目录
STL 的设计有通用性,string 和 vector 的使用有很多相似之处,二者用法重复的地方不在过多说明
总述

顺序表,由数组实现
Alloc 是空间配置器,内存池。以后会讲空间配置器跟这里是如何配合的
vector<char> strV;
string str;vector 不能替代 string:
1. string要求最后有\0,更好兼容c接口
2. string有很多他的专用接口函数
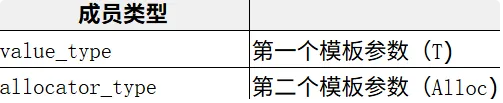
构造函数
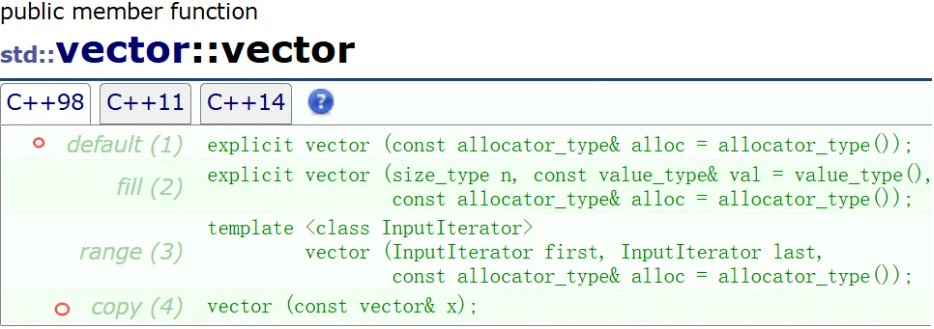
1. 无参构造 可以自己写内存池,但我们用它的就好
2. 构造并初始化 n 个 val
3. 用迭代器进行初始化构造
4. 拷贝构造
实例化可以给任意类型;迭代器区间可以是其他类型的迭代器
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1(5, 1);
vector<string> v2(5, "***");
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " "; // 1 1 1 1 1
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : v2)
{
cout << e << " "; // *** *** *** *** ***
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> v3(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for (auto e : v3)
{
cout << e << " "; // 1 1 1 1 1
}
cout << endl;
string str("hello world");
vector<char> v4(str.begin(), str.end());
for (auto e : v4)
{
cout << e; // hello world
}
cout << endl;
// 迭代器底层可能是指针
int a[] = { 16,2,77,29 };
vector<int> v5(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
for (auto e : v5)
{
cout << e << " "; // 16 2 77 29
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}单参数的构造函数支持隐式类型转换:
string 支持单参数的构造函数,参数是 const char
==> const char* 的字符串可以隐式类型转换成 string
所以可以 v.push_back("张三");
vector<vector<int>> vv;
vector<string> v;
string name1("张三");
v.push_back(name1);
v.push_back(string("张三")); // 匿名对象
v.push_back("张三");class A
{
int _a;
public:
A(int a)
:_a(a)
{}
};
A a1(1);
A a1 = 1;迭代器
构造函数中有一些迭代器举例
都是 [ ) 的区间
vector 的3种遍历方法:↓
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(4);
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : v)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}排序:↓
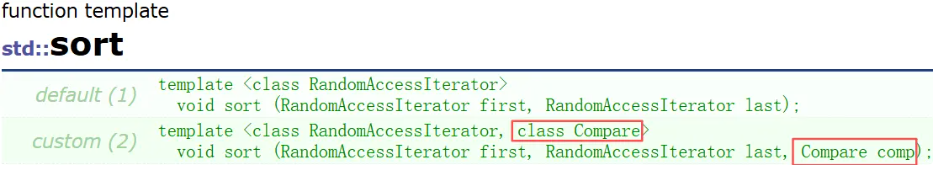
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm> // 算法头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = { 16,2,77,29,3 };
vector<int> v1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 升序
//sort(v1.rbegin(), v1.rend()); // 降序
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 迭代器底层可能是指针
sort(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
for (auto e : a)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}降序的函数写法:↓
int a[] = { 16,2,77,29,3 };
vector<int> v1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
// 降序
//greater<int> gt;
//sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), gt);
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<int>()); // 匿名对象
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl; // 给空格也排序了
string str("hello world");
sort(str.begin(), str.end()); // dehllloorw
cout << str << endl; reserve、resize
