01 前言
因为受到疫情影响在家学习效率底下(就是自己懒+菜),估计蓝桥杯做慈善了,也临时抱下佛脚
02 STL初识
2.1 STL的诞生
C++的面向对象的泛型编程思想,目的就是复用性提升,大多情况下,数据结构和算法都未能有一套标准,导致被迫从事大量的重复工作,为了建立数据结构和算法的一套标准,诞生了STL
2.2 STL的基本概念
- STL(Standard Template Library)标准模板库
- STL广义上分为:容器(container)算法(algorithm)迭代器(iterator)
- 容器和算法之间通过迭代器进行无缝连接
- STL几乎所有的代码都采用了模板类或者模板函数
2.3 STL六大组件
STL答题分六大组件,分别是:容器、算法、迭代器、仿函数、适配器(配接器)、空间配置器
1、容器:各种数据结构,如vector、list、deque、set、map等,用来存放数据
2、算法:各种常用算法,如sort、find、copy、for_each等
3、迭代器:扮演了容器与算法之间的胶合剂
4、仿函数:行为类似函数,可作为算法的某种策略
5、适配器:一种用来修饰容器或者仿函数或迭代器接口的东西
6、空间适配器:负责空间的配置与管理
2.4 STL中容器、算法、迭代器
2.4.1 容器
STL容器就是将运用广泛的一些数据结构实现出来,常用的数据结构:数组, 链表,树, 栈, 队列, 集合, 映射表 等
容器分为序列式容器和关联式容器
序列式容器:强调值的排序,序列式容器中的每个元素均有固定的位置
关联式容器:二叉树结构,各元素之间没有 严格的物理上的顺序关系
2.4.2 算法
有限的步骤,解决逻辑或数学上的问题,这一门学科我们叫做算法(Algorithms)
算法分为质变算法和非质变算法
质变算法:是指运算过程中会更改区间内的元素的内容。例如拷贝,替换,删除等等
非质变算法:是指运算过程中不会更改区间内的元素内容,例如查找、计数、遍历、寻找极值等等
2.4.3 迭代器
提供一种方法,使之能够依序寻访某个容器所含的各个元素,而又无需暴露该容器的内部表示方式
每个容器都有自己专属的迭代器
迭代器使用非常类似于指针,初学阶段我们可以先理解迭代器为指针
迭代器种类:
- 输入迭代器 功能:对数据的只读访问 支持运算:只读,支持++、==、!=
- 输出迭代器 功能:对数据的只写访问 支持运算:只写,支持++
- 前量迭代器 功能:读写操作,并能向前推进迭代器 支持运算:读写,支持++、==、!=
- 双向迭代器 功能:读写操作,并能向前和向后操作 支持运算:读写,支持++、–
- 随机访问迭代器 功能:读写操作,可以以跳跃的方式访问任意数据,功能强的迭代器 支持运算:读写,支持++、–、[n]、-n、<、<=、>、>=
常用的容器中迭代器种类为双向迭代器,和随机访问迭代器
2.5 容器算法迭代器初识
2.5.1 vector存放内置数据类型
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void print(int val)
{
cout << val << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> vec;
vec.push_back(10);
vec.push_back(20);
vec.push_back(30);
vector<int>::iterator pBegin = vec.begin(); // begin()读取第一位
vector<int>::iterator pEnd = vec.end(); // end()读取最后一位的下一位
// 利用while循环遍历输出
while (pBegin != pEnd)
{
cout << *pBegin << endl;
pBegin++;
}
// 利用for循环遍历输出
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
//利用for_each算法遍历输出
for_each(vec.begin(), vec.end(), print);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
vector<int> xx创建int类型名为xx的vector容器.push_bach(xx)将xx存放进容器中vector<int>::iteratorvector<int>类型的迭代器,可以暂时理解为指针,它作用下的变量需要通过*号来访问内容for_each(vector<...>::iterator _First, vector<...>::iterator _Last, void(*_Func)(int val))是algorithm中的遍历算法
2.5.2 Vector存放自定义的数据类型
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
void set_Person(string name, int age)
{
this->name = name;
this->age = age;
}
string name;
int age;
};
void Print(string key, int vule)
{
cout << key << " " << vule << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<Person> vec;
Person p1;
p1.set_Person("aaa", 10);
Person p2;
p2.set_Person("bbb", 20);
Person p3;
p3.set_Person("ccc", 30);
Person p4;
p4.set_Person("ddd", 40);
vec.push_back(p1);
vec.push_back(p2);
vec.push_back(p3);
vec.push_back(p4);
vector<Person>::iterator pBegin = vec.begin();
vector<Person>::iterator pEnd = vec.end();
while (pBegin != pEnd)
{
cout << pBegin->name << " " << pBegin->age << endl;
pBegin++;
}
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); it++)
{
cout << it->name << " " << it->age << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
vector<Person*> vec2;
Person q1;
q1.set_Person("aaa", 10);
Person q2;
q2.set_Person("bbb", 20);
vec2.push_back(&q1);
vec2.push_back(&q2);
for (vector<Person*>::iterator it = vec2.begin(); it != vec2.end(); it++)
{
cout << q1.name << q1.age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
这里我们定义了一个自己定义的Person类
2.5.3 Vector容器嵌套容器
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<vector<int>>v;
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
vector<int> v3;
for (int i = 1; i <= 4; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i + 1);
v2.push_back(i + 2);
v3.push_back(i + 3);
}
v.push_back(v1);
v.push_back(v2);
v.push_back(v3);
for (vector<vector<int>>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator vit = (*it).begin(); vit != (*it).end(); vit++)
{
cout << *vit << " " << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
这里我们再vector中嵌套了一个vector<int>,相当于一个二维数组,就是存储容器的容器
再遍历这个容器时,我们需要先遍历存储容器的容器,然后嵌套一个for循环来遍历存储int类型的容器
03 STL-常用容器
3.1 string容器
3.1.1 string基本概念
本质:
- string时C++风格的字符串,而string本质上是一个类
string和char的区别:
char*是一个指针string是一个类,类内部封装了char*,管理这个字符串,是一个char*型的容器
特点:
string类内部封装了很多成员方法
例如:查找find,拷贝copy,删除delate,替换replace,插入insertstring管理char*所分配的内存,不用担心复制越界和取值越界等,由类内部进行复制
3.1.2 string构造函数
构造函数原型:
string()创建一个空字符串,例如string str,string str(const char *str)string(const char *str)使用字符串str初始化string(const string& str)使用一个string对象初始化另一个string对象,拷贝字符串string(int n, char c)使用n个字符c初始化
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
string s1; // 无参构造
string s2(str);
const char* str = "hello world";
string s3(s2);
string s4(10, 'a');
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.1.3 string赋值操作
功能描述:
- 给string字符串进行赋值
赋值的函数原型:
string& operator=(const char* s)char*类型字符串 赋值给当前的字符串string& operator=(const string &s)把字符串s赋给当前的字符串string& operator=(char c)字符赋值给当前的字符串string& assign(const char *s)把字符串s赋给当前的字符串string& assign(const char *s, int n)把字符串s的前n个字符赋给当前的字符串string& assign(const string &s)把字符串s赋给当前字符串string& assign(int n, char c)用n个字符c赋给当前字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
string str1 = "hello world";
string str2 = str1;
string str3 = "w";
string str4;
str4.assign("hello C++");
string str5;
str5.assign(str4, 5);
string str6;
str6.assign(str5);
string str7;
str7.assign(10, 'w');
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
cout << "str2 = " << str2 << endl;
cout << "str3 = " << str3 << endl;
cout << "str4 = " << str4 << endl;
cout << "str5 = " << str5 << endl;
cout << "str6 = " << str6 << endl;
cout << "str7 = " << str7 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
str1 = hello world
str2 = hello world
str3 = w
str4 = hello C++
str5 = C++
str6 = C++
str7 = wwwwwwwwww
3.1.4 string字符串拼接
string& operator+=(const char* str)重载+=操作符string& operator+=(const char c)重载+=操作符string& operator+=(const string& str)重载+=操作符string& append(const char *s)把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾string& append(const char *s, int n)把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾string& append(const string &s)同operator+=(const string& str)string& append(const string &s, int pos, int n)字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
//string& operator+=(const char* str) 重载+=操作符
string str1 = "I";
str1 += " Love";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//string& operator+=(const char c) 重载+=操作符
str1 += " ";
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//string& operator+=(const string& str) 重载+=操作符
string str2 = "study";
str1 += str2;
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//string& append(const char *s) 把字符串s连接到当前字符串结尾
string str3 = ", but ";
str1.append(str3);
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//string& append(const char* s, int n) 把字符串s的前n个字符连接到当前字符串结尾
str1.append("I don't abcde", 7);
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//string& append(const string &s) 同operator+=(const string& str)
string str4 = " like";
str1.append(str4);
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
//string& append(const string &s, int pos, int n) 字符串s中从pos开始的n个字符连接到字符串结尾
str1.append(" playing talking", 0, 8);
cout << "str1 = " << str1 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.1.5 string查找和替换
功能描述:
- 查找:查找指定字符串是否存在
- 替换:在指定的位置替换字符串
函数原型:
int find(const string& str, int pos = 0) const查找str第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int find(const char* s, int pos = 0) const查找s第一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int find(const char* s, int pos, int n) const从pos位置查找s的前n个字符第一次位置int find(const char c, int pos = 0) const查找字符c第一次出现位置int rfind(const string& str, int pos = npos) const查找str最后一次位置,从pos开始查找int rfind(const char* s, int pos = npos) const查找s最后一次出现位置,从pos开始查找int rfind(const char* s, int pos, int n) const从pos查找s的前n个字符最后一次位置int rfind(const char c, int pos = 0) const查找字符c最后一次出现位置string& replace(int pos, int n, const string& str)替换从pos开始n个字符为字符串strstring& replace(int pos, int n,const char* s)替换从pos开始的n个字符为字符串s
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void Find()
{
string str1 = "abcdefgde";
int pos = str1.find("de");
cout << "pos = " << pos << endl;
int rpos = str1.rfind("de"); // find从左往右查找,rfind从右往左查找,返回int类型的数字
cout << "rpos = " << rpos << endl;
}
void replace()
{
string str = "abcdefg";
str.replace(2, 2, "1111"); // 从序列号2开始,往后的2个字符替换成1111字符,后面的序列号会自动往后倒
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
Find();
replace();
return 0;
}
find从左往右查找,rfind从右往左查找,返回int类型的数字,查找不到会返回-1
**注意:**查找不到会返回-1
3.1.6 string字符串比较
功能描述:
- 字符串之间的比较
比较方式:
字符串比较是按字符的ASCII码进行对比
=返回 0>返回 1<返回 -1
函数原型:
int compare(const string &s) const与字符串s比较int compare(const char *s) const与字符串s比较
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
string str1 = "hello";
string str2 = "hello";
string str3 = "s";
string str4 = "a";
int a = str1.compare(str2);
int b = str3.compare(str4);
int c = str4.compare(str3);
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
cout << "c = " << c << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
a = 0
b = 1
c = -1
3.1.7 string字符存取
string中单个字符存取方式有两种
char& operator[](int n)通过[]方式取字符char& at(int n)通过at方法获取字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)
{
cout << str.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
str[0] = 'x';
str.at(1) = 'x';
cout << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
h e l l o
h e l l o
xxllo
3.1.8 string插入和删除
功能描述:
- 对string字符串进行插入和删除字符操作
函数原型:
string& insert(int pos, const char* s)插入字符串string& insert(int pos, int n, char c)在指定位置插入n个字符cstring& erase(int pos, int n = npos)删除从Pos开始的n个字符
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
str.insert(1, "222");
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
str.erase(1, 3);
cout << "str = " << str << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
str = h222ello
str = hello
3.1.9 string字串
功能描述:
- 从字符串中获取想要的子串
函数原型:
string substr(int pos = 0, int n = npos) const返回由pos开始的n个字符组成的字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
string str = "hello";
string subStr = str.substr(1, 3);
cout << "subStr = " << subStr << endl;
}
void test02()
{
cout << "请输入您的邮箱:";
string email;
cin >> email;
int pos = email.find("@");
cout << "欢迎您 " << email.substr(0, pos) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
3.2 vector容器
3.2.1 vector基本概念
功能:
- vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组
vector与普通数组的区别:
- 不同之处在于数组是静态空间,而vector可以动态扩展
动态扩展:
- 并不是在原空间之后续接新空间,而是找更大的内存空间,然后将原数据拷贝新空间,释放原空间

- vector容器的迭代器是支持随机访问的迭代器
3.2.2 vector构造函数
功能描述:
- 创建vector容器
函数原型:
vector<T> v采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数vector(v.begin(), v.end())将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身vector(n, elem)构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身vector(const vector &vec)拷贝构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int> vec)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//vector(v.begin(), v.end()) 将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身
vector<int>v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v2);
//vector(n, elem) 构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身
vector<int>v3(10, 111);
printVector(v3);
//vector(const vector & vec) 拷贝构造函数
vector<int>v4(v3);
printVector(v4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.2.3 vector赋值操作
功能描述:
- 给vector容器进行赋值
函数原型:
vector& operator=(const vector &vec)重载等号操作符assign(beg, end)将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身assign(n, elem)将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//vector& operator=(const vector & vec) 重载等号操作符
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//assign(beg, end) 将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身
vector<int>v2;
v2.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v2);
//assign(n, elem) 将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身
vector<int>v3;
v3.assign(10, 121);
printVector(v3);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.2.4 vector容器和大小
功能描述:
- 对vector容器的容量和大小操作
函数原型:
empty()判断容器是否为空,为空则返回True,不为空则返回Falsecapacity()容器的容量size()返回容器中元素的个数resize(int num)重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除resize(int num, elem)重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//empty() 判断容器是否为空,若不为空则返回false,为空则返回true
if (v1.empty())
{
cout << "v1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "v1不为空" << endl;
}
///capacity() 容器的容量
cout << v1.capacity() << endl;
//size() 返回容器中元素的个数
cout << v1.size() << endl;
//resize(int num) 重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值0填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
v1.resize(15);
cout << v1.size() << endl;
printVector(v1);
v1.resize(5);
printVector(v1);
//resize(int num, elem) 重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
v1.resize(15, 8);
printVector(v1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
v1不为空
13
10
15
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 4
0 1 2 3 4 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8 8
3.2.5 vector插入和删除
功能描述:
- 对vector容器进行插入、删除操作
函数原型:
push_back(ele)尾部插入元素elepop_back()删除最后一个元素insert(const_iterator pos, ele)迭代器指向位置pos插入元素eleinsert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele)迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素eleerase(const_iterator pos)删除迭代器指向的元素erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end)删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素clear()删除容器中所有元素
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
//push_back(ele) 尾部插入元素ele
v1.push_back(10);
v1.push_back(20);
v1.push_back(30);
v1.push_back(40);
printVector(v1);
//pop_back() 删除最后一个元素
v1.pop_back();
printVector(v1);
//insert(const_iterator pos, ele) 迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 888);
printVector(v1);
//insert(const_iterator pos, int count,ele) 迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
v1.insert(v1.end(), 6, 6);
printVector(v1);
//erase(const_iterator pos) 删除迭代器指向的元素
v1.erase(v1.begin());
printVector(v1);
//erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end) 删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素
v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end());
if (v1.empty())
{
cout << "v1已为空" << endl;
}
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 6, 10);
printVector(v1);
//clear() 删除容器中所有元素
v1.clear();
if (v1.empty())
{
cout << "v1已为空" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
10 20 30 40
10 20 30
888 10 20 30
888 10 20 30 6 6 6 6 6 6
10 20 30 6 6 6 6 6 6
v1已为空
10 10 10 10 10 10
v1已为空
3.2.6 vector数据存储
功能描述:
- 对vector中的数据的存取操作
函数原型:
at(int idx)返回索引idx所指的数据operator[]返回索引idx所指的数据front()返回容器中第一个数据元素back()返回容器中最后一个数据元素
