obs_graphics_thread
在 obs_graphics_thread 线程中
所有画面源的合成,画面显示以及视频输出都在这个函数里触发
主要有以下三点
- 根据设置的视频输出帧率,每间隔固定时间处理所有源的输入,并融合成一张图像缓存起来
- 如果开启推流和录像,则通过信号通知视频输出线程编码输出视频帧
- 渲染视频到UI窗口,使用户可以编辑推流画面
bool obs_graphics_thread_loop(struct obs_graphics_context *context)
{
// 记录处理当前帧的绝对时间,用来统计一帧图像耗时
uint64_t frame_start = os_gettime_ns();
uint64_t frame_time_ns;
// raw_active表示是否开始视频输出,控制着视频渲染线程和视频输出线程之间的通信
update_active_states();
profile_start(context->video_thread_name);
gs_enter_context(obs->video.graphics);
gs_begin_frame();
gs_leave_context();
//1. tick_sources()遍历每个sources;
//调用所有source的tick函数,更新添加的所有视频源一帧图像
//检查并处理视频的状态(show or hide)是否需要改变
profile_start(tick_sources_name);
context->last_time =
tick_sources(obs->video.video_time, context->last_time);
profile_end(tick_sources_name);
#ifdef _WIN32
MSG msg;
while (PeekMessage(&msg, NULL, 0, 0, PM_REMOVE)) {
TranslateMessage(&msg);
DispatchMessage(&msg);
}
#endif
//2. output_frame()输出当前视频帧
//负责图像的合成并缓存到视频帧队列,此时保存的是原始视频格式
//如果开启推流或者录像,会发送信号通知视频输出线程从视频帧队列取出一帧视频编码输出
profile_start(output_frame_name);
output_frames();
profile_end(output_frame_name);
//3. 调用render_displays()将当前视频画面显示在窗口中
//渲染视频帧到UI窗口
profile_start(render_displays_name);
render_displays();
profile_end(render_displays_name);
//执行需要在 obs_graphics_thread线程中处理的任务,通过obs_queue_task注册任务
//通过全局搜索 obs_queue_task注册任务接口,只有窗口采集,桌面采集两个源里面用到
//将这两个源的销毁工作放到渲染线程中去做
execute_graphics_tasks();
//计算处理一帧视频的耗时
frame_time_ns = os_gettime_ns() - frame_start;
profile_end(context->video_thread_name);
profile_reenable_thread();
//休眠 等待下一个间隔的到来
video_sleep(&obs->video, &obs->video.video_time, context->interval);
context->frame_time_total_ns += frame_time_ns;
context->fps_total_ns += (obs->video.video_time - context->last_time);
context->fps_total_frames++;
//休眠 等待下一个间隔的到来
if (context->fps_total_ns >= 1000000000ULL) {
// 计算视频的实际帧率
obs->video.video_fps =
(double)context->fps_total_frames /
((double)context->fps_total_ns / 1000000000.0);
//计算处理一帧图像的平均耗时,可以理解为生成一帧图像的耗时
//如果耗时大于设置fps的帧间隔,则视频处理能力不足,推流的实际帧率不满足设置的帧率
//视频的处理存在性能瓶颈,需要做优化处理
obs->video.video_avg_frame_time_ns =
context->frame_time_total_ns /
(uint64_t)context->fps_total_frames;
context->frame_time_total_ns = 0;
context->fps_total_ns = 0;
context->fps_total_frames = 0;
}
return !stop_requested();
} 视频渲染线程与视频输出线程之间的配合
视频渲染线程负责生产视频帧,视频输出线程负责消耗视频帧,两个线程共同操作一个视频帧缓存队列,是一个标准的1对1生产者-消费者模型。
两个线程的操作的视频帧缓存队列定义在 obs_core -> obs_core_video -> video_output -> cache
可以看到是一个数组实现的一个固定大小的队列
struct obs_core {
...
struct obs_core_video video;
}
typedef struct video_output video_t;
struct obs_core_video {
...
video_t *video;
}
struct video_output {
...
struct cached_frame_info cache[MAX_CACHE_SIZE];
}
static inline void output_frame(struct obs_core_video_mix *video)
{
const bool raw_active = video->raw_was_active;
