T1
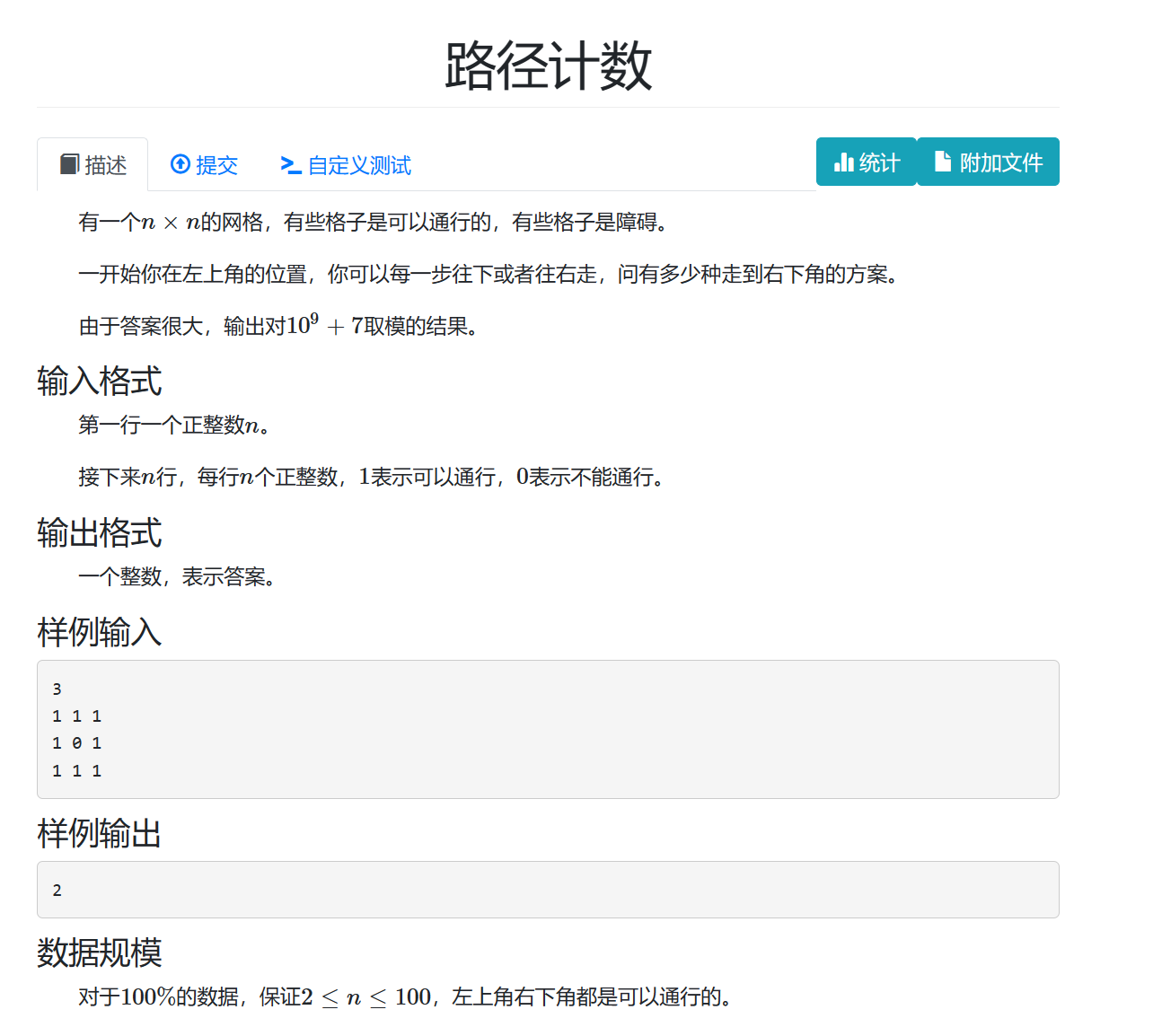
思路:开两个二维数组,一个用来记录能否通行,另外一个用来dp。
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n;
int m[105][105];
long long f[105][105] = { 0 };
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int o = 1; o <= n; o++)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &m[o][i]);
}
}
f[1][1] = 1;
for (int o = 1; o <= n; o++)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (m[o][i] == 1)
{
f[o][i] += f[o - 1][i] + f[o][i - 1];
f[o][i] %= 1000000007;
}
}
}
printf("%lld", f[n][n]);
return 0;
}T2
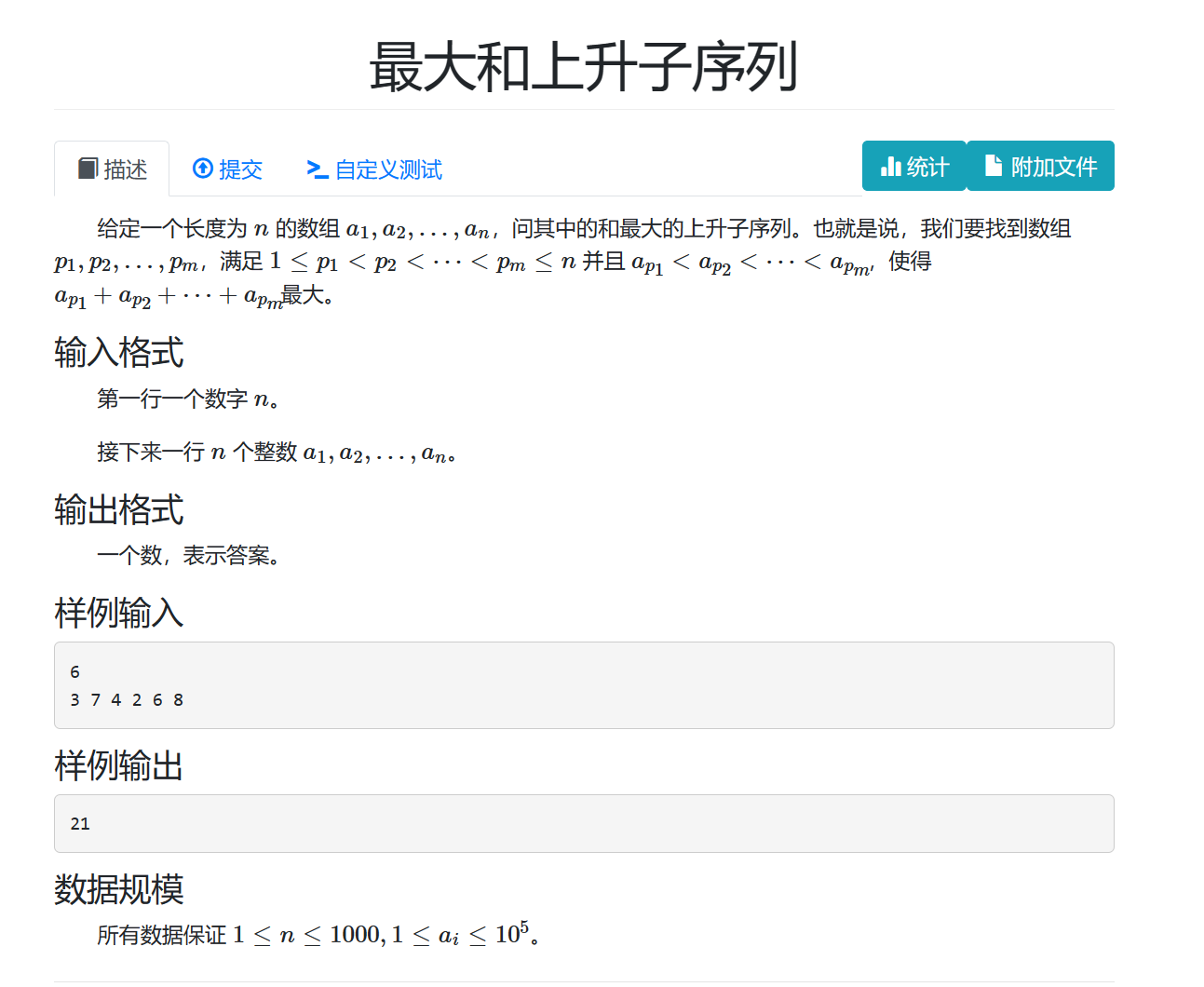
思路:dp,如果满足上升,那么比较较小数处当前值+较大数和较大数当前值即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int n;
int f[1005];
long long a[100005];
int main()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
long long m = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &f[i]);
a[f[i]] = f[i];
}
for (int o = 0; o <n; o++)
{
