本文没有使用现有的框架,仅使用最原始的代码创建神经网络实现对sin函数的学习。
1.导入相关库
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt2.准备输入数据和正确答案数据(对应的label)
input_data = np.arange(0, np.pi*2, 0.1) #输入
correct_data = np.sin(input_data) #对应的label
input_data = (input_data-np.pi)/np.pi #将输入收敛到-1.0~1.0的范围之内
n_data = len(correct_data) #数据数量3.各个设定值
n_in = 1 #输入层的神经元数量
n_mid = 3 #中间层的神经元数量
n_out = 1 #输出层的神经元数量
wb_width = 0.01 #权重和偏置的扩散程度
eta = 0.1 #学习系数
epoch = 2001 #迭代次数
interval = 200 #显示进度的间隔实践4.中间层
class MiddleLayer:
def __init__(self, n_upper, n): #初始化设置
self.w = wb_width * np.random.randn(n_upper, n) #权重(矩阵)
self.b = wb_width * np.random.randn(n) #偏置(向量)
def forward(self, x): #正向传播
self.x = x
u = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b
self.y = 1/(1 + np.exp(-u)) #sigmoid函数
def backward(self, grad_y):
delta = grad_y * (1 - self.y) * self.y #sigmoid函数的微分
self.grad_w = np.dot(self.x.T, delta)
self.grad_b = np.sum(delta, axis = 0)
self.grad_x = np.dot(delta, self.w.T)
def update(self, delta): #权重和偏置的更新
self.w -= eta * self.grad_w
self.b -= eta * self.grad_b5.输出层
class OutputLayer:
def __init__(self, n_upper, n): #初始化设置
self.w = wb_width * np.random.randn(n_upper, n) #权重(矩阵)
self.b = wb_width * np.random.randn(n) #偏置(向量)
def forward(self, x): #正向传播
self.x = x
u = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b
self.y = u #恒等函数
def backward(self, t): #反向传播
delta = self.y - t
self.grad_w = np.dot(self.x.T, delta)
self.grad_b = np.sum(delta, axis = 0)
self.grad_x = np.dot(delta, self.w.T)
def update(self, delta): #权重和偏置的更新
self.w -= eta * self.grad_w
self.b -= eta * self.grad_b6.各个网络层的初始化
middle_layer = MiddleLayer(n_in, n_mid)
output_layer = OutputLayer(n_mid, n_out)7.神经网络学习
for i in range(epoch):
#随机打乱索引值
index_random = np.arange(n_data)
np.random.shuffle(index_random)
#用于结果的显示
total_error = 0
plot_x = []
plot_y = []
for idx in index_random:
x = input_data[idx:idx+1]
t = correct_data[idx:idx+1]
#正向传播
middle_layer.forward(x.reshape(1,1)) #将输入转换为矩阵
output_layer.forward(middle_layer.y)
#反向传播
output_layer.backward(t.reshape(1,1)) #将正确答案转为矩阵
middle_layer.backward(output_layer.grad_x)
#权重和偏置的更新
middle_layer.update(eta)
output_layer.update(eta)
if i%interval == 0:
y = output_layer.y.reshape(-1)
#误差的计算
total_error += 1.0/2.0 * np.sum(np.square(y-t)) #平方和误差
plot_x.append(x)
plot_y.append(y)
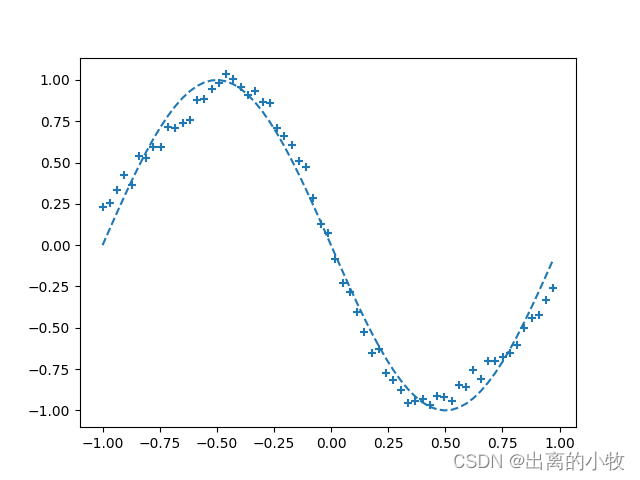
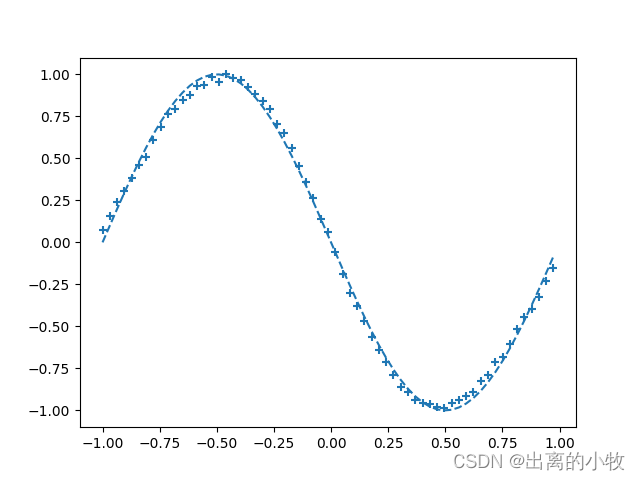
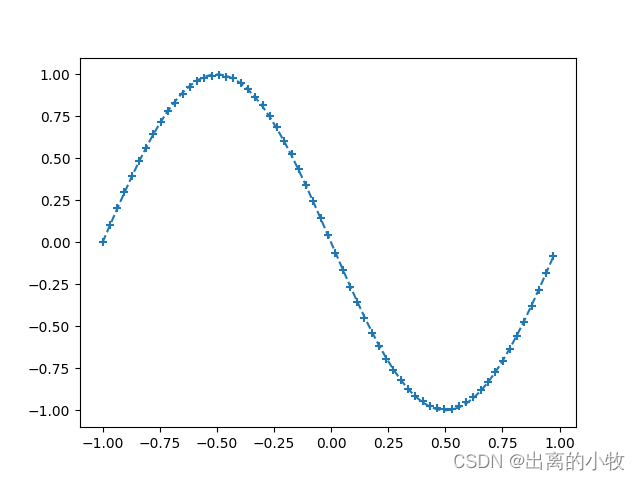
if i%interval == 0:
plt.plot(input_data, correct_data, linestyle = "dashed")
plt.scatter(plot_x, plot_y, marker = "+")
plt.show()
print("Epoch:" + str(i) + "/" + str(epoch),