和 string 一样,reserve 只改变 _capacity;resize 也改变有效数据个数 _size
vector<int> v1;
//v1.reserve(10);
v1.resize(10);
for (size_t i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v1[i] = i;
// 如果用 v1.reserve(10); 应该这样写
// v1.push_back(i);
}
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;使用 reserve 会发生越界访问,程序直接挂掉。
因为 reserve 只改变了 _capacity,此时 s 的 有效数据个数_size == 0
重载的 [ ] 是按有效数据来的,会断言检查
元素访问
对越界的检查:
operator [ ]:assert断言
at:抛异常

data 类似于 c_str
value 是 T,返回 T* ==> 返回 T类对象 数组的指针
增删查改
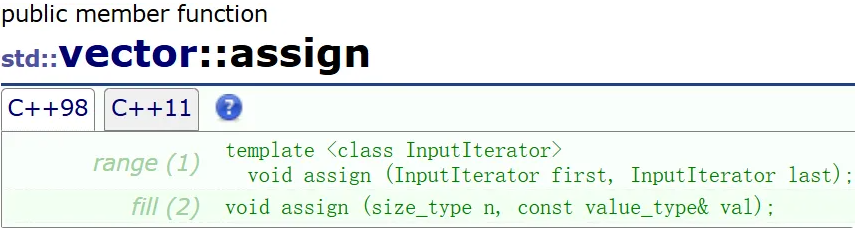
当前值清了,重新赋值
int a[] = { 29,3,33,43,3,2,3,3,2 };
vector<int> v1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
v1.assign(5, 1);
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " "; // 1 1 1 1 1
}
cout << endl;尾插:push_back
尾删:pop_back
没有直接提供头插、头删,可以用 insert、erase
string 是以下标插入。往后都是迭代器

在某个位置插入1个、n个值;迭代区间
int a[] = { 16,2,77,29,3,33 };
vector<int> v1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
// 头删
v1.erase(v1.begin());
// 头插
v1.insert(v1.begin(), 100);
// 删除第3个数据
v1.erase(v1.begin() + 2);
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " "; // 100 2 29 3 33
}
cout << endl; vector<int> v1(3, 100); // 100 100 100
vector<int>::iterator it = v1.begin();
std::vector<int> v2(2, 400);
v1.insert(it + 2, v2.begin(), v2.end()); // 100 100 400 400 100
int a[] = { 501,502,503 };
v1.insert(v1.begin(), a, a + 3);
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " "; // 501 502 503 100 100 400 400 100
}
cout << endl;查找(算法库)
想删除3,但是不知道3在哪,用算法库里的find
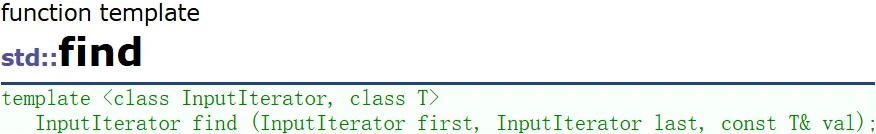
迭代器失效
int a[] = { 29,3,33,43,3,2,3,3,2 };
vector<int> v1(a, a + sizeof(a) / sizeof(int));
//vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);
auto pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3);
//if (pos != v1.end())
//{
// v1.erase(pos);
//}
// 删除所有的3 -- 涉及迭代器失效!后面解决
while (pos != v1.end())
{
v1.erase(pos);
// pos = find(pos + 1, v1.end(), 3); // 迭代器失效
pos = find(v1.begin(), v1.end(), 3); // 成功,但是效率低
}
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;模拟实现
模版不能声明、定义分离,模版进阶时讲
vector.h
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
namespace qtw
{
template<class T>
class vector
{
public:
typedef T* iterator;
typedef const T* const_iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return _start;
}
iterator end()
{
return _finish;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _start;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _finish;
}
vector()
//:_start(nullptr)
//,_finish(nullptr)
//,_endofstorage(nullptr)
// 成员变量给了缺省值,这里就不用在初始化列表初始化了
{ }
vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
resize(n, val);
}
vector(int n, const T& val = T()) // 为什么加这个构造函数? 注意事项 4.
