这两天都在看红黑树,第一次听说这种数据结构是在大学,当时听不大懂,第二次是在一篇博客上面了解到,当时是分析的jdk1.8的ConcurrentHashMap当某一个链表的节点数达到8个会采用红黑树的数据结构,当时没看懂,后面查看很多博客,也翻阅了数据结构的书,稍微理解了很多。
概念和源码
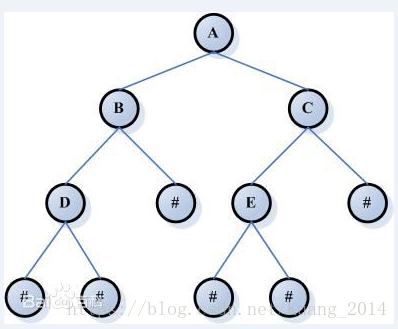
二叉树:二叉树是一个连通的无环图,并且每一个顶点的度不大于3。有根二叉树还要满足根结点的度不大于2。有了根结点之后,每个顶点定义了唯一的父结点,和最多2个子结点。
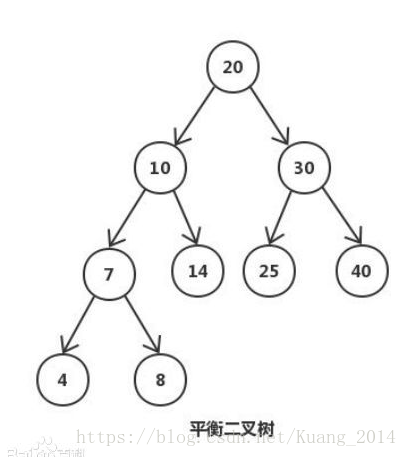
平衡二叉树:平衡二叉树又被称为AVL树(区别于AVL算法),它是一棵二叉排序树,且具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
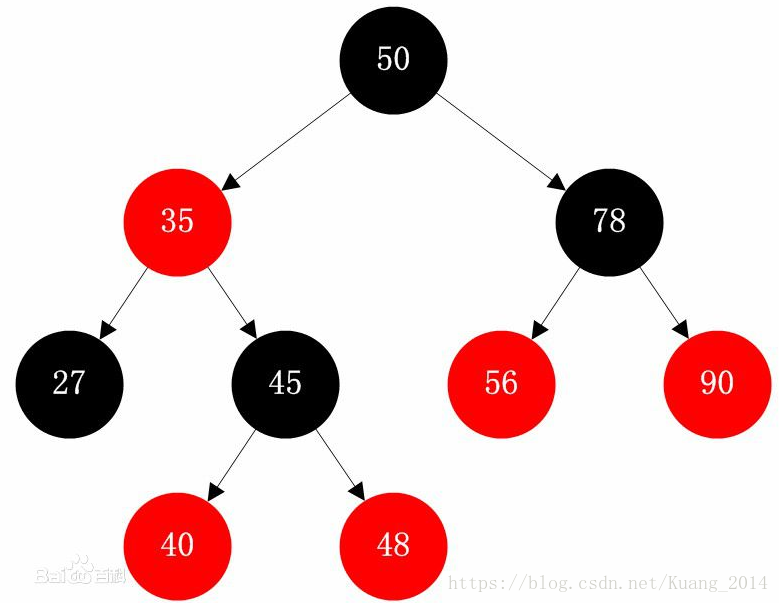
红黑树:红黑树又称红-黑二叉树,它首先是一颗二叉树,它具体二叉树所有的特性。同时红黑树更是一颗自平衡的排序二叉树(平衡二叉树的一种实现方式)。
红黑树具有5个特性:
性质1. 节点是红色或黑色。
性质2. 根节点是黑色。
性质3 每个叶节点(NIL节点,空节点)是黑色的。
性质4 每个红色节点的两个子节点都是黑色。(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
性质5. 从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
红黑树在函数式编程中也特别有用,在这里它们是最常用的持久数据结构之一,它们用来构造关联数组和集合,在突变之后它们能保持为以前的版本。除了O(log n)的时间之外,红黑树的持久版本对每次插入或删除需要O(log n)的空间。
网上找到一个红黑树的源码实现:
/**
* Java 语言: 红黑树
*
* @author skywang
* @date 2013/11/07
*/
public class RBTree<T extends Comparable<T>> {
private RBTNode<T> mRoot; // 根结点
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
public class RBTNode<T extends Comparable<T>> {
boolean color; // 颜色
T key; // 关键字(键值)
RBTNode<T> left; // 左孩子
RBTNode<T> right; // 右孩子
RBTNode<T> parent; // 父结点
public RBTNode(T key, boolean color, RBTNode<T> parent, RBTNode<T> left, RBTNode<T> right) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public T getKey() {
return key;
}
public String toString() {
return ""+key+(this.color==RED?"(R)":"B");
}
}
public RBTree() {
mRoot=null;
}
private RBTNode<T> parentOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node!=null ? node.parent : null;
}
private boolean colorOf(RBTNode<T> node) {
return node!=null ? node.color : BLACK;
}
private boolean isRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
return ((node!=null)&&(node.color==RED)) ? true : false;
}
private boolean isBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
return !isRed(node);
}
private void setBlack(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node!=null)
node.color = BLACK;
}
private void setRed(RBTNode<T> node) {
if (node!=null)
node.color = RED;
}
private void setParent(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
if (node!=null)
node.parent = parent;
}
private void setColor(RBTNode<T> node, boolean color) {
if (node!=null)
node.color = color;
}
/*
* 前序遍历"红黑树" 中左右
*/
private void preOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null) {
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
preOrder(tree.left);
preOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void preOrder() {
preOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 中序遍历"红黑树" 左中右
*/
private void inOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null) {
inOrder(tree.left);
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
inOrder(tree.right);
}
}
public void inOrder() {
inOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* 后序遍历"红黑树" 左右中
*/
private void postOrder(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if(tree != null)
{
postOrder(tree.left);
postOrder(tree.right);
System.out.print(tree.key+" ");
}
}
public void postOrder() {
postOrder(mRoot);
}
/*
* (递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private RBTNode<T> search(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
if (x==null)
return x;
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
return search(x.left, key);
else if (cmp > 0)