"Error:" + str(total_error/n_data))完整代码:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
input_data = np.arange(0, np.pi*2, 0.1) #输入
correct_data = np.sin(input_data) #对应的label
input_data = (input_data-np.pi)/np.pi #将输入收敛到-1.0~1.0的范围之内
n_data = len(correct_data) #数据数量
n_in = 1 #输入层的神经元数量
n_mid = 3 #中间层的神经元数量
n_out = 1 #输出层的神经元数量
wb_width = 0.01 #权重和偏置的扩散程度
eta = 0.1 #学习系数
epoch = 2001 #迭代次数
interval = 200 #显示进度的间隔实践
class MiddleLayer:
def __init__(self, n_upper, n): # 初始化设置
self.w = wb_width * np.random.randn(n_upper, n) # 权重(矩阵)
self.b = wb_width * np.random.randn(n) # 偏置(向量)
def forward(self, x): # 正向传播
self.x = x
u = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b
self.y = 1 / (1 + np.exp(-u)) # sigmoid函数
def backward(self, grad_y):
delta = grad_y * (1 - self.y) * self.y # sigmoid函数的微分
self.grad_w = np.dot(self.x.T, delta)
self.grad_b = np.sum(delta, axis=0)
self.grad_x = np.dot(delta, self.w.T)
def update(self, delta): # 权重和偏置的更新
self.w -= eta * self.grad_w
self.b -= eta * self.grad_b
class OutputLayer:
def __init__(self, n_upper, n): # 初始化设置
self.w = wb_width * np.random.randn(n_upper, n) # 权重(矩阵)
self.b = wb_width * np.random.randn(n) # 偏置(向量)
def forward(self, x): # 正向传播
self.x = x
u = np.dot(x, self.w) + self.b
self.y = u # 恒等函数
def backward(self, t): # 反向传播
delta = self.y - t
self.grad_w = np.dot(self.x.T, delta)
self.grad_b = np.sum(delta, axis=0)
self.grad_x = np.dot(delta, self.w.T)
def update(self, delta): # 权重和偏置的更新
self.w -= eta * self.grad_w
self.b -= eta * self.grad_b
middle_layer = MiddleLayer(n_in, n_mid)
output_layer = OutputLayer(n_mid, n_out)
for i in range(epoch):
# 随机打乱索引值
index_random = np.arange(n_data)
np.random.shuffle(index_random)
# 用于结果的显示
total_error = 0
plot_x = []
plot_y = []
for idx in index_random:
x = input_data[idx:idx + 1]
t = correct_data[idx:idx + 1]
# 正向传播
middle_layer.forward(x.reshape(1, 1)) # 将输入转换为矩阵
output_layer.forward(middle_layer.y)
# 反向传播
output_layer.backward(t.reshape(1, 1)) # 将正确答案转为矩阵
middle_layer.backward(output_layer.grad_x)
# 权重和偏置的更新
middle_layer.update(eta)
output_layer.update(eta)
if i%interval == 0:
y = output_layer.y.reshape(-1)
# 误差的计算
total_error += 1.0 / 2.0 * np.sum(np.square(y - t)) # 平方和误差
plot_x.append(x)
plot_y.append(y)
if i%interval == 0:
plt.plot(input_data, correct_data, linestyle="dashed")
plt.scatter(plot_x, plot_y, marker="+")
plt.show()
print("Epoch:" + str(i) + "/" + str(epoch),
"Error:" + str(total_error / n_data))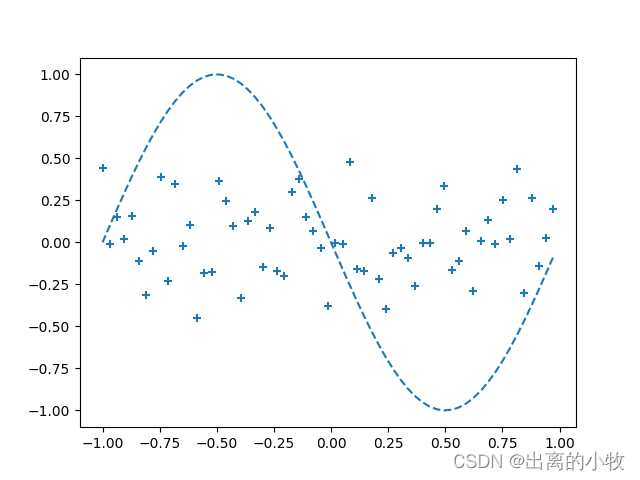























 345
345











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