for (int i = o+1; i < n; i++)
{
if (f[i] > f[o])
{
a[f[i]] = max(a[f[o]]+f[i],a[f[i]]);
m = max(m, a[f[i]]);
}
}
}
printf("%lld", m);
return 0;
}T3

思路:先对每次操作后的每位数进行预处理,写出你、次操作后单一的该数字会变成几位数,最后根据预处理结果累加即可。
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include"stdio.h"
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
long long f[200050][10];
for (int i = 0; i <= 9; i++)f[0][i] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= 200010; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= 9; j++)f[i][j - 1] = f[i - 1][j];
f[i][9] = (f[i - 1][1] + f[i - 1][0]) % 1000000007;
}
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++)
{
int a[10] = { 0 };
int m;
char str[20];
int res = 0;
scanf("%s %d", &str, &m);
int len = strlen(str);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
res += f[m][str[i] - '0'];
res %= 1000000007;
}
printf("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}T4

思路:将x轴方向和y轴的距离差除以最小公倍数后以pair的形式存入;最后放入set中去重;
#include<iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
long long n, x[505], y[505];
long long gcd(long long x, long long y)
{
if (x < 0)x *= (-1);
if (y < 0)y *= (-1);
long long tmp;
if (x < y)
{
tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
while (y>0)
{
tmp = x % y;
x = y, y = tmp;
}
return x;
}
int main()
{
long long ans = 0;
cin>>n;
set<pair<long long,long long>>s;
int time;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin>>x[i] >> y[i];
}
for (int o = 0; o < n; o++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (i == o)continue;
long long dx = x[o] - x[i];
long long dy = y[o] - y[i];
time = gcd(dx, dy);
pair<long long, long long >p;
p.first = dx / time;
p.second = dy / time;
if (!s.count(p))
{
ans++;
s.insert(p);
}
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}T5