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
//at(int idx) 返回索引idx所指的数据
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//operator[] 返回索引idx所指的数据
for (int i = 0; i < v1.size(); i++)
{
cout << v1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//front() 返回容器中第一个数据元素
cout << v1.front() << endl;
//back() 返回容器中最后一个数据元素
cout << v1.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0
9
3.2.7 vector互换容器
功能描述:
- 实现两个容器内元素进行互换
函数原型:
swap(vec)将vec与本身的元素互换
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int>& v)
{
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>v2;
for (int i = 9; i >= 0; i--)
{
v2.push_back(i);
}
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printVector(v1);
printVector(v2);
v1.swap(v2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
printVector(v1);
printVector(v2);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
交换前:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
交换后:
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
swap()通常用于所见空间
void test02()
{
vector<int>v3;
for (int i = 1; i <= 10000; i++)
{
v3.push_back(i);
}
cout << "v3的容量:" << v3.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v3的大小:" << v3.size() << endl;
v3.resize(3);
cout << "v3的容量:" << v3.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v3的大小:" << v3.size() << endl;
vector<int>(v3).swap(v3);
cout << "v3的容量:" << v3.capacity() << endl;
cout << "v3的大小:" << v3.size() << endl;
}
在resize大小缩小一后,它的空间是不会变小的,还是那么大,那么就会浪费很多空间,所以我们很有必要申请一个匿名空间
vector<int>(v).swap(v)用于缩小空间
out:
v3的容量:12138
v3的大小:10000
v3的容量:12138
v3的大小:3
v3的容量:3
v3的大小:3
3.2.8 vector预留空间
功能描述:
- 减少vector在动态扩展容量时的扩展次数
函数原型:
reserve(int len)容器预留len个元素长度,预留位置不初始化,元素不可访问
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
int* p = NULL;
int num = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
if (p != &v1[0])
{
p = &v1[0];
num++;
}
}
cout << "v1拓展的次数" << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
v1拓展的次数30
这里我们可以看出v3存储十万个数字,拓展了30次的空间,当我们事先知道需要那么多空间,为此预留空间时:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int>v1;
int* p = NULL;
int num = 0;
v1.reserve(100000);
for (int i = 1; i <= 100000; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
if (p != &v1[0])
{
p = &v1[0];
num++;
}
}
cout << "v1拓展的次数" << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
当我们用v1.reserve(100000)事先预留那么多空间时,我们拓展的次数就是一次了
out:
v1拓展的次数1
但是我觉得这样就没有使用vector容器的意义了,还不如用数组
3.3 depue容器
3.3.1 depue容器基本概念
功能:
- 双端数组,可以对头端进行插入删除操作
deque与vector区别:
vector对于头部的插入删除效率低,数据量越大,效率越低deque相对而言,对头部的插入删除速度会比vector快vector访问元素时的速度会比deque快,这和两者内部实现有关
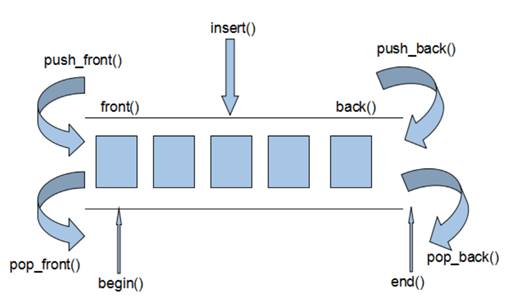
deque内部工作原理:
deque内部有个中控器,维护每段缓冲区中的内容,缓冲区中存放真实数据- 中控器维护的是每个缓冲区的地址,使得使用
deque时像一片连续的内存空间

deque容器的迭代器也是支持随机访问的
3.3.2 deque构造函数
功能描述:
deque容器构造
函数原型:
deque<T> deqT默认构造形式deque(beg, end)构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身。deque(n, elem)构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。deque(const deque &deq)拷贝构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int> d1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeque(d1);
deque<int> d2(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeque(d2);
deque<int> d3(10, 121);
printDeque(d3);
deque<int> d4(d3);
printDeque(d4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.3.3 赋值操作
功能描述:
- 给deque容器进行赋值
函数原型:
deque& operator=(const deque &deq)重载等号操作符assign(beg, end)将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。assign(n, elem)将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
deque<int> d1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeque(d1);
//deque& operator=(const deque &deq) 重载等号操作符
deque<int> d2;
d2 = d1;
printDeque(d2);
//assign(beg, end) 将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身
deque<int> d3;
d3.assign(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeque(d3);
//assign(n, elem) 将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身
deque<int> d4;
d4.assign(10, 121);
printDeque(d4);
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121
3.3.4 deque大小操作
功能描述:
- 对deque容器的大小进行操作
函数原型:
deque.empty()判断容器是否为空,为空则返回True,不为空则返回Falsedeque.size()返回容器中元素的个数deque.resize(num)重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除deque.resize(num, elem)重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int> d1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
printDeque(d1);
if (d1.empty())
{
cout << "d1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "d1不为空" << endl;
cout << "d1的大小为:" << d1.size() << endl;
}
d1.resize(15);
printDeque(d1);
d1.resize(15, 1);
printDeque(d1);
d1.resize(5);
printDeque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
d1不为空
d1的大小为:10
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 2 3 4
3.3.5 deque插入和删除
功能描述:
- 向deque容器中插入和删除数据
函数原型:
两端插入操作:
push_back(elem)在容器尾部添加一个数据push_front(elem)在容器头部插入一个数据pop_back()删除容器最后一个数据pop_front()删除容器第一个数据
指定位置操作:
insert(pos,elem)在pos位置插入一个elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置insert(pos,n,elem)在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值insert(pos,beg,end)在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值clear()清空容器的所有数据erase(beg,end)删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置erase(pos)删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int> d1;
//push_back(elem) 在容器尾部添加一个数据
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(30);
//push_front(elem) 在容器头部插入一个数据
d1.push_front(20);
d1.push_front(40);
printDeque(d1);
//pop_back() 删除容器最后一个数据
d1.pop_back();
printDeque(d1);
//pop_front() 删除容器第一个数据
d1.pop_front();
printDeque(d1);
}
void test02()
{
deque<int> d1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
//insert(pos, elem) 在pos位置插入一个elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置
d1.insert(d1.begin(), 999);
printDeque(d1);
//insert(pos, n, elem) 在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值
deque<int>::iterator it = d1.begin();
it++;
d1.insert(it, 3, 888);
printDeque(d1);
//insert(pos, beg, end) 在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值
deque<int> d2;
d2.push_back(1);
d2.push_back(2);
d1.insert(d1.begin(), d2.begin(), d2.end());
printDeque(d1);
//clear() 清空容器的所有数据
d2.clear();
printDeque(d2);
//erase(pos) 删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置
d1.erase(d1.begin());
printDeque(d1);
//erase(beg, end) 删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置
d1.erase(d1.begin(), d1.end());
printDeque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
通过迭代器deque<int>::iterator it = d1.begin(); it ++;可以更改位置
3.3.6 数据存取
功能描述:
- 对deque中的数据的存取操作
函数原型:
at(int idx)返回索引idx所指的数据operator[]返回索引idx所指的数据front()返回容器中第一个数据元素back()返回容器中最后一个数据元素
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
deque<int> d1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
d1.push_back(i);
}
//at(int idx) 返回索引idx所指的数据
for (int i = 0; i < d1.size(); i++)
{
cout << d1.at(i) << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//operator[] 返回索引idx所指的数据
for (int i = 0; i < d1.size(); i++)
{
cout << d1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//front() 返回容器中第一个数据元素
cout << d1.front() << endl;
//back() 返回容器中最后一个数据元素
cout << d1.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
0
9
3.3.7 deque排序
功能描述:
- 利用算法实现对deque容器进行排序
算法:
sort(iterator beg, iterator end)对beg和end区间内元素进行排序
