本节关注 yield curve strategy,先介绍一些相关概念,再介绍在不同 yield curve 变化下对应的策略(有预期就应该属于active strategy)
Yield curve slope is often defined as the difference in basis points between the yield-to-maturity on a long-maturity bond and the yield-to-maturity on a shorter-maturity bond
Yield curve shape or curvature is the relationship between 长中短期的YTM,A common measure of yield curve curvature is the butterfly spread
butterfly spread 的公式其实是(midpoint YTM 减 长短期YTM的(线性)中点)/2,所以convcave(凹)形状的 YTM 就是有 positive butterfly spread;而convex(凸)就是negative(即朝第四象限方向凸出,下图为convex):

一般的yield curve应认为是有positive butterfly spread:
最易混淆的地方是接着有引入了2个非常相似的概念,我按目前的理解整理了一下:
butterfly move 和 butterfly view
positive butterfly movement是蝴蝶起飞(即中间下降,两端上升),往往是会产生negative butterfly spread
negative butterfly (spread) view 即 positive butterfly (move)
一般说 positive butterfly 是指 positive butterfly (move)即中期 YTM 降,两端升,所以要long bullet(bond)& short barbell(bonds)
由固收2的知识 portfolio convexity statistic 可知:
All else equal, bonds with longer durations have higher convexity than bonds with shorter durations
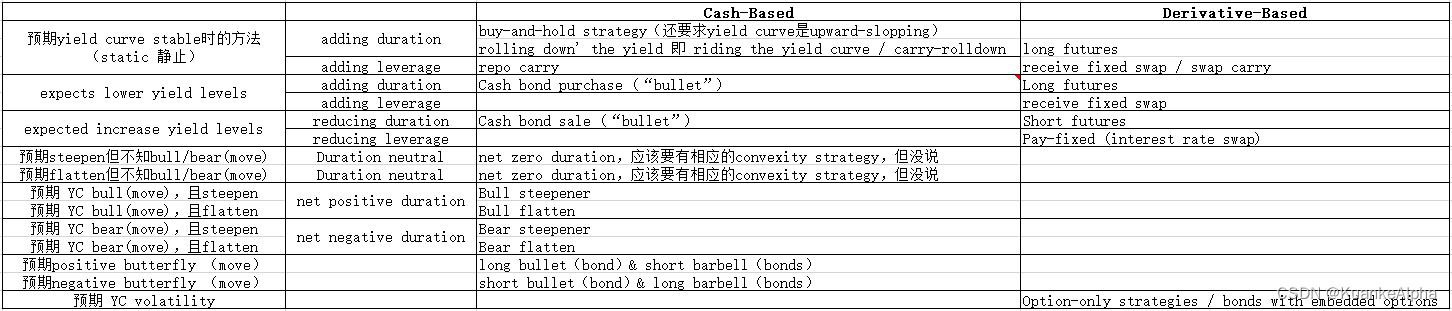
零散的概念介绍完,直接总结不同expected yield curve move下对应的策略,主要是两大类 cash-based 和 derivative-based:
两个简单的小计算:
(1)持有一个10年期的半年付息的 coupon = 4% 的bond,YTM=5%,预期半年后YTM下降50bp
Price appreciation = PV(1/Y=5%, N=20, CF=100*4%/2, FV=100) - PV(1/Y=5%-0.005%, N=19, CF=100*4%/2, FV=100)
可以将price appreciation拆分成 rolldown return 和 E(change in yield curve):
rolldown return = PV(1/Y=5%, N=20, CF=100*4%/2, FV=100) - PV(1/Y=5%, N=19, CF=100*4%/2, FV=100)
E(change in yield curve) = PV(1/Y=5%, N=19, CF=100*4%/2, FV=100) - PV(1/Y=5%-0.005%, N=19, CF=100*4%/2, FV=100)
* rolldown return 是假设 yield curve unchange
* 计 E(xxx) 要其他不变,所以要用 YTM 折19期 vs 新的 YTM 折19期
(2)持有一个10年期的半年付息的 receive fixed swap,swap rate = 4%,预期半年后 swap rate下降50bp
Swap MTM (mark-to-market) gain = fixed leg - floating leg = PV(1/Y=(4%-0.005%)/2, N=19, CF=4%/2, FV=100) - 100,其中floating leg = par
目前讲的应该都是instantaneous(立即的)yield curve change
a divergent rate level view implies an expectation of a parallel shift in the yield curve
在固收2的笔记中展示的 upward/downward & steepen/flatten 图其实不是很准确,因为steepen/flatten 是指 yield curve 的变化而不是一个静止的形态:
steepen 的核心是 long-term 与 short-term YTM 是 widen;而 flatten 则是 narrowing
steepen为例:长期升得比短期多;长期跌得比短期少;长期升短期跌
由上面的策略总结图可知:bull steepen 是一种strategy,同时也可以是描述 bull(move)steepen(move),要根据具体情境理解
Interest rate put and call options are generally based upon a bond’s price, not yield-to-maturity
补充一些策略:

call option adds convexity to the portfolio
涉及跨币种的:
carry trade across currencies:an investor borrows short-term in one currency and invests in another higher-yielding currency(其实可以也是short-term,但higher-yield的)
还有一种 cross-currency carry trade,这其实就是carry trade(借低利率的去投高利率的,只是涉及跨币种而已),另类投资章节补充了carry trade的特点:
Interest rate and credit risks are hedged because long and short positions have the same duration and credit exposure
the key concern is liquidity risk
另一个例子:
USD-JPY cross-currency basis swap involving:the exchange of floating JPY for floating USD payments & a pay-fixed USD interest rate swap(pay fixed 就是 basis)
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