{
resize(n, val);
}
// [first, last)
//vector(iterator first, iterator last) 不这样写
// 这样写只能使用vector的迭代器初始化(不通用)
// 类模板里面还可以再套模板
template<class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
vector(const vector<T>& v) // 传统
{
_start = new T[v.capacity()];
//memcpy(_start, v._start, sizeof(T) * v.size()); 深拷贝的自定义类型对象会出问题
for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
{
_start[i] = v._start[i];
}
_finish = _start + v.size();
_endofstorage = _start + v.capacity();
}
//vector(const vector<T>& v) // 复用
//{
// reserve(v.capacity());
// for (auto e : v)
// {
// push_back(e);
// }
//}
void swap(vector<T>& v)
{
std::swap(_start, v._start);
std::swap(_finish, v._finish);
std::swap(_endofstorage, v._endofstorage);
}
vector<T>& operator=(vector<T> v) // 现代写法
{
swap(v);
return *this;
}
~vector()
{
if (_finish)
{
delete[] _start;
_start = _finish = _endofstorage = nullptr;
}
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
size_t sz = size(); // 保存size,下面会被迫改变
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start)
{
//memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * size()); 深拷贝的自定义类型对象会出问题
for (size_t i = 0; i < sz; i++)
{
tmp[i] = _start[i];
}
delete[] _start;
}
_start = tmp; // 间接改变了size
_finish = _start + sz;
_endofstorage = _start + n;
}
}
// T类型的匿名对象,调用T的默认构造。所以自己写类,默认构造要自己提供
// C++模板出来后,对内置类型升级:内置类型也有构造函数
void resize(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
if (n < size())
{
_finish = _start + n;
}
else
{
reserve(n);
while (_finish != _start + n)
{
*_finish = val;
_finish++;
}
}
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
if (_finish == _endofstorage)
{
size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
}
*_finish = x;
_finish++;
//insert(end(), x);
}
size_t size() const
{
return _finish - _start;
}
size_t capacity() const
{
return _endofstorage - _start;
}
iterator& operator[](size_t pos)
{
assert(pos < size());
return *(_start + pos);
}
const_iterator& operator[](size_t pos) const
{
assert(pos < size());
return *(_start + pos);
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
if (_finish == _endofstorage)
{
size_t len = pos - _start;
size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
pos = _start + len; // 相对位置,重置迭代器位置
}
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
*(end + 1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = x;
_finish++;
return pos;
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos >= _start && pos < _finish);
iterator it = pos + 1;
while (it != _finish)
{
*(it - 1) = *it;
++it;
}