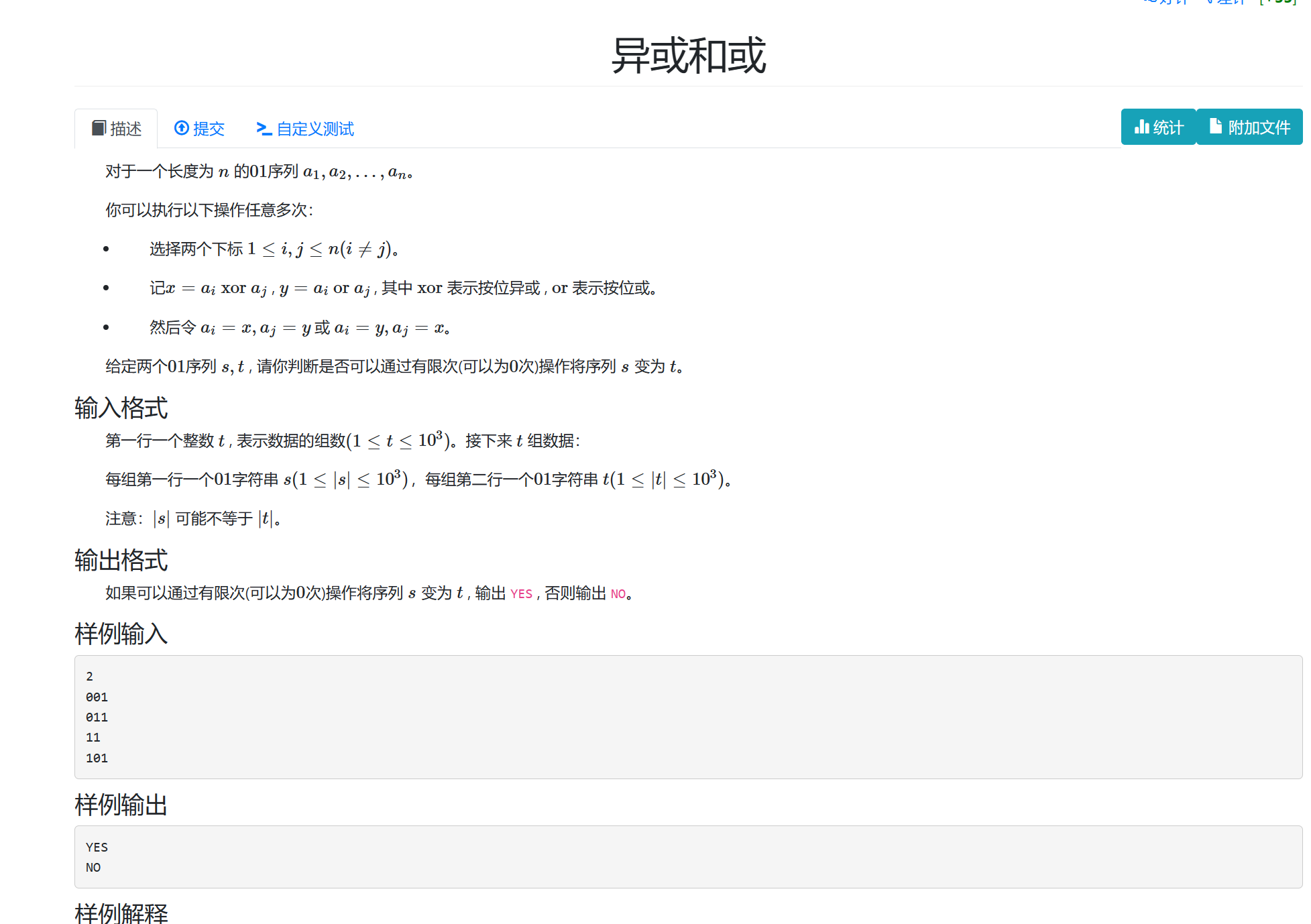
思路:
//0 1 --》1 1;
//0 0 --》0 0
//1 1 —》 0 1
#include<iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
//0 1 :1 1;
//0 0 : 0 0
//1 1 : 0 1
int main()
{
int t;
cin>>t;
for (int h = 0; h < t; h++)
{
string str1, str2;
cin >> str1 >> str2;
int len;
if ((len=str1.length()) != str2.length())
{
cout << "NO\n";
continue;
}
if (str1 == str2)
{
cout << "YES\n";
continue;
}
bool siu = 0;
int tmp;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (str1[i] == '1')
{
siu = 1;
tmp = i;
break;
}
}
if (str1[tmp] == str2[tmp])
{
cout << "YES\n";
continue;
}
bool qq = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (str2[i] == '1' && i != tmp)
{
cout << "YES\n";
qq = 1;
break;
}
}
if (qq == 0)cout << "NO\n";
}
return 0;
}T6
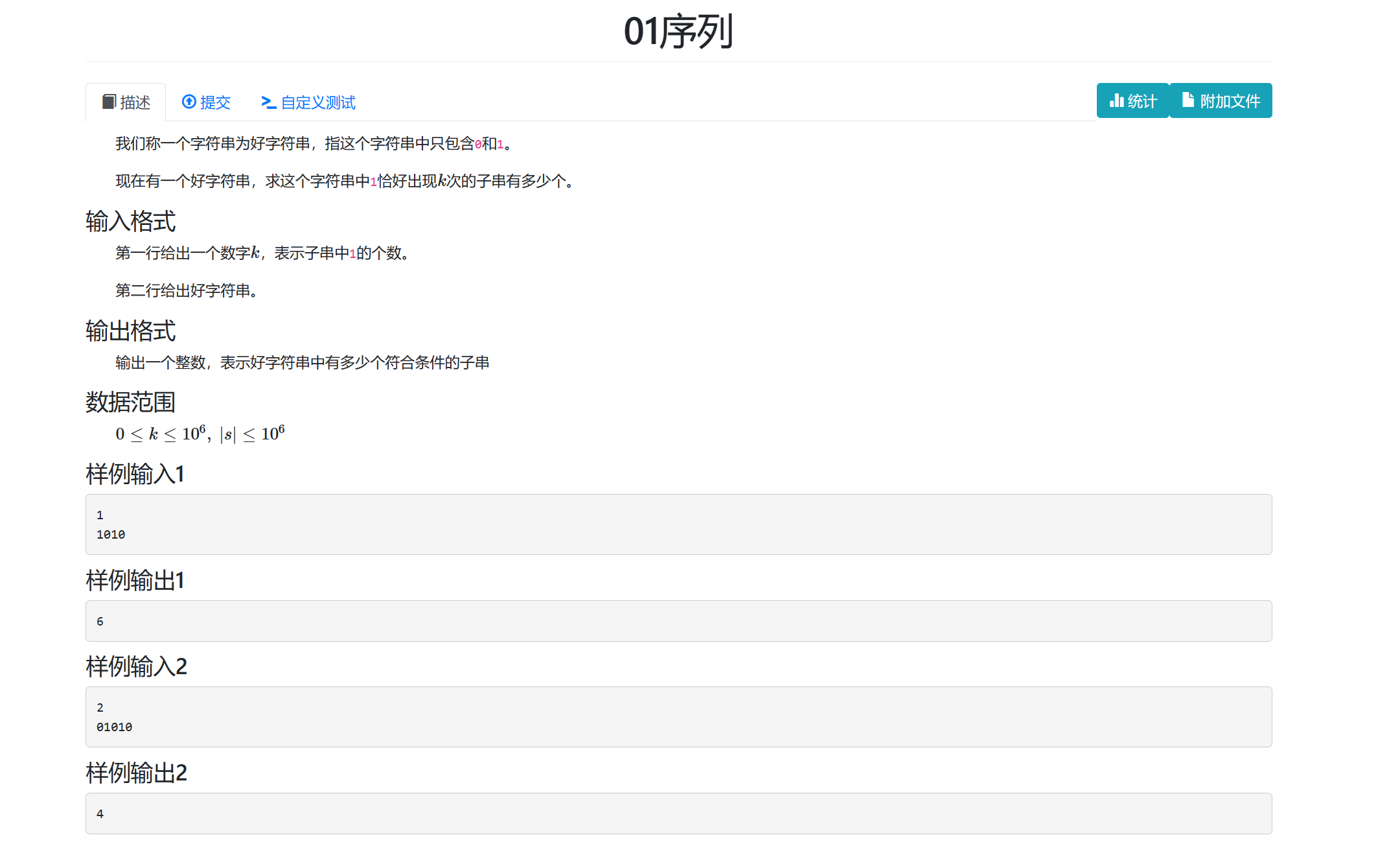
思路:将连续的零的个数存入一个一维数组,这样结果就为数组中下标相差k的两组连续零的个数分别加一后的乘积的累加
#include<iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int k;
