10 Risk Management
10.1 Overview of Risk Management
In the realm of most projects, it's almost a given that certain tasks won't neatly fit within the planned timelines and
budgets. Consequently, it becomes essential to craft a well-thought-out risk management plan – one that can help
identify, evaluate, respond to, monitor, and report potential risks. The risk management blueprint for the UNSW
Student Network Project will meticulously adhere to the recommended PMBOK process to spell out how risks will be
assessed and addressed.
The UNSW Student Network Project's risk management strategy will go through various phases, encompassing risk
management planning, risk pinpointing, risk evaluation, the formulation of risk responses, and the supervision of
those responses. In-depth insights into risk management methodologies and strategies will be found in Appendix.
While this project may differ in objectives and characteristics from others, the fundamentals of risk management
remain universally applicable. By devising a comprehensive risk management plan, the UNSW Student Network
Project can adeptly navigate the inevitable challenges and keep the project on a smooth course. This plan will
provide invaluable assistance to the project team, allowing them to develop a deeper understanding of potential
risks and take the necessary steps to mitigate any adverse impacts on the project's progress.
10.2 Risk Identification (Risk Breakdown Structure)
The team utilizes the Risk Breakdown Structure methodology to identify and categorize risks. This is achieved by
assessing project risks, developing contingency plans, and prioritizing them in a risk register using a severity matrix.
10.2.1 Project risks
• Technical Risk:
Insufficient Server Resources: Insufficient server resources during peak usage cause slow system
performance or system downtime.
Website Not User-Friendly: Unclear UI, or confusing interfaces can cause difficult to use the system.
Functions Not Working Properly: Some functions not well designed and the effectiveness of the system will
decrease.
• Budget Risks:
Inaccurate Cost Estimations: The risk of initial cost estimates being incorrect.
Unforeseen Price Increases: The risk of unexpected price increase in equipment, or software required for the
project.
Supplier Reliability: The risk of selected suppliers not delivering goods or services on time.
Budget Overruns: Exceeding the procurement budget due to unexpected costs, supplier price change.
• Security Risk:
Database Information Leakage: Data breach or vulnerability that leads to database information.
API Permission Lose Control: Unauthorized access may occur.
• Stakeholder Risk:
Not Meeting the Expectations of Stakeholders: Failing to meet stakeholder expectations.
Not Meeting Legal Requirements: Non-compliance with legal and regulatory requirements will result in legal
actions, fines.
Poor Communication with Stakeholders: Ineffective communication with stakeholders may result in
misunderstandings.
10.3 Risk Assessment
The Risk Assessment aims to provide a comprehensive evaluation of potential risks and uncertainties that may
impact our project's success. It is a critical component of our project management process, allowing us to identify,
analyse, and mitigate risks effectively.
This is the Risk Assessment Matrix:

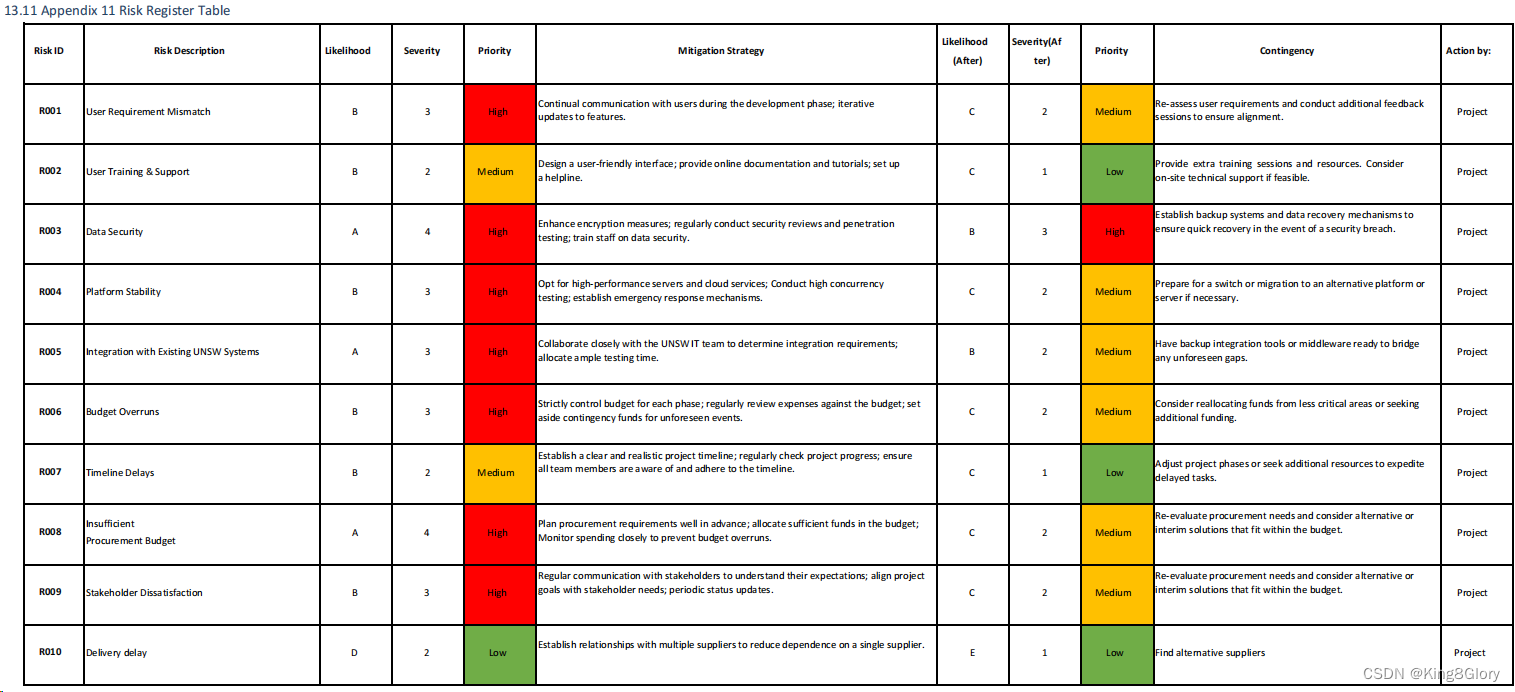
10.4 Risk Register
The Risk Register is a structured document that provides a comprehensive overview of identified risks within our
project or procurement process. This essential tool facilitates effective risk management by recording critical
information about each risk.
Risk Register Table can be found in Appendix 11.
After changing request:
10 Risk Management
10.1 Overview of Risk Management
In the realm of most projects, it's almost a given that certain tasks won't neatly fit within the planned timelines and
budgets. Consequently, it becomes essential to craft a well-thought-out risk management plan – one that can help
identify, evaluate, respond to, monitor, and report potential risks. The risk management blueprint for the UNSW
Student Network Project will meticulously adhere to the recommended PMBOK process to spell out how risks will be
assessed and addressed.
The UNSW Student Network Project's risk management strategy will go through various phases, encompassing risk
management planning, risk pinpointing, risk evaluation, the formulation of risk responses, and the supervision of
those responses. In-depth insights into risk management methodologies and strategies will be found in Appendix.
While this project may differ in objectives and characteristics from others, the fundamentals of risk management
remain universally applicable. By devising a comprehensive risk management plan, the UNSW Student Network
Project can adeptly navigate the inevitable challenges and keep the project on a smooth course. This plan will
provide invaluable assistance to the project team, allowing them to develop a deeper understanding of potential
risks and take the necessary steps to mitigate any adverse impacts on the project's progress.
Due to changes in the project plan, the risk assessment will change, which will mainly be reflected in changes in the
budget, changes in the estimated completion time of the project, and changes in procurement management.
25
10.2 Risk Identification (Risk Breakdown Structure)
The team utilizes the Risk Breakdown Structure methodology to identify and categorize risks. This is achieved by
assessing project risks, developing contingency plans, and prioritizing them in a risk register using a severity matrix.
10.2.1 Project risks
• Technical Risk:
Insufficient Server Resources: Insufficient server resources during peak usage cause slow system
performance or system downtime.
Website Not User-Friendly: Unclear UI, or confusing interfaces can cause difficult to use the system.
Functions Not Working Properly: Some functions not well designed and the effectiveness of the system will
decrease.
Slow development progress: The estimated completion time of the project is shortened, requiring faster
development speed.
• Budget Risks:
Inaccurate Cost Estimations: The risk of initial cost estimates being incorrect.
Unforeseen Price Increases: The risk of unexpected price increase in equipment, or software required for the
project.
Supplier Reliability: The risk of selected suppliers not delivering goods or services on time.
Budget Overruns: Exceeding the procurement budget due to unexpected costs, supplier price change.
Budget changes: As the project schedule is completed ahead of schedule, there will be changes to the
budget.
• Security Risk:
Database Information Leakage: Data breach or vulnerability that leads to database information.
API Permission Lose Control: Unauthorized access may occur.
• Stakeholder Risk:
Not Meeting the Expectations of Stakeholders: Failing to meet stakeholder expectations.
Not Meeting Legal Requirements: Non-compliance with legal and regulatory requirements will result in legal
actions, fines.
• Poor Communication with Stakeholders: Ineffective communication with stakeholders may result in
misunderstandings.
Due to changes in the project plan, the following is required:
• Delivery Delays: Due to changes in the project plan, the likelihood of delivery delays occurring for various
reasons will significantly increase.
• Supplier Inability to Meet Requirements: Due to changes in the project plan, the originally planned
suppliers may not be able to meet the supply requirements.




















 604
604











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