return search(x.right, key);
else
return x;
}
public RBTNode<T> search(T key) {
return search(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* (非递归实现)查找"红黑树x"中键值为key的节点
*/
private RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(RBTNode<T> x, T key) {
while (x!=null) {
int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
x = x.right;
else
return x;
}
return x;
}
public RBTNode<T> iterativeSearch(T key) {
return iterativeSearch(mRoot, key);
}
/*
* 查找最小结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最小结点。
*/
private RBTNode<T> minimum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while(tree.left != null)
tree = tree.left;
return tree;
}
public T minimum() {
RBTNode<T> p = minimum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/*
* 查找最大结点:返回tree为根结点的红黑树的最大结点。
*/
private RBTNode<T> maximum(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree == null)
return null;
while(tree.right != null)
tree = tree.right;
return tree;
}
public T maximum() {
RBTNode<T> p = maximum(mRoot);
if (p != null)
return p.key;
return null;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的后继结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值大于该结点"的"最小结点"。
*/
public RBTNode<T> successor(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在右孩子,则"x的后继结点"为 "以其右孩子为根的子树的最小结点"。
if (x.right != null)
return minimum(x.right);
// 如果x没有右孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则"x的后继结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (02) x是"一个右孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有左孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的后继结点"。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y!=null) && (x==y.right)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 找结点(x)的前驱结点。即,查找"红黑树中数据值小于该结点"的"最大结点"。
*/
public RBTNode<T> predecessor(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 如果x存在左孩子,则"x的前驱结点"为 "以其左孩子为根的子树的最大结点"。
if (x.left != null)
return maximum(x.left);
// 如果x没有左孩子。则x有以下两种可能:
// (01) x是"一个右孩子",则"x的前驱结点"为 "它的父结点"。
// (01) x是"一个左孩子",则查找"x的最低的父结点,并且该父结点要具有右孩子",找到的这个"最低的父结点"就是"x的前驱结点"。
RBTNode<T> y = x.parent;
while ((y!=null) && (x==y.left)) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(x)进行左旋转
*
* 左旋示意图(对节点x进行左旋):
* px px
* / /
* x y
* / \ --(左旋)-. / \ #
* lx y x ry
* / \ / \
* ly ry lx ly
*
*
*/
private void leftRotate(RBTNode<T> x) {
// 设置x的右孩子为y
RBTNode<T> y = x.right;
// 将 “y的左孩子” 设为 “x的右孩子”;
// 如果y的左孩子非空,将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子的父亲”
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != null)
y.left.parent = x;
// 将 “x的父亲” 设为 “y的父亲”
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = y; // 如果 “x的父亲” 是空节点,则将y设为根节点
} else {
if (x.parent.left == x)
x.parent.left = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
else
x.parent.right = y; // 如果 x是它父节点的左孩子,则将y设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “x” 设为 “y的左孩子”
y.left = x;
// 将 “x的父节点” 设为 “y”
x.parent = y;
}
/*
* 对红黑树的节点(y)进行右旋转
*
* 右旋示意图(对节点y进行左旋):
* py py
* / /
* y x
* / \ --(右旋)-. / \ #
* x ry lx y
* / \ / \ #
* lx rx rx ry
*
*/
private void rightRotate(RBTNode<T> y) {
// 设置x是当前节点的左孩子。
RBTNode<T> x = y.left;
// 将 “x的右孩子” 设为 “y的左孩子”;
// 如果"x的右孩子"不为空的话,将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子的父亲”
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right != null)
x.right.parent = y;
// 将 “y的父亲” 设为 “x的父亲”
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null) {