cin >> k;
int a[1000005]={ 0 };
string str;
cin >> str;
long long len = str.length(),ans=0,res=0;
int cnt = 0;
int tot = 0;
if (k == 0)
{
for (long long i = 0; i <= len; i++)
{
if (str[i] == '0')ans++;
else
{
res += (ans * (ans + 1)) / 2;
ans = 0;
}
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (str[i] == '0')
{
a[cnt]++;
}
else cnt++;
}
for (int i = k; i <= cnt; i++)
{
res += (a[i]+1) * (a[i - k]+1);
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}T7
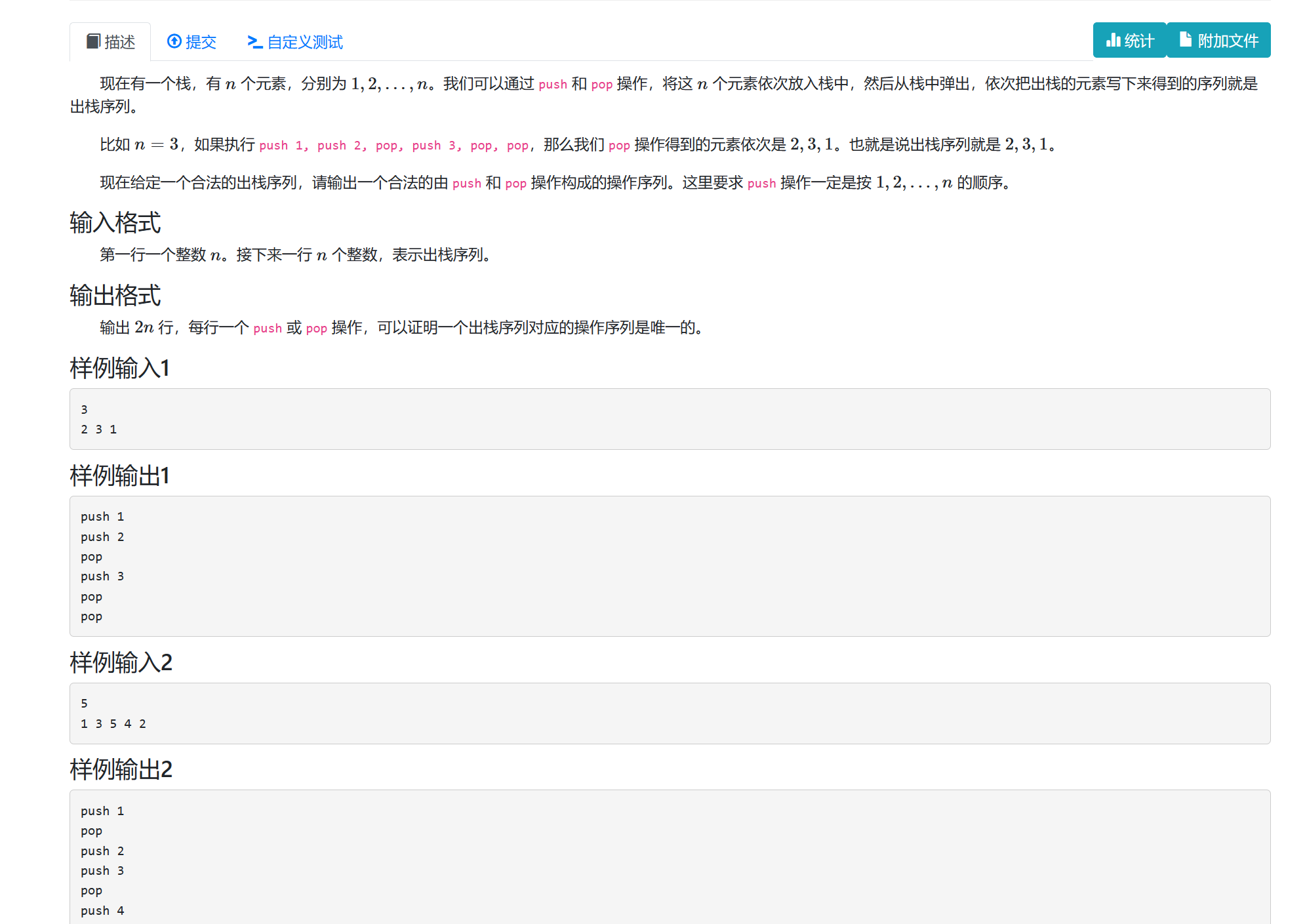
栈中元素单调增,所以如果栈顶元素小于需弹出的元素,则需继续push,若相等,则pop
#include<iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int a[100005];
stack<int> num;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
}
num.push(-1);
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (num.top() == a[i])
{
printf("pop\n");
num.pop();
continue;
}
int k = i;
while (num.top() < a[i])
{