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <deque>
using namespace std;
void printDeque(const deque<int>& d)
{
for (deque<int>::const_iterator it = d.begin(); it != d.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
deque<int> d1;
d1.push_back(10);
d1.push_back(20);
d1.push_front(40);
d1.push_front(121);
printDeque(d1);
sort(d1.begin(), d1.end()); // 从小到大升序
printDeque(d1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
121 40 10 20
10 20 40 121
对于支持随机访问的迭代器的容器,都可以利用sort算法直接对其进行访问
vector也可以利用sort进行排序
3.4 案例-评委打分
3.4.1 案例描述
- 有5名选手:选手ABCDE,10个评委分别对每一名选手打分,去除最高分,去除评委中最低分,取平均分
3.4.2 案例实现
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
int Score;
string Name;
Person(string name,int score)
{
this->Name = name;
this->Score = score;
}
};
void createPerson(vector<Person>& v)
{
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
string name = "选手";
name += nameSeed[i];
int score = 0;
Person p(name, score);
v.push_back(p);
}
}
void setScore(vector<Person>& v)
{
for (vector<Person>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
deque<int> sco;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
int score = rand() % 41 + 60;
sco.push_back(score);
}
sort(sco.begin(), sco.end());
sco.pop_back();
sco.pop_front();
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < sco.size(); i++)
{
sum += sco[i];
}
int avg = sum / sco.size();
it->Score = avg;
}
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
vector<Person> v; // 存储选手
createPerson(v);
setScore(v);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i].Name << "的分数为:" << v[i].Score << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.5 stack 容器
3.5.1 stack基本概念
概念:stack是一种先进后出的数据结构,它只有一个出口
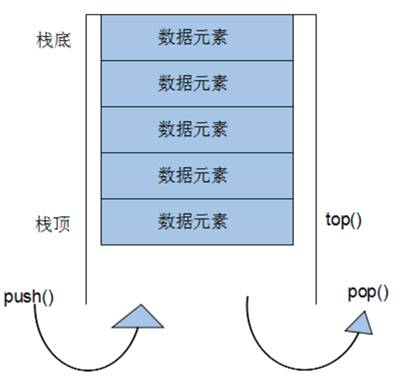
栈中只有顶端的元素才可以被外界使用,因此栈不允许有遍历行为
栈中进入数据称为 — 入栈 push
栈中弹出数据称为 — 出栈 pop
在《啊哈,算法》中回文判断,钓鱼牌就是用到栈的思想
3.5.2 stack常用接口
功能描述:
- 栈容器常用的对外接口
构造函数:
stack<T> stkstack采用模板类实现, stack对象的默认构造形式stack(const stack &stk)拷贝构造函数
赋值操作:
stack& operator=(const stack &stk)重载等号操作符
数据存取:
push(elem)向栈顶添加元素pop()从栈顶移除第一个元素top()返回栈顶元素
大小操作:
empty()判断堆栈是否为空size()返回栈的大小
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
stack<int> s;
s.push(10);
s.push(20);
s.push(30);
s.push(40);
cout << "栈的大小:" << s.size() << endl;
while (!s.empty())
{
cout << "栈顶:" << s.top() << endl;
s.pop();
}
cout << "栈的大小:" << s.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
栈的大小:4
栈顶:40
栈顶:30
栈顶:20
栈顶:10
栈的大小:0
3.6 queue容器
3.6.1 queue基本概念
概念:Queue时一种先进先出的数据结构,它有两个接口
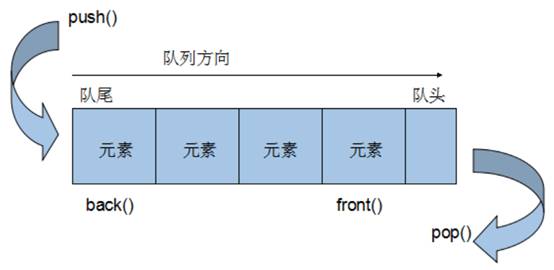
队列容器允许从一端新增元素,从另一端移除元素
队列中只有队头和队尾才可以被外界使用,因此队列不允许有遍历行为
队列中进数据称为 — 入队 push
队列中出数据称为 — 出队 pop
3.6.1 queue常用接口
功能描述:
- 栈容器常用的对外接口
构造函数:
queue<T> que;queue采用模板类实现,queue对象的默认构造形式queue(const queue &que)拷贝构造函数
赋值操作:
queue& operator=(const queue &que)重载等号操作符
数据存取:
push(elem)往队尾添加元素pop()从队头移除第一个元素back()返回最后一个元素front()返回第一个元素
大小操作:
empty()判断堆栈是否为空size()返回栈的大小
3.7 list容器
3.7.1 list基本概念
功能:将数据进行链式存储
链表(list)是一种物理存储单元上非连续的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接实现的
链表的组成:链表由一系列节点组成
结点的组成:一个存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域
STL中链表是一个双向循环链表
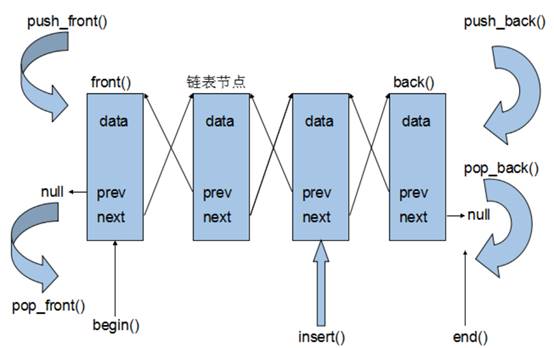
由于链表的存储方式并不是连续的内存空间,因此链表list中的迭代器只支持前移和后移,属于双向迭代器
list的优点:
- 采用动态存储分配,不会造成内存浪费和溢出
- 链表执行插入和删除操作十分方便,修改指针即可,不需要移动大量元素
list的缺点:
- 链表灵活,但是空间(指针域) 和 时间(遍历)额外耗费较大
- List有一个重要的性质,插入操作和删除操作都不会造成原有list迭代器的失效,这在vector是不成立的。
总结:STL中List和vector是两个最常被使用的容器,各有优缺点
3.7.2 list构造函数
功能描述:
- 创建list容器
函数原型:
list<T> lstlist采用采用模板类实现,对象的默认构造形式list(beg,end)构造函数将[beg, end)区间中的元素拷贝给本身list(n,elem)构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身list(const list &lst)拷贝构造函数
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
printList(L1);
list<int> L2(L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L2);
list<int> L3(L1);
printList(L3);
list<int> L4(10, 121);
printList(L4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
3.7.3 list赋值和交换
功能描述:
- 给list容器进行赋值,以及交换list容器
函数原型:
assign(beg, end)将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身assign(n, elem)将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身list& operator=(const list &lst)重载等号操作符swap(lst)将lst与本身的元素互换
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
printList(L1);
//assign(beg, end) 将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身
list<int> L2;
L2.assign(L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L2);
//assign(n, elem) 将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身
list<int> L3;
L3.assign(10, 121);
printList(L3);
//list& operator=(const list & lst) 重载等号操作符
list<int> L4;
L4 = L3;
printList(L4);
}
void test02()
{
list<int> L1;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
L1.push_back(i);
}
list<int> L2;
L2.push_back(10);
L2.push_back(50);
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
L1.swap(L2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
out:
10 20 30 40
10 20 30 40
121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121
121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121 121
交换前:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 50
交换后:
10 50
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
3.7.4 list大小操作
功能描述:
- 对list容器的大小进行操作
函数原型:
size()返回容器中元素的个数empty()判断容器是否为空resize(num)重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除resize(num, elem)重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
//size() 返回容器中元素的个数
list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
cout << "L1容器大小为:" << L1.size() << endl;
//empty() 判断容器是否为空
if (L1.empty())
{
cout << "L1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "L1不为空" << endl;
}
//resize(num) 重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
L1.resize(2);
printList(L1);
L1.resize(8);
printList(L1);
//resize(num, elem) 重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置,如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
L1.resize(10, 8);
printList(L1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
L1容器大小为:3
L1不为空
10 20
10 20 0 0 0 0 0 0
10 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 8 8
3.7.5 list插入和删除
功能描述:
- 对list容器进行数据的插入和删除
函数原型:
(elem)在容器尾部加入一个元素pop_back()删除容器中最后一个元素push_front(elem)在容器开头插入一个元素pop_front()从容器开头移除第一个元素insert(pos,elem)在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置insert(pos,n,elem)在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值insert(pos,beg,end)在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值clear()移除容器的所有数据erase(beg,end)删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置erase(pos)删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置remove(elem)删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int> L1;
//push_back(elem) 在容器尾部加入一个元素
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
printList(L1);
//pop_back() 删除容器中最后一个元素
L1.pop_back();
printList(L1);
//push_front(elem) 在容器开头插入一个元素
L1.push_front(121);
printList(L1);
//pop_front() 从容器开头移除第一个元素
L1.pop_front();
printList(L1);
//insert(pos, elem) 在pos位置插elem元素的拷贝,返回新数据的位置
L1.insert(L1.begin(), 888);
//insert(pos, n, elem) 在pos位置插入n个elem数据,无返回值
L1.insert(L1.end(), 4, 666);
printList(L1);
//insert(pos, beg, end) 在pos位置插入[beg,end)区间的数据,无返回值
list<int> L2;
L2 = L1;
L2.insert(L2.begin(), L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L2);
//clear() 移除容器的所有数据
L2.clear();
printList(L2);
//erase(beg, end) 删除[beg,end)区间的数据,返回下一个数据的位置