const bool gpu_active = video->gpu_was_active;
//当前纹理坐标 前一个纹理坐标
int cur_texture = video->cur_texture;
int prev_texture = cur_texture == 0 ? NUM_TEXTURES - 1
: cur_texture - 1;
//定义栈变量frame 用来存放从显存里面map出来的图像数据
struct video_data frame;
bool frame_ready = 0;
memset(&frame, 0, sizeof(struct video_data));
//进入obs图形子系统
profile_start(output_frame_gs_context_name);
gs_enter_context(obs->video.graphics);
profile_start(output_frame_render_video_name);
GS_DEBUG_MARKER_BEGIN(GS_DEBUG_COLOR_RENDER_VIDEO,
output_frame_render_video_name);
//渲染一帧视频纹理到output_texture
render_video(video, raw_active, gpu_active, cur_texture);
GS_DEBUG_MARKER_END();
profile_end(output_frame_render_video_name);
if (raw_active) {
//通过调用obs的图形子系统api gs_stagesurface_map 从surfaces获取到显存的图像数据指针
//将图像数据指针存放在上面定义的栈变量frame中,
//obs图形子系统对openGL D3D的图形api进行了封装,对外提供统一接口进行图像的渲染和存取
//这也是obs-studio项目中牛逼的一个技术点
profile_start(output_frame_download_frame_name);
frame_ready = download_frame(video, prev_texture, &frame);
profile_end(output_frame_download_frame_name);
}
profile_start(output_frame_gs_flush_name);
gs_flush();
profile_end(output_frame_gs_flush_name);
//离开obs图形子系统
gs_leave_context();
profile_end(output_frame_gs_context_name);
//如果开启推流或者录制,并且 download_frame成功,则输出视频帧
if (raw_active && frame_ready) {
struct obs_vframe_info vframe_info;
circlebuf_pop_front(&video->vframe_info_buffer, &vframe_info,
sizeof(vframe_info));
//给视频帧打上时间戳
frame.timestamp = vframe_info.timestamp;
profile_start(output_frame_output_video_data_name);
//保存视频帧到队列,并通知视频发送线程工作
output_video_data(video, &frame, vframe_info.count);
profile_end(output_frame_output_video_data_name);
}
if (++video->cur_texture == NUM_TEXTURES)
video->cur_texture = 0;
}调用 render_video(),渲染视频数据
static inline void render_video(struct obs_core_video_mix *video,
bool raw_active, const bool gpu_active,
int cur_texture)
{
gs_begin_scene();
gs_enable_depth_test(false);
gs_set_cull_mode(GS_NEITHER);
render_main_texture(video);
if (raw_active || gpu_active) {
gs_texture_t *const *convert_textures = video->convert_textures;
gs_stagesurf_t *const *copy_surfaces =
video->copy_surfaces[cur_texture];
size_t channel_count = NUM_CHANNELS;
gs_texture_t *output_texture = render_output_texture(video);
#ifdef _WIN32
if (gpu_active) {
convert_textures = video->convert_textures_encode;
copy_surfaces = video->copy_surfaces_encode;
channel_count = 1;
gs_flush();
}
#endif
if (video->gpu_conversion) {
render_convert_texture(video, convert_textures,
output_texture);
}
#ifdef _WIN32
if (gpu_active) {
gs_flush();
output_gpu_encoders(video, raw_active);
}
#endif
if (raw_active) {
stage_output_texture(video, cur_texture,
convert_textures, output_texture,
copy_surfaces, channel_count);
}
}
gs_set_render_target(NULL, NULL);