this.mRoot = x; // 如果 “y的父亲” 是空节点,则将x设为根节点
} else {
if (y == y.parent.right)
y.parent.right = x; // 如果 y是它父节点的右孩子,则将x设为“y的父节点的右孩子”
else
y.parent.left = x; // (y是它父节点的左孩子) 将x设为“x的父节点的左孩子”
}
// 将 “y” 设为 “x的右孩子”
x.right = y;
// 将 “y的父节点” 设为 “x”
y.parent = x;
}
/*
* 红黑树插入修正函数
*
* 在向红黑树中插入节点之后(失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* node 插入的结点 // 对应《算法导论》中的z
*/
private void insertFixUp(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> parent, gparent;
// 若“父节点存在,并且父节点的颜色是红色”
while (((parent = parentOf(node))!=null) && isRed(parent)) {
gparent = parentOf(parent);
//若“父节点”是“祖父节点的左孩子”
if (parent == gparent.left) {
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.right;
if ((uncle!=null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// Case 2条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子
if (parent.right == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
leftRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子。
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
rightRotate(gparent);
} else { //若“z的父节点”是“z的祖父节点的右孩子”
// Case 1条件:叔叔节点是红色
RBTNode<T> uncle = gparent.left;
if ((uncle!=null) && isRed(uncle)) {
setBlack(uncle);
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
node = gparent;
continue;
}
// Case 2条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是左孩子
if (parent.left == node) {
RBTNode<T> tmp;
rightRotate(parent);
tmp = parent;
parent = node;
node = tmp;
}
// Case 3条件:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右孩子。
setBlack(parent);
setRed(gparent);
leftRotate(gparent);
}
}
// 将根节点设为黑色
setBlack(this.mRoot);
}
/*
* 将结点插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* node 插入的结点 // 对应《算法导论》中的node
*/
private void insert(RBTNode<T> node) {
int cmp;
RBTNode<T> y = null;
RBTNode<T> x = this.mRoot;
// 1. 将红黑树当作一颗二叉查找树,将节点添加到二叉查找树中。
while (x != null) {
y = x;
cmp = node.key.compareTo(x.key);
if (cmp < 0)
x = x.left;
else
x = x.right;
}
node.parent = y;
if (y!=null) {
cmp = node.key.compareTo(y.key);
if (cmp < 0)
y.left = node;
else
y.right = node;
} else {
this.mRoot = node;
}
// 2. 设置节点的颜色为红色
node.color = RED;
// 3. 将它重新修正为一颗二叉查找树
insertFixUp(node);
}
/*
* 新建结点(key),并将其插入到红黑树中
*
* 参数说明:
* key 插入结点的键值
*/
public void insert(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node=new RBTNode<T>(key,BLACK,null,null,null);
// 如果新建结点失败,则返回。
if (node != null)
insert(node);
}
/*
* 红黑树删除修正函数
*
* 在从红黑树中删除插入节点之后(红黑树失去平衡),再调用该函数;
* 目的是将它重新塑造成一颗红黑树。
*
* 参数说明:
* node 待修正的节点
*/
private void removeFixUp(RBTNode<T> node, RBTNode<T> parent) {
RBTNode<T> other;
while ((node==null || isBlack(node)) && (node != this.mRoot)) {
if (parent.left == node) {
other = parent.right;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
leftRotate(parent);
other = parent.right;
}
if ((other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right==null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.right==null || isBlack(other.right)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.left);
setRed(other);
rightRotate(other);
other = parent.right;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.right);
leftRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
} else {
other = parent.left;
if (isRed(other)) {
// Case 1: x的兄弟w是红色的
setBlack(other);
setRed(parent);
rightRotate(parent);
other = parent.left;
}
if ((other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) &&
(other.right==null || isBlack(other.right))) {