L1.erase(L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L1);
//erase(pos) 删除pos位置的数据,返回下一个数据的位置
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.erase(L1.begin());
printList(L1);
//remove(elem) 删除容器中所有与elem值匹配的元素
L1.remove(20);
printList(L1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
10 20 30 40
10 20 30
121 10 20 30
10 20 30
888 10 20 30 666 666 666 666
888 10 20 30 666 666 666 666 888 10 20 30 666 666 666 666
20
3.7.6 list数据存取
功能描述:
- 对list容器中数据进行存取
函数原型:
front()返回第一个元素。back()返回最后一个元素。
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
//front() 返回第一个元素
cout << L1.front() << endl;
//back() 返回最后一个元素
cout << L1.back() << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
10
40
3.7.7 list反转和排序
功能描述:
- 将容器中的元素反转,以及将容器中的数据进行排序
函数原型:
reverse()反转链表sort()链表排序,由于不支持随机访问,所以只能用list内置的排序算法,而不支持公共的排序算法
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>& L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
cout << "反转前:" << endl;
printList(L1);
//reverse() 反转链表
L1.reverse();
cout << "反转后:" << endl;
printList(L1);
}
void test02()
{
list<int> L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(8);
L1.push_back(17);
//sort() 链表排序
cout << "排序前:" << endl;
printList(L1);
cout << "排序后:" << endl;
L1.sort();
printList(L1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
out:
反转前:
10 20 30 40
反转后:
40 30 20 10
排序前:
10 20 8 17
排序后:
8 10 17 20
3.8 set/multiset容器
3.8.1 set基本概念
简介:
- 所有元素都会在插入时自动被排序
本质:
set/multiset属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现
set和multiset区别:
- set不允许容器中有重复的元素
- multiset允许容器中有重复的元素
3.8.2 set构造和赋值
功能描述:
- 创建set容器以及赋值
构造:
set<T> st默认构造函数:set(const set &st)拷贝构造函数
赋值:
set& operator=(const set &st)重载等号操作符
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void printSet(const set<int>& s)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(20);
s1.insert(40);
printSet(s1);
set<int> s2(s1);
printSet(s2);
set<int> s3;
s3 = s1;
printSet(s3);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
10 20 30 40
10 20 30 40
10 20 30 40
set只能用inset()进行插入元素,set容器中会自动帮我们拍好序,升序,当插入重复的元素的时候,是无效的
3.8.3 set大小和交换
功能描述:
- 统计set容器大小以及交换set容器
函数原型:
size()返回容器中元素的数目,如果有重复元素不会统计empty()判断容器是否为空swap(st)交换两个集合容器
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void printSet(const set<int>& s)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(100);
s1.insert(200);
s1.insert(150);
printSet(s1);
if (s1.empty())
{
cout << "s1为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "s1不为空" << endl;
cout << "s1容器的大小:" << s1.size() << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(121);
set<int> s2;
s2.insert(676);
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printSet(s1);
printSet(s2);
s1.swap(s2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
printSet(s1);
printSet(s2);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
out:
100 150 200
s1不为空
s1容器的大小:3
交换前:
121
676
交换后:
676
121
3.8.4 set插入和删除
功能描述:
- set容器进行插入数据和删除数据
函数原型:
insert(elem)在容器中插入元素clear()清除所有元素erase(pos)删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器erase(beg, end)删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器erase(elem)删除容器中值为elem的元素
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void printSet(const set<int>& s)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set<int> s1;
//insert(elem) 在容器中插入元素
s1.insert(12);
s1.insert(16);
s1.insert(13);
printSet(s1);
//clear() 清除所有元素
s1.clear();
printSet(s1);
//erase(pos) 删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器
s1.insert(12);
s1.insert(16);
s1.insert(13);
s1.erase(s1.begin());
printSet(s1);
//erase(beg, end) 删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器
s1.erase(s1.begin(), s1.end());
printSet(s1);
//erase(elem) 删除容器中值为elem的元素
s1.insert(12);
s1.insert(16);
s1.insert(13);
s1.erase(16);
printSet(s1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
set容器中的erase()和list容器中的remove()都可以删除指定的元素
3.8.5 set查找和统计
功能描述:
- 对set容器进行查找数据以及统计数据
函数原型:
find(key)查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回set.end()count(key)统计key的元素个数,对于set而言统计要么是0要么是1,而multiset才会大于1
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
void printSet(const set<int>& s)
{
for (set<int>::const_iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(30);
printSet(s1);
set<int>::iterator pos = s1.find(30);
if (pos != s1.end())
{
cout << "找到了该元素:" << *pos << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到该元素" << endl;
}
cout << s1.count(30) << endl;
cout << s1.count(70) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
10 30 40
找到了该元素:30
1
0
3.8.6 set和multiset区别
区别:
- set不可以插入重复数据,而multiset可以
- set插入数据的同时会返回插入结果,表示插入是否成功
- multiset不会检测数据,因此可以插入重复数据
set不能插入重复的元素pair<iterator, bool> insertset会返回一个bool类型的值表示是否插入成功
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
set<int> s1;
pair<set<int>::iterator, bool> ret = s1.insert(10);
if (ret.second)
{
cout << "第一次插入成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "第一次插入失败" << endl;
}
ret = s1.insert(10);
if (ret.second)
{
cout << "第二次插入成功" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "第二次插入失败" << endl;
}
multiset<int> ms;
ms.insert(20);
ms.insert(20);
for (multiset<int>::iterator it = ms.begin(); it != ms.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
out:
第一次插入成功
第二次插入失败
20 20
3.8.7 pair对组创建
功能描述:
- 成对出现的数据,利用对组可以返回两个数据
两种创建方式:
pair<type, type> p ( value1, value2 )pair<type, type> p = make_pair( value1, value2 )
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
//pair<type, type> p ( value1, value2 )
pair<string, int> p1("lili", 20);
cout << "姓名:" << p1.first << "年龄:" << p1.second << endl;
//pair<type, type> p = make_pair( value1, value2 )
pair<string, int> p2;
p2 = make_pair("qq", 30);
cout << "姓名:" << p2.first << " 年龄:" << p2.second << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
姓名:lili年龄:20
姓名:qq 年龄:30
3.8.8 set容器排序
学习目标:
- set容器默认排序规则为从小到大,掌握如何改变排序规则
主要技术点:
- 利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则
需要注意的是在vs2019中建立仿函数需要加const,不然会报错
const bool operator()(类型 v1, 类型 v2) const
int类型
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
class MyCompare
{
public:
const bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const
{
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void test01()
{
set<int> s1;
s1.insert(10);
s1.insert(40);
s1.insert(30);
s1.insert(20);
for (set<int>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
set<int, MyCompare> s2;
s2.insert(10);
s2.insert(40);
s2.insert(30);
s2.insert(20);
for (set<int, MyCompare>::iterator it = s2.begin(); it != s2.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
10 20 30 40
40 30 20 10
自定义类型
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
class MyCompare
{
public:
const bool operator()(Person p1, Person p2)const
{
return p1.m_Age > p2.m_Age;
}
};
void test01()
{
set<Person, MyCompare> s1;
Person p1("A", 30);
Person p2("B", 10);
Person p3("C", 50);
Person p4("D", 20);
s1.insert(p1);
s1.insert(p2);
s1.insert(p3);
s1.insert(p4);
for (set<Person, MyCompare>::iterator it = s1.begin(); it != s1.end(); it++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << it->m_Name << " 年龄:" << it->m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
姓名:C 年龄:50
姓名:A 年龄:30
姓名:D 年龄:20
姓名:B 年龄:10
3.9 map/multimap容器
3.9.1 map基本概念
简介:
- map中所有元素都是pair
- pair中第一个元素为key(键值),起到索引作用,第二个元素为value(实值)
- 所有元素都会根据元素的键值自动排序(注意是根据key排序)