_finish--;
return pos;
}
private:
iterator _start = nullptr;
iterator _finish = nullptr;
iterator _endofstorage = nullptr;
};
}注意事项
1.
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
size_t sz = size(); // 保存size,下面会被迫改变
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start)
{
memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * size());
delete[] _start;
}
_start = tmp; // 改变了size
_finish = _start + sz;
_endofstorage = _start + n;
}
}
size_t size() const
{
return _finish - _start;
}用 _start 计算 size;_start = tmp 这一步间接改变了 size
如果不保存 size, _finish = _start + size(); _finish 拿到的是0x00000000这个进程地址空间
所以,要么加上 size_t sz = size(); 这句,要么先算 _finish 再算 _start
2. 扩容引发迭代器失效
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
assert(pos >= _start && pos <= _finish);
if (_finish == _endofstorage)
{
size_t len = pos - _start;
size_t newcapacity = capacity() == 0 ? 4 : capacity() * 2;
reserve(newcapacity);
pos = _start + len; // 相对位置,重置迭代器位置
}
iterator end = _finish - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
*(end + 1) = *end;
--end;
}
*pos = x;
_finish++;
return pos;
}void qtw_test1()
{
qtw::vector<int> v;
v.push_back(1); v.push_back(2);
v.push_back(3); v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(5); v.push_back(5);
v.push_back(5);
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl; // 1 2 3 4 5 5 5
v.insert(v.begin(), 100);
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl; // 100 1 2 3 4 5 5 5
qtw::vector<int>::iterator p = v.begin() + 3;
v.insert(p, 300);
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl; // 100 1 2 300 3 4 5 5 5
// 高危行为
*p += 10;
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl; // 100 1 2 300 3 4 5 5 5
}insert扩容以后迭代器可能会失效;所以insert扩容以后就不要使用这个形参迭代器了
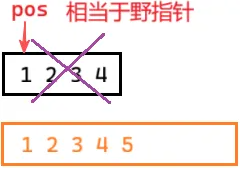
erase以后,迭代器失效了,不能访问
vs进行强制检查,访问会直接报错
void qtw_test2()
{
std::vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1); v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(2); v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4); v1.push_back(5);
v1.push_back(6);
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl;
auto it = v1.begin();
v1.erase(it);
cout << *it << endl;
++it;
cout << *it << endl;
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl;
}程序直接挂掉
怎么解决?接收返回值
void qtw_test2()
{
std::vector<int> v1;
v1.push_back(1); v1.push_back(2);
v1.push_back(2); v1.push_back(3);
v1.push_back(4); v1.push_back(5);
v1.push_back(6);
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl;
auto it = v1.begin();
while (it != v1.end())
{