// Case 2: x的兄弟w是黑色,且w的俩个孩子也都是黑色的
setRed(other);
node = parent;
parent = parentOf(node);
} else {
if (other.left==null || isBlack(other.left)) {
// Case 3: x的兄弟w是黑色的,并且w的左孩子是红色,右孩子为黑色。
setBlack(other.right);
setRed(other);
leftRotate(other);
other = parent.left;
}
// Case 4: x的兄弟w是黑色的;并且w的右孩子是红色的,左孩子任意颜色。
setColor(other, colorOf(parent));
setBlack(parent);
setBlack(other.left);
rightRotate(parent);
node = this.mRoot;
break;
}
}
}
if (node!=null)
setBlack(node);
}
/*
* 删除结点(node),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* node 删除的结点
*/
private void remove(RBTNode<T> node) {
RBTNode<T> child, parent;
boolean color;
// 被删除节点的"左右孩子都不为空"的情况。
if ( (node.left!=null) && (node.right!=null) ) {
// 被删节点的后继节点。(称为"取代节点")
// 用它来取代"被删节点"的位置,然后再将"被删节点"去掉。
RBTNode<T> replace = node;
// 获取后继节点
replace = replace.right;
while (replace.left != null)
replace = replace.left;
// "node节点"不是根节点(只有根节点不存在父节点)
if (parentOf(node)!=null) {
if (parentOf(node).left == node)
parentOf(node).left = replace;
else
parentOf(node).right = replace;
} else {
// "node节点"是根节点,更新根节点。
this.mRoot = replace;
}
// child是"取代节点"的右孩子,也是需要"调整的节点"。
// "取代节点"肯定不存在左孩子!因为它是一个后继节点。
child = replace.right;
parent = parentOf(replace);
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = colorOf(replace);
// "被删除节点"是"它的后继节点的父节点"
if (parent == node) {
parent = replace;
} else {
// child不为空
if (child!=null)
setParent(child, parent);
parent.left = child;
replace.right = node.right;
setParent(node.right, replace);
}
replace.parent = node.parent;
replace.color = node.color;
replace.left = node.left;
node.left.parent = replace;
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
return ;
}
if (node.left !=null) {
child = node.left;
} else {
child = node.right;
}
parent = node.parent;
// 保存"取代节点"的颜色
color = node.color;
if (child!=null)
child.parent = parent;
// "node节点"不是根节点
if (parent!=null) {
if (parent.left == node)
parent.left = child;
else
parent.right = child;
} else {
this.mRoot = child;
}
if (color == BLACK)
removeFixUp(child, parent);
node = null;
}
/*
* 删除结点(z),并返回被删除的结点
*
* 参数说明:
* tree 红黑树的根结点
* z 删除的结点
*/
public void remove(T key) {
RBTNode<T> node;
if ((node = search(mRoot, key)) != null)
remove(node);
}
/*
* 销毁红黑树
*/
private void destroy(RBTNode<T> tree) {
if (tree==null)
return ;
if (tree.left != null)
destroy(tree.left);
if (tree.right != null)
destroy(tree.right);
tree=null;
}
public void clear() {
destroy(mRoot);
mRoot = null;
}
/*
* 打印"红黑树"
*
* key -- 节点的键值
* direction -- 0,表示该节点是根节点;
* -1,表示该节点是它的父结点的左孩子;
* 1,表示该节点是它的父结点的右孩子。
*/
private void print(RBTNode<T> tree, T key, int direction) {
if(tree != null) {
if(direction==0) // tree是根节点
System.out.printf("%2d(B) is root\n", tree.key);
else // tree是分支节点
System.out.printf("%2d(%s) is %2d's %6s child\n", tree.key, isRed(tree)?"R":"B", key, direction==1?"right" : "left");
print(tree.left, tree.key, -1);
print(tree.right,tree.key, 1);
}
}
public void print() {
if (mRoot != null)
print(mRoot, mRoot.key, 0);
}
}里面具体实现了插入,删除,左旋,右旋,前序遍历,中序遍历,后序遍历,查找结点(两种方式),找最小节点,找最大节点等方法。
性能测试:
看完源码,我便想测试一下红黑树的插入,删除,查询性能,我分别用了数组结构的ArrayList,数组+链表实现的HashSet来做测试,hashSet底层实现就是HashMap,也是我们经常用到的数据结构,一并测试一下。
public static void main(String[] args) {
int size = 100000;
List<String> testData = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> needDel = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
testData.add(1000000 + i + "");
//这样取比较均匀