相当于python中的字典键值对
本质:
- map/multimap属于关联式容器,底层结构是用二叉树实现
优点:
- 可以根据key值快速找到value值
map和multimap区别:
- map不允许容器中有重复key值元素
- multimap允许容器中有重复key值元素
和set/multiset的分别差不多,但是map/multimap是区分于key值,而value值可以重复
3.9.2 map构造和赋值
功能描述:
- 对map容器进行构造和赋值操作
函数原型:
构造:
map<T1, T2> mpmap默认构造函数map(const map &mp)拷贝构造函数
赋值:
map& operator=(const map &mp)重载等号操作符
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void printMap(map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << (*it).first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
map<int, int> m1;
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 40));
m1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
printMap(m1);
map<int, int> m2(m1);
printMap(m2);
map<int, int> m3;
m3 = m1;
printMap(m3);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
key = 1 value = 10
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
key = 4 value = 40
key = 1 value = 10
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
key = 4 value = 40
key = 1 value = 10
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
key = 4 value = 40
3.9.3 map大小和交换
功能描述:
- 统计map容器大小以及交换map容器
函数原型:
size()返回容器中元素的数目empty()判断容器是否为空swap(st)交换两个集合容器
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void printMap(const map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::const_iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 40));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
//size() 返回容器中元素的数目
//empty() 判断容器是否为空
if (mp1.empty())
{
cout << "mp1容器为空" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "mp1容器不为空" << endl;
cout << "mp1大小为:" << mp1.size() << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(4, 40));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
map<int, int> mp2;
mp2.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 11));
mp2.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 22));
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
printMap(mp1);
printMap(mp2);
//swap(st) 交换两个集合容器
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
mp1.swap(mp2);
printMap(mp1);
printMap(mp2);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
out:
mp1容器不为空
mp1大小为:4
交换前:
key = 1 value = 10
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
key = 4 value = 40
key = 1 value = 11
key = 2 value = 22
交换后:
key = 1 value = 11
key = 2 value = 22
key = 1 value = 10
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
key = 4 value = 40
3.9.4 map插入和删除
功能描述:
- map容器进行插入数据和删除数据
函数原型:
insert(elem)在容器中插入元素map.inset(pair<类型,类型>(key, value))map.inset(make_pair(key, value))map.inset(map<类型,类型>::value_type(key, value))map[key] = value
clear()清除所有元素erase(pos)删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器erase(beg, end)删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器erase(key)删除容器中值为key的元素
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void printMap(const map<int, int>& m)
{
for (map<int, int>::const_iterator it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
map<int, int> mp1;
//insert(elem) 在容器中插入元素
//第一种插入方式
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
//第二种插入方式
mp1.insert(make_pair(2, 20));
//第三种插入方式
mp1.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(3, 30));
//第四种插入方式
mp1[4] = 40;
printMap(mp1);
//erase(pos) 删除pos迭代器所指的元素,返回下一个元素的迭代器
map<int, int>::iterator pos = mp1.erase(mp1.begin());
cout << pos->first << endl;
printMap(mp1);
//erase(key) 删除容器中值为key的元素
mp1.erase(4);
printMap(mp1);
//clear() 清除所有元素
//erase(beg, end) 删除区间[beg,end)的所有元素 ,返回下一个元素的迭代器
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
key = 1 value = 10
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
key = 4 value = 40
2
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
key = 4 value = 40
key = 2 value = 20
key = 3 value = 30
3.9.5 map查找和统计
功能描述:
- 对map容器进行查找数据以及统计数据
函数原型:
find(key)查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回map.end()count(key)统计key的元素个数,对于key来说,只有0或者1返回值,对multikey可以有大于1的值
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
map<int, int> mp1;
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(1, 10));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(2, 20));
mp1.insert(pair<int, int>(3, 30));
//find(key) 查找key是否存在,若存在,返回该键的元素的迭代器;若不存在,返回map.end()
map<int, int>::iterator pos = mp1.find(4);
if (pos != mp1.end())
{
cout << pos->first << " " << pos->second << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "没有这个key" << endl;
}
//count(key) 统计key的元素个数
cout << mp1.count(2) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
没有这个key
1
3.9.6 map容器排序
利用仿函数,可以改变排序规则
map排序是根据key来进行排序的,默认为从小到大升序,可以利用仿函数该排序规则
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
class MyCompare
{
public:
const bool operator()(int v1, int v2) const
{
return v1 > v2;
}
};
void test01()
{
map<int, int, MyCompare>mp1;
mp1[1] = 10;
mp1[2] = 20;
mp1[3] = 30;
mp1[4] = 40;
for (map<int, int, MyCompare>::iterator it = mp1.begin(); it != mp1.end(); it++)
{
cout << "key = " << it->first << " value = " << it->second << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
key = 4 value = 40
key = 3 value = 30
key = 2 value = 20
key = 1 value = 10
3.10 员工案例
3.10.1 案例描述
- 公司今天招聘了10个员工(ABCDEFGHIJ),10名员工进入公司之后,需要指派员工在那个部门工作
- 员工信息有: 姓名 工资组成;部门分为:策划、美术、研发
- 随机给10名员工分配部门和工资
- 通过multimap进行信息的插入 key(部门编号) value(员工)
- 分部门显示员工信息
3.10.2 实现步骤
1.创建10名员工,放到vector中
2.遍历vector容器,取出每个员工,进行随机分组
3.分组后,将员工部门编号作为key,具体员工作为value,放入到multimap容器中
4.分部门显示员工信息
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <ctime>
#define MEISHU 0
#define CEHUA 1
#define YANFA 2
using namespace std;
class Worker
{
public:
Worker(string name, int salary)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Salary = salary;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Salary;
};
void creatWorker(vector<Worker>& v)
{
string nameSeed = "ABCDEFGHIJ";
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
Worker worker("A", 0);
worker.m_Name = "员工";
worker.m_Name += nameSeed[i];
worker.m_Salary = rand() % 10000 + 10000;
v.push_back(worker);
}
}
void makeGroup(vector<Worker>& v, multimap<int, Worker>& m)
{
for (vector<Worker>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
int group = rand() % 3;
m.insert(pair<int, Worker>(group, *it));
}
}
void showWorkerGroup(multimap<int, Worker>& m)
{
cout << "美术部门:" << endl;
multimap<int, Worker>::iterator pos = m.find(MEISHU);
int count = m.count(MEISHU);
int index = 1;
for (; pos != m.end() && index <= count; pos++, index++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " 薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "策划部门:" << endl;
pos = m.find(CEHUA);
count = m.count(CEHUA);
index = 1;
for (; pos != m.end() && index <= count; pos++, index++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " 薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;
}
cout << endl;
cout << "研发部门:" << endl;
pos = m.find(YANFA);
count = m.count(YANFA);
index = 1;
for (; pos != m.end() && index <= count; pos++, index++)
{
cout << "姓名:" << pos->second.m_Name << " 薪资:" << pos->second.m_Salary << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
// 1、创建员工
vector<Worker> vWorker;
creatWorker(vWorker);
// 2、员工分组
multimap<int, Worker> mWorker;
makeGroup(vWorker, mWorker);
// 3、打印信息
showWorkerGroup(mWorker);
return 0;
}
4 STL-函数对象
4.1 函数对象