printf("push %d\n", ++cnt);//cout << "push " << ++cnt << endl;
num.push(cnt);
}
printf("pop\n");//cout << "pop\n";
num.pop();
}
return 0;
}T8
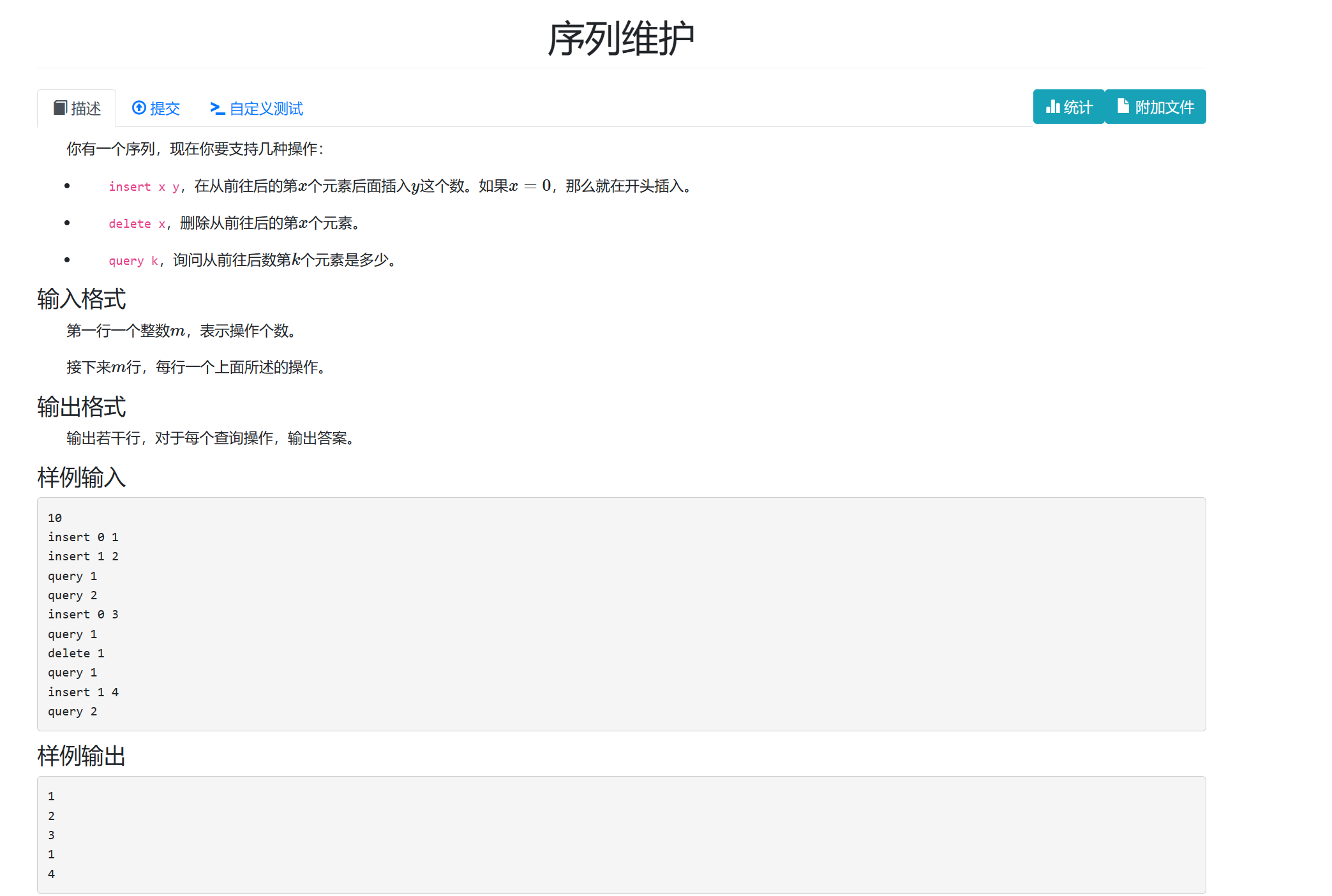
思路:考察vector的使用
#include<iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
vector<int>c;
string op;
int m;
scanf("%d", &m);
int x, y, k;
for (int z = 0; z < m; z++)
{
scanf("%s",&op);
if (op == "insert")
{
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);//cin >> x >> y;
c.insert(c.begin() + x, y);
}
else if (op == "delete")
{
scanf("%d", &x);//cin >> x;
c.erase (c.begin()+x-1);
}
else
{
scanf("%d", &k);//cin >> k;
cout << c[k - 1]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}T9
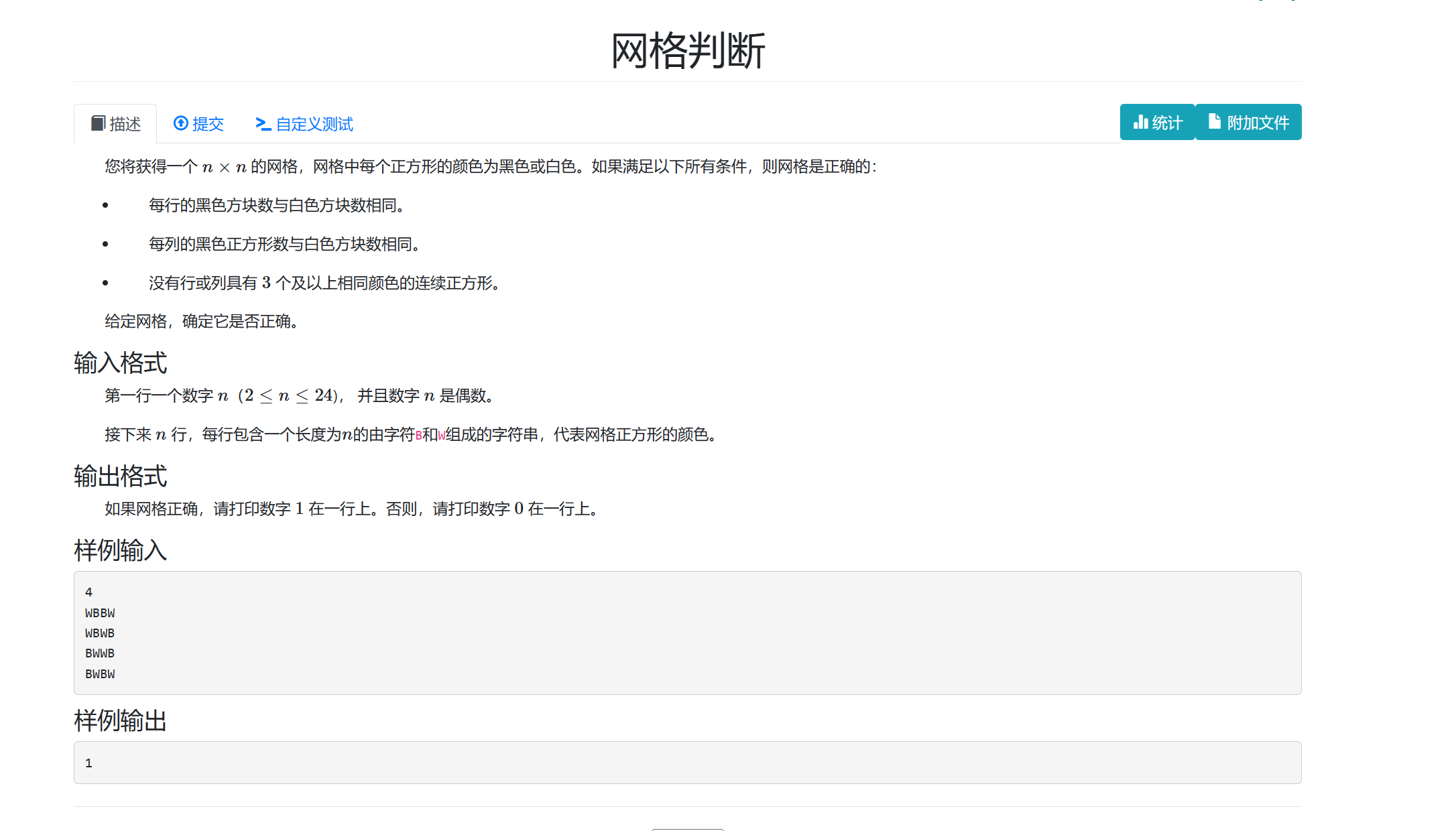
需要记录输入到某个位置时,该行与该列之前的是什么颜色,如果相同,计数器加,如果不同,更新颜色,计数器化一。
#include<iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int hb[27] = { 0 }, hw[27] = { 0 }, lb[27] = { 0 }, lw[27] = { 0 };