if (i % 19 == 0) {
needDel.add(1000000 + i + "");
}
}
Collections.shuffle(testData);
System.out.println("基本数据长度:"+size);
System.out.println("需要删除的长度" + needDel.size());
testRBTree(testData,needDel);
testHashSet(testData,needDel);
testArrayList(testData, needDel);
}
private static void testRBTree(List<String> list, List<String> del) {
System.out.println("红黑树:");
RBTree<String> tree = new RBTree<String>();
long a = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : list) {
tree.insert(str);
}
long b = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("插入时间:" + (b - a));
long c = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : del) {
tree.search(str);
}
long d = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("查询时间:" + (d - c));
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : del) {
tree.remove(str);
}
long f = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("删除时间:" + (f - e));
}
private static void testHashSet(List<String> list, List<String> del) {
System.out.println("集合:");
Set<String> set = new HashSet<String>();
long a = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : list) {
set.add(str);
}
long b = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("插入时间:" + (b - a));
long c = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : del) {
set.contains(str);
}
long d = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("查询时间:" + (d - c));
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : del) {
set.remove(str);
}
long f = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("删除时间:" + (f - e));
}
private static void testArrayList(List<String> oldList, List<String> del) {
System.out.println("数列:");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
long a = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : oldList) {
list.add(str);
}
long b = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("插入时间:" + (b - a));
long c = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : del) {
list.contains(str);
}
long d = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("查询时间:" + (d - c));
long e = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (String str : del) {
list.remove(str);
}
long f = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("删除时间:" + (f - e));
}分别测试10w,500w,1000w三种数据结构的增删改耗时,由于arrayList在10w的时候删除和按对象查找数据太慢,后面两个数据量就没有必要再做了。
实验数据:
基本数据长度:100000
需要删除的长度5263
红黑树:
插入时间:125
查询时间:16
删除时间:0
集合:
插入时间:94
查询时间:0
删除时间:15
数列:
插入时间:16
查询时间:5886
删除时间:6027
基本数据长度:1000000
需要删除的长度52631
红黑树:
插入时间:2144
查询时间:63
删除时间:79
集合:
插入时间:510
查询时间:37
删除时间:36
基本数据长度:5000000
需要删除的长度263157
红黑树:
插入时间:16146
查询时间:274
删除时间:250
集合:
插入时间:4904
查询时间:145
删除时间:125
基本数据长度:10000000
需要删除的长度526315
红黑树:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Java heap space
at com.zengame.snipertest.collections.RBTree.insert(RBTree.java:446)
at com.zengame.snipertest.collections.RBTreeTest.testRBTree(RBTreeTest.java:47)
at com.zengame.snipertest.collections.RBTreeTest.main(RBTreeTest.java:36)
从上面的结果深有体会:
1.数据量1w以下,不管你是增删改都建议用ArrayList,速度都极快,之后不建议是因为扩容的时候需要复制,查找的时候会全部遍历,删除的时候需要复制,成本太大。
2.数据量达到1w以上,如果没有删除操作还是建议用ArrayList,通过索引get和insert操作还是其他数据结构中最快的。
3.数据量达到1w以上,有删除操作,建议用HashSet数据结构,hashSet性能稍微优于RBTree。
4.数据量达到1w以上,如果需要有排序操作的,不用考虑了,直接用RBTree,因为他的中序遍历就是排好序的。
其实每种数据结构都有自己的特点,他们组合之后又会产生一些奇妙的结果,就像hashSet,他就是数组和链表的集合,当初设计这些数据结构的人真是牛逼。





















 3925
3925











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