4.1.1 函数对象概念
概念:
- 重载函数调用操作符的类,其对象常被称为函数对象
- 函数对象使用重载的()时,行为类似函数调用,也叫仿函数
本质:
- 函数对象(仿函数)是一个类,不是一个函数
4.1.2 函数对象的使用
特点:
- 函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用, 可以有参数,可以有返回值
- 函数对象超出普通函数的概念,函数对象可以有自己的状态
- 函数对象可以作为参数传递
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class MyAdd
{
public:
int operator()(int v1, int v2)
{
return v1 + v2;
}
};
class MyPrint
{
public:
MyPrint()
{
this->count = 0;
}
void operator()(string test)
{
cout << test << endl;
count++;
}
int count;
};
void test01()
{
MyAdd add;
int num = add(4, 6);
cout << num << endl;
}
void test02()
{
MyPrint MyPrint;
MyPrint("hello c++");
MyPrint("hello c++");
cout << MyPrint.count << endl;
}
void DoPrint(MyPrint& mp, string test)
{
mp(test);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
MyPrint Print;
DoPrint(Print, "hello c++");
return 0;
}
out:
10
hello c++
hello c++
2
hello c++
4.2 谓词
4.2.1 谓词概念
概念:
- 返回bool类型的仿函数称为谓词
- 如果
operator()接受一个参数,那么叫做一元谓词 - 如果
operator()接受两个参数,那么叫做二元谓词
4.2.2 一元谓词
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class GreatFive
{
public:
bool operator()(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreatFive());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "没有满足条件的数" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << *it << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
6
4.2.3 二元谓词
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class MyCompare
{
public:
bool operator()(int val1, int val2)
{
return val1 > val2;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(40);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), MyCompare());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
10 20 30 40 50
50 40 30 20 10
4.3 内建函数对象
4.3.1 内建函数对象意义
概念:
- STL内建了一些函数对象
分类:
- 算术仿函数
- 关系仿函数
- 逻辑仿函数
用法:
- 这些仿函数所产生的对象,用法和一般函数完全相同
- 使用内建对象,需要引入头文件
#include<function>
4.3.2 算数仿函数
功能描述:
- 实现四则运算
- 其中negate是一元运算,其他都是二元运算
仿函数原型:
template<class T> T plus<T>加法仿函数template<class T> T minus<T>减法仿函数template<class T> T multiplies<T>乘法仿函数template<class T> T divides<T>除法仿函数template<class T> T modulus<T>取模仿函数template<class T> T negate<T>取反仿函数
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
//template<class T> T plus<T> 加法仿函数
plus<int> Plus;
cout << "plus:" << Plus(39, 21) << endl;
//template<class T> T minus<T> 减法仿函数
minus<int> Minus;
cout << "minus:" << Minus(92, 21) << endl;
//template<class T> T multiplies<T> 乘法仿函数
multiplies<int> Multiplies;
cout << "multiplies:" << Multiplies(2, 3) << endl;
//template<class T> T divides<T> 除法仿函数
divides<int> Divides;
cout << "divides:" << Divides(7, 2) << endl;
//template<class T> T modulus<T> 取模仿函数
modulus<int> Modulus;
cout << "modulus:" << Modulus(8, 5) << endl;
//template<class T> T negate<T> 取反仿函数
negate<int> Negate;
cout << "negate:" << Negate(30) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
plus:60
minus:71
multiplies:6
divides:3
modulus:3
negate:-30
4.3.3 关系仿函数
功能描述:
- 实现关系对比
仿函数原型:
template<class T> bool equal_to等于template<class T> bool not_equal_to不等于template<class T> bool greater<T>大于template<class T> bool greater_equal<T>大于等于template<class T> bool less<T>小于template<class T> bool less_equal<T>小于等于
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
4.3.4 逻辑仿函数
功能描述:
- 实现逻辑运算
函数原型:
template<class T> bool logical_and<T>逻辑与template<class T> bool logical_or<T>逻辑或template<class T> bool logical_not<T>逻辑非
STL-常用算法
概述:
- 算法主要是由头文件
<algorithm> <functional> <numeric>组成 <algorithm>是所有STL头文件中最大的一个,范围涉及到比较、 交换、查找、遍历操作、复制、修改等等<numeric>体积很小,只包括几个在序列上面进行简单数学运算的模板函数<functional>定义了一些模板类,用以声明函数对象
5.1 常用遍历算法
算法简介:
for_each遍历容器transform搬运容器到另一个容器中
5.1.1 for_each
功能描述:
- 实现遍历容器
函数原型:
for_each(iterator beg, iterator end, _func)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void Print(int val)
{
cout << val << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for_each(v.begin(), v.end(), Print);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
5.1.2 transform
功能描述:
- 搬运容器到另一个容器中
函数原型:
transform(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, _func)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
class Transform
{
public:
int operator()(int v)
{
return v;
}
};
void Print(int v)
{
cout << v << " ";
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(v.size());
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin(),Transform());
for_each(vTarget.begin(), vTarget.end(), Print);
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
5.2 常用查找算法
算法简介:
find查找元素find_if按条件查找元素adjacent_find查找相邻重复元素binary_search二分查找法count统计元素个数count_if按条件统计元素个数
5.2.1 find
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素,找到返回指定元素的迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器end()
函数原型:
find(iterator beg, iterator end, value)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->m_Name = name;
this->m_Age = age;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p)
{
if (p.m_Name == this->m_Name && p.m_Age == this->m_Age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 5);
if (pos == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到相应元素" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了相应元素:" << *pos << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
vector<Person> person;
Person p1("aaa", 14);
Person p2("bbb", 15);
Person p3("ccc", 18);
person.push_back(p1);
person.push_back(p2);
person.push_back(p3);
vector<Person>::iterator pos = find(person.begin(), person.end(), p3);
if (pos == person.end())
{
cout << "没有这个人" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "name: " << pos->m_Name << "age: " << pos->m_Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
out:
找到了相应元素:5
name: cccage: 18
5.2.2 find_if
功能描述:
- 按条件查找元素
函数原型:
find_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->Name = name;
this->Age = age;
}
string Name;
int Age;
};
bool GreaterFive(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
bool Greater20(const Person& p)
{
return p.Age > 20;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator pos = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive);
if (pos == v.end())
{
cout << "没有找到大于5的数" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "找到了大于5的数" << endl;
}
}
void test02()
{
Person p1("aaa", 30);
Person p2("bbb", 10);
Person p3("ccc", 20);
vector<Person> p;
p.push_back(p1);
p.push_back(p2);
p.push_back(p3);
vector<Person>::iterator pos = find_if(p.begin(), p.end(), Greater20);
if (pos == p.end())
{
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "naem: " << pos->Name << " " << "age: " << pos->Age << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
5.2.3 adjacent_find
功能描述:
- 查找相邻重复元素
函数原型:
adjacent_find(iterator beg, iterator end)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(3);
vector<int>::iterator pos = adjacent_find(v.begin(), v.end());
if (pos == v.end())
{
cout << "没有" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "有" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
5.2.4 binary_search
功能描述:
- 查找指定元素是否存在
函数原型:
bool binary_search(iterator beg, iterator end, value)
注意: 二分查找法查找效率很高,在无序序列中不可用
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
bool ret = binary_search(v.begin(), v.end(), 8);
if (ret)
{
cout << "找到了" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "未找到" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
5.2.5 count
功能描述:
- 统计元素个数