char c[27][27];
int cnth = 0, cntl[27] = {0};
char preh, prel[27];
for (int h = 0; h < n; h++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> c[h][i];
}
prel[h] = 'q';
}
for (int h = 0; h < n; h++)
{
preh = 'q';
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (c[h][i] == 'W')
{
hw[h]++;
lw[i]++;
}
else
{
hb[h]++;
lb[i]++;
}
if (c[h][i] == preh)
{
cnth++;
}
else
{
if (cnth >= 3)
{
cout << "0";
return 0;
}
cnth = 1;
preh = c[h][i];
}
if (c[h][i] == prel[i])
{
cntl[i]++;
if (cntl[i] == 3)
{
cout << "0";
return 0;
}
}
else
{
cntl[i] = 1;
prel[i] = c[h][i];
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (hw[i] != hb[i] || lw[i] != lb[i])
{
cout << '0';
return 0;
}
}
cout << '1';
return 0;
}T10
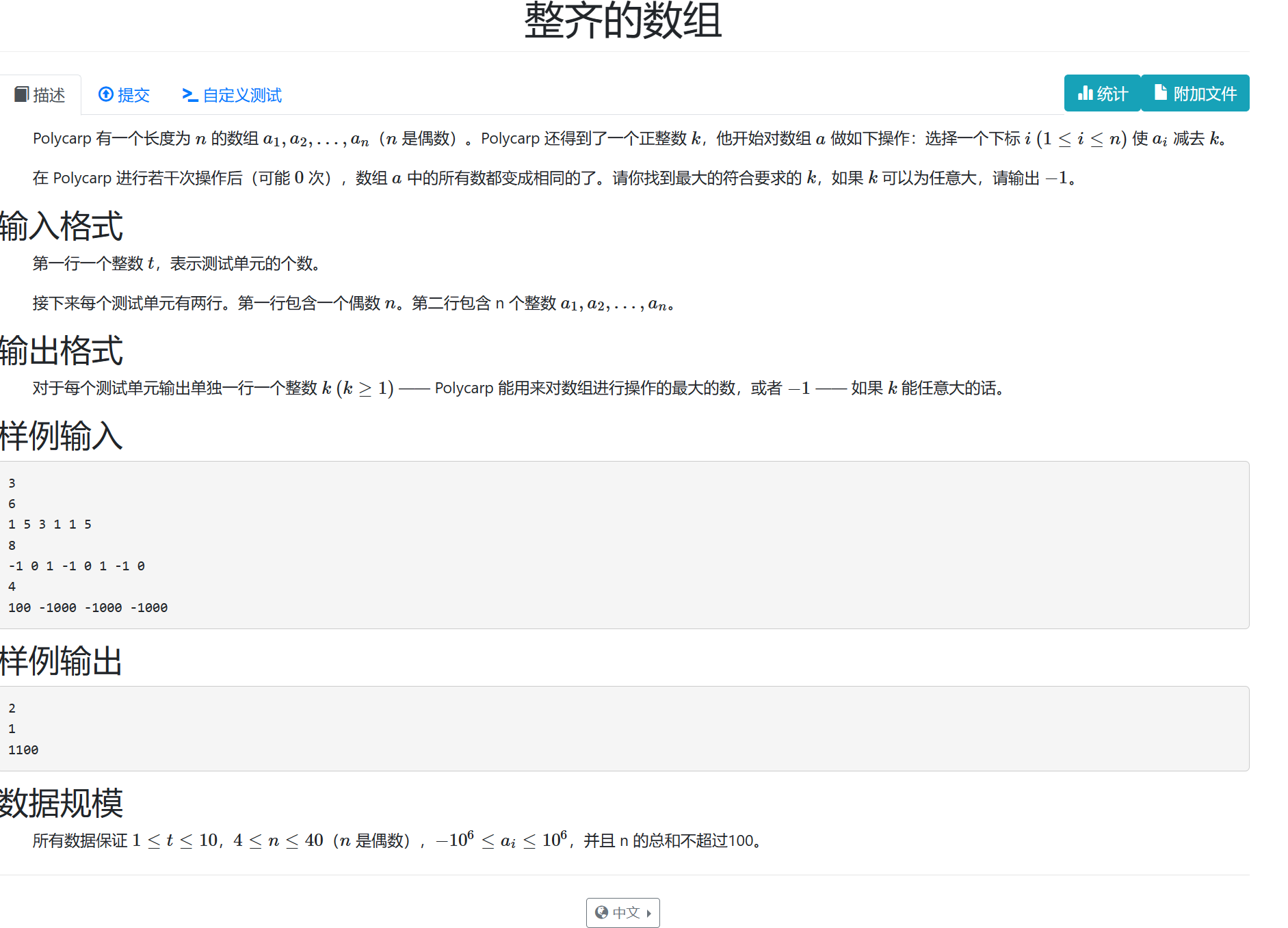
思路:
先用set去重、排序,然后用一维数组取出,定义gcd函数找出两个数的最大公约数,之后用每个数与最小的那个数的差值与之前的最大公约数再求一次最大公约数即可。
#include<iostream>
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<string.h>
#include<set>
#include<set>
#include<utility>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int x, int y)
{
if (x < 0)x *= (-1);
if (y < 0)y *= (-1);
int tmp;
if (x < y)
{
tmp = x; x = y; y = tmp;
}
while (y > 0)
{
tmp = x % y;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
return x;
}
int main()
{
int t;
cin >> t;
for (int qq = 0; qq < t; qq++)
{
set<int> s;
int tmp, n;
cin >> n;
for (int wx = 0; wx < n; wx++)
{
cin >> tmp;
s.insert(tmp);
}
if (s.size() == 1)
{
cout << "-1";
continue;
}
int num[105],cnt=0;
for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); it++)
{
num[cnt++] = *it;
}
set<int> c;
for (int i = 1; i < cnt; i++)
{
num[i] -= num[0];
}
for (int i = 2; i < cnt; i++)
{
num[i] = gcd(num[i], num[i - 1]);
}
cout << num[cnt - 1] << endl;
}
return 0;
}






















 1088
1088

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