gs_enable_blending(true);
gs_end_scene();
}在开启推流和录像功能时,调用render_output_texture(),渲染输出帧,并保存在video->convert_textures和video->output_textures中;
调用stage_output_texture将画面保存到video->copy_surfaces;
再调用download_frame,从video->copy_surfaces中拷贝出当前视频帧数据到video_data *frame;
这样就拿到了需要输出的视频画面
将frame传入output_video_data(),在该函数中,调用video_output_lock_frame()函数,拷贝input->cache[last_add]给output_frame,需要注意的是,这个拷贝是将cache[]中的指针地址拷贝过来了,通过格式转换函数例如copy_rgb_frame,将input_frame中的数据内容拷贝到output_frame,实际上也就是将视频内容拷贝到了input->cache[last_add]中,再调用video_output_unlock_frame()函数,唤醒信号量video->update_semaphore,通知线程video_thread视频输出数据已就绪,执行数据输出、编码、rtmp推流。
函数output_video_data保存视频帧到缓存队列,并通知视频发送线程工作
static inline void output_video_data(struct obs_core_video_mix *video,
struct video_data *input_frame, int count)
{
const struct video_output_info *info;
//定义栈变量output_frame 其实待会是要将要缓存帧的首地址复制给他内部的data
struct video_frame output_frame;
bool locked;
//获取视频输出信息
info = video_output_get_info(video->video);
//如果有可以缓存的空间,就将缓存队列中可缓存空间的地址复制给output_frame
//output_frame就代理缓存视频的地址
//如果没有缓存空间返回false
locked = video_output_lock_frame(video->video, &output_frame, count,
input_frame->timestamp);
if (locked) {
//gpu_conversion在 OBSBasic::ResetVideo() 设置为true
if (video->gpu_conversion) {
//将图像数据从显存拷贝到内存
set_gpu_converted_data(&output_frame, input_frame,
info);
} else {
copy_rgbx_frame(&output_frame, input_frame, info);
}
//1.更新可缓存空间-1 2.发送信号量通知视频发送线程工作
video_output_unlock_frame(video->video);
}
}最后再调用render_displays()将当前视频画面显示在窗口中,sleep直到下一帧视频数据时间戳;
编码线程video_thread
在初始化视频时,启动了一个线程函数video_thread(),这个函数一直等待视频帧数据准备就绪的信号唤醒
static void *video_thread(void *param)
{
struct video_output *video = param;
os_set_thread_name("video-io: video thread");
const char *video_thread_name =
profile_store_name(obs_get_profiler_name_store(),
"video_thread(%s)", video->context.info.name);
while (os_sem_wait(video->data.update_semaphore) == 0) {
if (video->context.stop)
break;
profile_start(video_thread_name);
while (!video->context.stop && !video_output_cur_frame(&video->data)) {
video->data.total_frames++;
}
video->data.total_frames++;
profile_end(video_thread_name);
profile_reenable_thread();
}
return NULL;
}在输出的一帧视频画面合成后唤醒该信号,在video_output_unlock_frame()里触发该信号
void video_output_unlock_frame(video_d_t *video)
{
if (!video) return;
pthread_mutex_lock(&video->data_mutex);
video->available_frames--;
os_sem_post(video->update_semaphore);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&video->data_mutex);
}等到信号后执行video_output_cur_frame函数,获取视频缓存中第一帧,从video->inputs中获取输出类型调用编码器绑定的回调函数input->callback,receive_video(),进行视频数据编码,而video->update_semaphore 信号量是在所有画面合成完成后被唤醒;
video->inputs中保存的是输出类型,包括推流和录像,后面将会说到是如何添加的。
在receive_video中调用do_encode()进行编码;
在do_encode中根据不同的编码器名称进行编码回调,各个编码器模块在程序开始加载的时候会进行注册,编码完成后调用绑定的编码完成回调