if (*it % 2 == 0)
{
it = v1.erase(it); // 不接收属于迭代器失效
}
else
{
++it;
}
}
for (auto e : v) { cout << e << " "; }
cout << endl;
}总结:vector 的 erase和insert 迭代器对象后,不能再访问这个迭代器。迭代器失效了,访问结果是未定义
3. 深拷贝的自定义类型对象
vector(const vector<T>& v) // 传统
{
_start = new T[v.capacity()];
memcpy(_start, v._start, sizeof(T) * v.size()); //深拷贝的自定义类型对象会出问题
//for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++)
//{
// _start[i] = v._start[i];
//}
_finish = _start + v.size();
_endofstorage = _start + v.capacity();
}
void reserve(size_t n)
{
if (n > capacity())
{
size_t sz = size(); // 保存size,下面会被迫改变
T* tmp = new T[n];
if (_start)
{
memcpy(tmp, _start, sizeof(T) * size()); //深拷贝的自定义类型对象会出问题
//for (size_t i = 0; i < sz; i++)
//{
// tmp[i] = _start[i];
//}
delete[] _start;
}
_start = tmp; // 间接改变了size
_finish = _start + sz;
_endofstorage = _start + n;
}
}void qtw_test5()
{
qtw::vector<string> v;
v.push_back("111111111111111111");
v.push_back("222222222222222222");
v.push_back("333333333333333333");
v.push_back("444444444444444444");
v.push_back("555555555555555555");
for (auto& e : v) // 拷贝代价大,所以引用
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
qtw::vector<string> v1(v);
for (auto& e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}push_back "5",扩容时程序挂掉
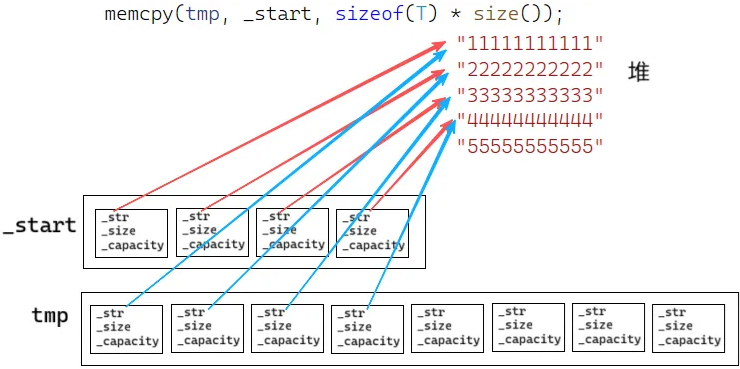
vector是深拷贝,但vector空间上存的是string对象
string对象应该是拷贝,但memcpy是浅拷贝
delete[] _start;当T是自定义类型时,一次调用vector里每个对象的析构函数,再释放整个空间
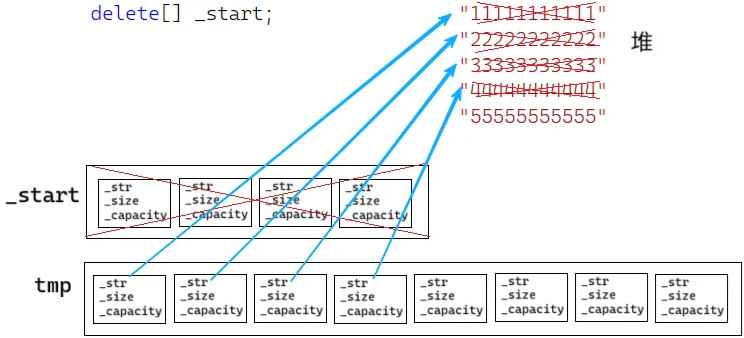
解决方案:
T是深拷贝的类,要调用赋值重载,实现类对象的深拷贝
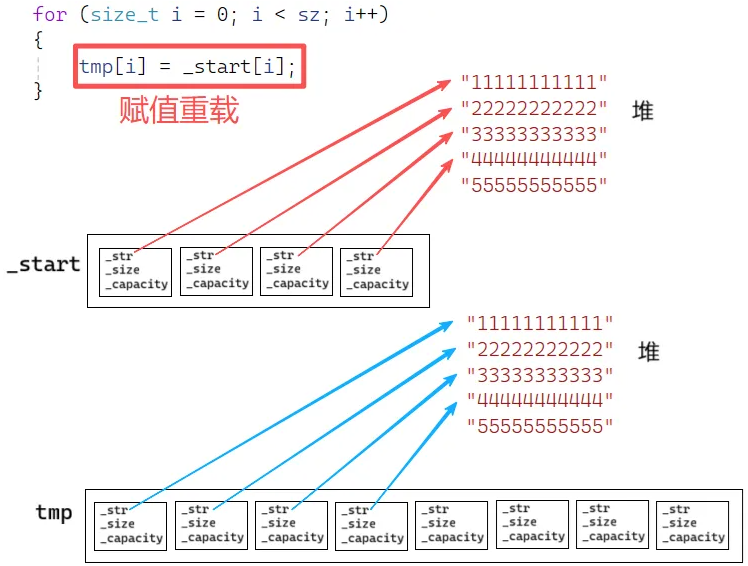
4.
vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
resize(n, val);
}
// [first, last)
//vector(iterator first, iterator last) 不这样写:只能使用vector的迭代器初始化(不通用)
// 类模板里面还可以再套模板
template<class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}void qtw_test6()
{
qtw::vector<int> v(10, 1); // 报错
qtw::vector<int> v1(10u, 1);
qtw::vector<string> v2(10, "1111");
}v1,v2没问题,v报错
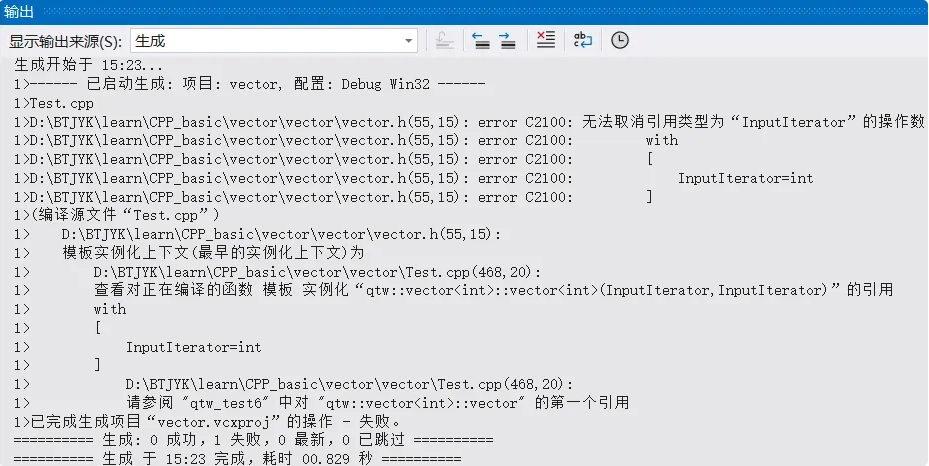
v 调用成了迭代器,迭代器更匹配。因为上面的构造函数一个是 size_t,一个是 int。v 的(10, 1)都是 int,调成了迭代器,first、last都被识别成 int,但 int 不能解引用,报错
v1让编译器把 10识别为size_t,1还是int,便因类型不同无法调用模板。和 v2 一样别无他选
库里面怎么解决的呢?
![]()
vector(size_t n, const T& val = T())
{
resize(n, val);
}
vector(int n, const T& val = T())
{
resize(n, val);
}
// [first, last)
//vector(iterator first, iterator last) 不这样写:只能使用vector的迭代器初始化(不通用)
// 类模板里面还可以再套模板
template<class InputIterator>
vector(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}本篇的分享就到这里了,感谢观看,如果对你有帮助,别忘了点赞+收藏+关注。
小编会以自己学习过程中遇到的问题为素材,持续为您推送文章























 996
996