函数原型:
count(iterator beg, iterator end, value)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->age = age;
this->Name = name;
}
bool operator==(const Person& p)
{
if (p.age == this->age)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
string Name;
int age;
};
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(20);
int i = count(v.begin(), v.end(), 20);
cout << i << endl;
}
void test02()
{
Person p1("aaa", 20);
Person p2("bbb", 30);
Person p3("ccc", 20);
vector<Person> p;
p.push_back(p1);
p.push_back(p2);
p.push_back(p3);
int age = count(p.begin(), p.end(), p1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
5.2.6 count_if
功能描述:
- 按条件统计元素个数
函数原型:
count_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
this->Name = name;
this->age = age;
}
string Name;
int age;
};
bool Greater18(const Person& p)
{
if (p.age > 18)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool GreaterFive(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
int num = count_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive);
cout << num << endl;
}
void test02()
{
Person p1("aa", 10);
Person p2("bb", 20);
Person p3("cc", 30);
vector<Person> p;
p.push_back(p1);
p.push_back(p2);
p.push_back(p3);
int num = count_if(p.begin(), p.end(), Greater18);
cout << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
5.3 常用排序算法
算法简介:
sort对容器内元素进行排序random_shuffle洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序merge容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中reverse反转指定范围的元素
5.3.1 sort
功能描述:
- 对容器内元素进行排序
函数原型:
sort(iterator beg, iterator end, _Pred)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(50);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
20 30 50
50 30 20
5.3.2 random_shuffle
功能描述:
- 洗牌 指定范围内的元素随机调整次序
函数原型:
random_shuffle(iterator beg, iterator end)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
random_shuffle(v.begin(), v.end());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
test01();
return 0;
}
5.3.3 merge
功能描述:
- 两个容器元素合并,并存储到另一容器中
函数原型:
merge(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest)
注意: 合并的两个容器必须是有序的(升序),合并后也是排好序的,并且目标容器需要先声明空间
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 3);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
merge(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vTarget.begin(); it != vTarget.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8 9 9 10 11 12
5.3.4 reverse
功能描述:
- 将容器内元素进行反转
函数原型:
reverse(iterator beg, iterator end)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
5.4 常用拷贝和替换算法
算法简介:
copy容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中replace将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素replace_if容器内指定范围满足条件的元素替换为新元素swap互换两个容器的元素
5.4.1 copy
功能描述:
- 容器内指定范围的元素拷贝到另一容器中
函数原型:
copy(iterator beg, iterator end, iterator dest)按值查找元素,找到返回指定位置迭代器,找不到返回结束迭代器位置
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(v.size());
copy(v.begin(), v.end(), vTarget.begin());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vTarget.begin(); it != vTarget.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
5.4.2 replace
功能描述:
- 将容器内指定范围的旧元素修改为新元素
函数原型:
replace(iterator beg, iterator end, oldvalue, newvalue)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "替换前:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
replace(v.begin(), v.end(), 4, 9);
cout << "替换后:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
替换前:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
替换后:
0 1 2 3 9 5 6 7 8 9
5.4.3 replace_if
功能描述:
- 将区间内满足条件的元素,替换成指定元素
函数原型:
replace_if(iterator beg, iterator end, _pred, newvalue)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool GreaterFive(int val)
{
return val > 5;
}
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "替换前:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
replace_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive, 888);
cout << "替换后:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
替换前:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
替换后:
0 1 2 3 4 5 888 888 888 888
5.4.4 swap
功能描述:
- 互换两个容器的元素
函数原型:
swap(container c1, container c2)
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 10);
}
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
swap(v1, v2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin(); it != v1.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
交换前:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
交换后:
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
5.5 常用算术生成算法
注意:
- 算术生成算法属于小型算法,使用时包含的头文件为
#include <numeric>
算法简介:
accumulate计算容器元素累计总和fill向容器中添加元素
5.5.1 accumulate
功能描述:
- 计算区间内 容器元素累计总和
函数原型:
accumulate(iterator beg, iterator end, value)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
int num = accumulate(v.begin(), v.end(), 0);
cout << num << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
5050
5.5.2 fill
功能描述:
- 向容器中填充指定的元素
函数原型:
fill(iterator beg, iterator end, value)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <numeric>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
fill(v.begin(), v.end(), 888);
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
888 888 888 888 888 888 888 888 888 888
5.6 常用集合算法
算法简介:
set_intersection求两个容器的交集set_union求两个容器的并集set_difference求两个容器的差集
5.6.1 set_intersection
功能描述:
- 求两个容器的交集
函数原型:
set_intersection(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest)
求交集的两个集合必须的有序序列,目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器中取小值,
set_intersection返回值既是交集中最后一个元素的位置
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 4);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(min(v1.size(), v2.size()));
set_intersection(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vTarget.begin(); it != vTarget.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
4 5 6 7 8 9 0 0 0 0
5.6.2 set_union
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的并集
函数原型:
set_union(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest)
求并集的两个集合必须的有序序列,目标容器开辟空间需要两个容器相加,
set_union返回值既是并集中最后一个元素的位置
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 4);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(v1.size() + v2.size());
set_union(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vTarget.begin(); it != vTarget.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 0 0 0 0 0 0
5.6.3 set_difference
功能描述:
- 求两个集合的差集
函数原型:
set_difference(iterator beg1, iterator end1, iterator beg2, iterator end2, iterator dest)
求差集的两个集合必须的有序序列,目标容器开辟空间需要从两个容器取较大值,
set_difference返回值既是差集中最后一个元素的位置
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)
{
v1.push_back(i);
v2.push_back(i + 4);
}
vector<int> vTarget;
vTarget.resize(max(v1.size(), v2.size()));
set_difference(v1.begin(), v1.end(), v2.begin(), v2.end(), vTarget.begin());
cout << "v1对v2的差集:";
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vTarget.begin(); it != vTarget.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
set_difference(v2.begin(), v2.end(), v1.begin(), v1.end(), vTarget.begin());
cout << "v2对v1的差集:";
for (vector<int>::iterator it = vTarget.begin(); it != vTarget.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
out:
v1对v2的差集:0 1 2 3 0 0 0 0 0 0
v2对v1的差集:10 11 12 13 0 0 0 0 0 0























 2204
2204











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