渲染

display 即需要将frame渲染到的窗口,这里遍历一遍,调用

在上面的接口中,调用draw接口 ,callback->draw即
void OBSBasic::RenderMain(void *data, uint32_t, uint32_t)
设置回调的地方:
auto addDisplay = [this](OBSQTDisplay *window) {
obs_display_add_draw_callback(window->GetDisplay(),
OBSBasic::RenderMain, this);
struct obs_video_info ovi;
if (obs_get_video_info(&ovi))
ResizePreview(ovi.base_width, ovi.base_height);
};
connect(ui->preview, &OBSQTDisplay::DisplayCreated, addDisplay);其中ui->preview 即obs的预览区域:
预览窗口
参照OBSBasic.ui

在 ui_OBSBasic.h中,可以看到
预览窗口对应的是 OBSBasicPreview : public OBSQTDisplay
这部分是怎么渲染的呢,
在void OBSBasic::OBSInit() 初始化中,有这么一段语句
auto addDisplay = [this] (OBSQTDisplay *window)
{
obs_display_add_draw_callback(window->GetDisplay(),
OBSBasic::RenderMain, this);
struct obs_video_info ovi;
if (obs_get_video_info(&ovi))
ResizePreview(ovi.base_width, ovi.base_height);
};
connect(ui->preview, &OBSQTDisplay::DisplayCreated, addDisplay);追踪下DisplayCreated信号
void OBSQTDisplay::CreateDisplay()
{
if (display || !windowHandle()->isExposed())
return;
QSize size = GetPixelSize(this);
gs_init_data info = {};
info.cx = size.width();
info.cy = size.height();
info.format = GS_RGBA;
info.zsformat = GS_ZS_NONE;
QTToGSWindow(winId(), info.window);
display = obs_display_create(&info);
emit DisplayCreated(this);
}由此可知,当预览窗口创建时,会发出displayCreated信号,该信号会触发addDisplay ,在此槽函数中,添加了OBS 渲染函数
/**
* Adds a draw callback for this display context
*
* @param display The display context.
* @param draw The draw callback which is called each time a frame
* updates.
* @param param The user data to be associated with this draw callback.
*/
EXPORT void obs_display_add_draw_callback(obs_display_t *display,
void (*draw)(void *param, uint32_t cx, uint32_t cy),
void *param);
/** Removes a draw callback for this display context */
EXPORT void obs_display_remove_draw_callback(obs_display_t *display,
void (*draw)(void *param, uint32_t cx, uint32_t cy),
void *param);摄像头数据的采集与渲染
采集
在win-dshow线程中
在 win-dshow中采集到摄像头数据回调
E:\opensrc\obs\obs-studio\plugins\win-dshow\win-dshow.cpp
void DShowInput::OnVideoData(const VideoConfig &config, unsigned char *data,
size_t size, long long startTime,
long long endTime, long rotation) {
......
获取数据帧
} else if (videoConfig.format == VideoFormat::YVYU ||
videoConfig.format == VideoFormat::YUY2 ||
videoConfig.format == VideoFormat::HDYC ||
videoConfig.format == VideoFormat::UYVY) {
frame.data[0] = data;
frame.linesize[0] = cx * 2;
}
......
拷贝该数据帧
obs_source_output_video2(source, &frame);
}
void obs_source_output_video2(obs_source_t *source,
const struct obs_source_frame2 *frame)
{
if (destroying(source))
return;
if (!frame) {
obs_source_output_video_internal(source, NULL);
return;
}
struct obs_source_frame new_frame = {0};
enum video_range_type range =
resolve_video_range(frame->format, frame->range);
// 拷贝该视频帧
for (size_t i = 0; i < MAX_AV_PLANES; i++) {
new_frame.data[i] = frame->data[i];
new_frame.linesize[i] = frame->linesize[i];
}
new_frame.width = frame->width;
new_frame.height = frame->height;
new_frame.timestamp = frame->timestamp;
new_frame.format = frame->format;
new_frame.full_range = range == VIDEO_RANGE_FULL;
new_frame.max_luminance = 0;
new_frame.flip = frame->flip;
new_frame.flags = frame->flags;
new_frame.trc = frame->trc;
memcpy(&new_frame.color_matrix, &frame->color_matrix,
sizeof(frame->color_matrix));
memcpy(&new_frame.color_range_min, &frame->color_range_min,
sizeof(frame->color_range_min));
memcpy(&new_frame.color_range_max, &frame->color_range_max,
sizeof(frame->color_range_max));
//放置到队列
obs_source_output_video_internal(source, &new_frame);
}
static void
obs_source_output_video_internal(obs_source_t *source,
const struct obs_source_frame *frame)
{
if (!obs_source_valid(source, "obs_source_output_video"))
return;
if (!frame) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&source->async_mutex);
source->async_active = false;
source->last_frame_ts = 0;
free_async_cache(source);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&source->async_mutex);
return;
}
struct obs_source_frame *output = cache_video(source, frame);
/* ------------------------------------------- */
pthread_mutex_lock(&source->async_mutex);
if (output) {
if (os_atomic_dec_long(&output->refs) == 0) {
obs_source_frame_destroy(output);
output = NULL;
} else {
//将frame 放置到 async_frames中
da_push_back(source->async_frames, &output);
source->async_active = true;
}
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&source->async_mutex);
}渲染
在graphics thread中obs_graphics_thread_loop
tick_sources
在 tick_sources 中 循环调用所有source , obs_source_video_tick中获取视频frame,等待渲染使用
tick_sources
->obs_source_video_tick
->async_tick


