定义的UI部件。了解这些基础部件的名字、角色和功能可以帮助你明智地决定你的app的UI设计。
这些UIKit提供的UI元素大概分成四个种类:
- Bars。Bars包含可以告诉用户他们在哪的上下文信息和帮助用户导航或发起动作的控制装置。
- Content Views。Content Views包含app的详细内容,并且可以使用滚动、插入、删除和元件重布局的行为。
- Controls。Controls执行动作或者展示信息。
- Temporary views。Temporary views短暂地出现来给用户重要的信息或者额外的选项和功能。
除了定义UI元素以外,UIKit还定义实施功能的对象,比如手势识别、绘图、可及性和印刷支持。
从编程上来说,一个UI元素是一类视图(view),因为它继承自UIView。一个视图知道怎么在屏幕上绘制它自己,也知道用户在它的边界内触摸了它。控制器(比如按钮和滑动条)、内容视图(比如集合视图和表视图)和临时视图(比如警告框和选取器)都是视图的一种。
为了管理你app中的一系列视图,你最好使用视图控制器(View Controller)。视图控制器可以协调视图的显示,执行用户交互下的功能,还可以管理从一个到另一个屏幕的过渡。比如说,“设置”使用了一个导航控制器来显示他的一系列视图。
这个例子展示了视图和视图控制器是如何结合着呈现一个iOS app的UI的。
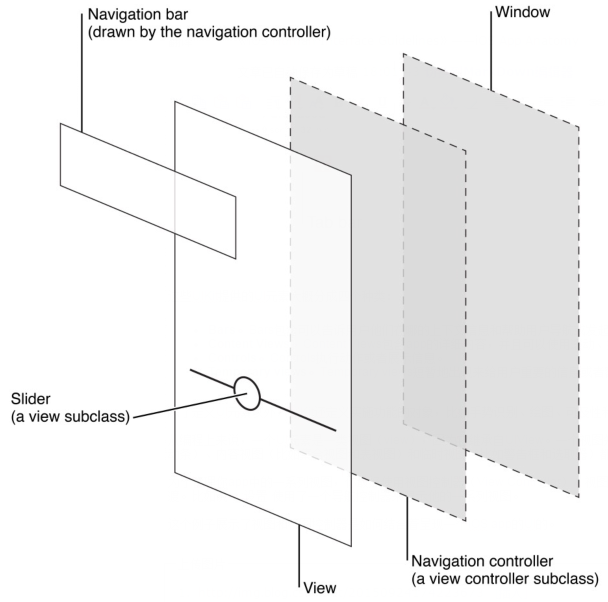
虽然开发者认为按照视图和视图控制器,用户趋于将一个iOS app当成一堆屏幕的集合去体验。从这个透视图看,一个屏幕(screen)广泛地符合一个app中清晰的视觉层次或者模型。
NOTE
一个iOS app包含一个window。但是——不同于PC端应用的window——一个iOS window没有可见的部分,并且它不能移动到其他的位置。大部分的iOS app只包含一个window;支持额外的显示屏的app可以有多个window。
在《iOS Human Interface Guidelines》中,单词screen是大多数用户所理解的意思。作为一个开发者,你也许会在其他地方读到screen,比如UIScreen中的对象术语,你可以用其连接一个额外的显示屏。
翻译自
苹果开发文档

























 439
439

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








