Heapsort-1:堆排序-1
Animation
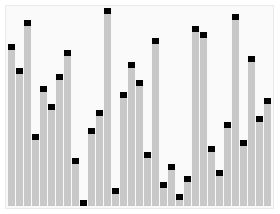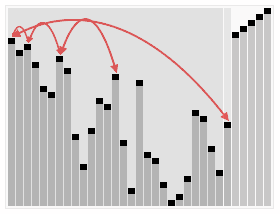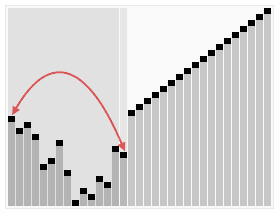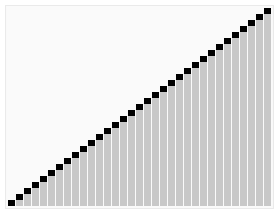
A run of the heapsort algorithm sorting an array of randomly permuted values. In the first stage of the algorithm the array elements are reordered to satisfy the heap property. Before the actual sorting takes place, the heap tree structure is shown briefly for illustration.

An example on heapsort.
Complexity
| Class | Sorting algorithm |
|---|---|
| Data structure | Array |
| Worst case performance | O(nlogn) |
| Best case performance | Ω(n) , O(nlogn) |
| Average case performance | O(nlogn) |
| Worst case space complexity | O(1) auxiliary |
Pseudo code
HEAPSORT(A)
BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A)
for i = A.length downto 2
exchange A[1] with A[i]
A.heap-size = A.heap-size - 1
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, 1)
BUILD-MAX-HEAP(A)
A.heap-size = A.length
for i = floor(A.length/2) downto 1
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, i)
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, i)
l = LEFT(i)
r = RIGHT(i)
if l <= A.heap-size and A[l] > A[i]
largest = l
else largest = i
if r <= A.heap-size and A[r] > A[largest]
largest = r
if largest != i
exchange A[i] with A[largest]
MAX-HEAPIFY(A, largest)
LEFT(i)
return 2i
RIGHT(i)
return 2i+1Java program
/**
* Created with IntelliJ IDEA.
* User: 1O1O
* Date: 12/2/13
* Time: 10:01 PM
* :)~
* Heapsort-1:Sorting by Selection:Internal Sorting
*/
public class Main {
public static int LEFT(int i){
return 2*i;
}
public static int RIGHT(int i){
return 2*i+1;
}
public static void MAX_HEAPIFY(int[] K, int i, int heapSize){
int l = LEFT(i);
int r = RIGHT(i);
int largest;
int temp;
if(l <= heapSize && K[l] > K[i]){
largest = l;
}else {
largest = i;
}
if(r <= heapSize && K[r] > K[largest]){
largest = r;
}
if(largest != i){
temp = K[largest];
K[largest] = K[i];
K[i] = temp;
MAX_HEAPIFY(K, largest, heapSize);
}
}
public static void BUILD_MAX_HEAP(int[] K, int heapSize){
for(int i=(int)Math.floor((K.length-1)/2); i>=1; i--){
MAX_HEAPIFY(K, i, heapSize);
}
}
public static void HEAPSORT(int[] K){
int heapSize = K.length-1;
int temp;
BUILD_MAX_HEAP(K, heapSize);
for(int i=K.length-1; i>=2; i--){
temp = K[i];
K[i] = K[1];
K[1] = temp;
heapSize--;
MAX_HEAPIFY(K, 1, heapSize);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 16;
int[] K = new int[17];
/*Prepare the data*/
K[1] = 503;
K[2] = 87;
K[3] = 512;
K[4] = 61;
K[5] = 908;
K[6] = 170;
K[7] = 897;
K[8] = 275;
K[9] = 653;
K[10] = 426;
K[11] = 154;
K[12] = 509;
K[13] = 612;
K[14] = 677;
K[15] = 765;
K[16] = 703;
/*Output unsorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Unsorted Ks:");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
System.out.println(i+":"+K[i]);
}
System.out.println();
/*Kernel of the Algorithm!*/
HEAPSORT(K);
/*Output sorted Ks*/
System.out.println("Sorted Ks:");
for(int i=1; i<=N; i++){
System.out.println(i+":"+K[i]);
}
}
}Outputs
Unsorted Ks:
1:503
2:87
3:512
4:61
5:908
6:170
7:897
8:275
9:653
10:426
11:154
12:509
13:612
14:677
15:765
16:703
Sorted Ks:
1:61
2:87
3:154
4:170
5:275
6:426
7:503
8:509
9:512
10:612
11:653
12:677
13:703
14:765
15:897
16:908Reference
<< Introduction to Algorithms >> Third Edition, THOMAS H. CORMEN, CHARLES E. LEISERSON, RONALD L. RIVEST, CLIFFORD STEIN
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heapsort























 636
636

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