static void async_tick(obs_source_t *source)
{
uint64_t sys_time = obs->video.video_time;
pthread_mutex_lock(&source->async_mutex);
if (deinterlacing_enabled(source)) {
deinterlace_process_last_frame(source, sys_time);
} else {
if (source->cur_async_frame) {
remove_async_frame(source, source->cur_async_frame);
source->cur_async_frame = NULL;
}
source->cur_async_frame = get_closest_frame(source, sys_time);
}
source->last_sys_timestamp = sys_time;
if (deinterlacing_enabled(source))
filter_frame(source, &source->prev_async_frame);
filter_frame(source, &source->cur_async_frame);
if (source->cur_async_frame)
source->async_update_texture =
set_async_texture_size(source, source->cur_async_frame);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&source->async_mutex);
}

output_frames

render_displays
将数据渲染到UI
遍历每一个UI层的display
static inline void render_displays(void)
{
struct obs_display *display;
if (!obs->data.valid)
return;
gs_enter_context(obs->video.graphics);
/* render extra displays/swaps */
pthread_mutex_lock(&obs->data.displays_mutex);
display = obs->data.first_display;
while (display) {
render_display(display);
display = display->next;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&obs->data.displays_mutex);
gs_leave_context();
}
录屏采集
obs_graphics_thread_loop(obs_graphics_context * context)
tick_sources
tick_sources(unsigned __int64 cur_time, unsigned __int64 last_time)
obs_source_video_tick(obs_source * source, float seconds)
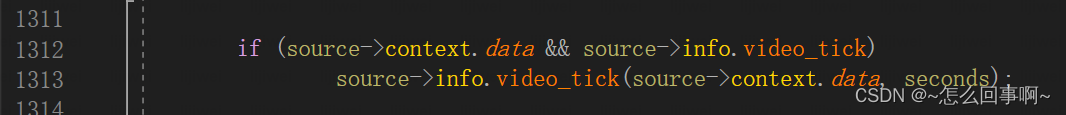
video_tick 进行数据采集,采集的数据放到了source->context.data中,数据读取到后进行渲染
video_tick 在每个插件对应的结构体中进行初始化,例如window-capture 屏幕捕获
struct obs_source_info duplicator_capture_info = {
.id = "monitor_capture",
.type = OBS_SOURCE_TYPE_INPUT,
.output_flags = OBS_SOURCE_VIDEO | OBS_SOURCE_CUSTOM_DRAW |
OBS_SOURCE_DO_NOT_DUPLICATE | OBS_SOURCE_SRGB,
.get_name = duplicator_capture_getname,
.create = duplicator_capture_create,
.destroy = duplicator_capture_destroy,
.video_render = duplicator_capture_render,
.video_tick = duplicator_capture_tick,
.update = duplicator_capture_update,
.get_width = duplicator_capture_width,
.get_height = duplicator_capture_height,
.get_defaults = duplicator_capture_defaults,
.get_properties = duplicator_capture_properties,
.icon_type = OBS_ICON_TYPE_DESKTOP_CAPTURE,
.video_get_color_space = duplicator_capture_get_color_space,
};
source->info.video_tick 即

duplicator_capture_tick 即屏幕采集
在 duplicator_capture_tick 中会调用

其中 capture即
struct duplicator_capture {
obs_source_t *source;
pthread_mutex_t update_mutex;
char monitor_id[128];
char id[128];
char alt_id[128];
char monitor_name[64];
enum display_capture_method method;
bool reset_wgc;
HMONITOR handle;
bool capture_cursor;
bool force_sdr;
bool showing;
LONG logged_width;
LONG logged_height;
long x;
long y;
int rot;
uint32_t width;
uint32_t height;
gs_duplicator_t *duplicator;
float reset_timeout;
struct cursor_data cursor_data;
void *winrt_module;
struct winrt_exports exports;
struct winrt_capture *capture_winrt;
};duplicator即
struct gs_duplicator : gs_obj {
ComPtr<IDXGIOutputDuplication> duplicator;
gs_texture_2d *texture;
bool hdr = false;
enum gs_color_space color_space = GS_CS_SRGB;
float sdr_white_nits = 80.f;
int idx;
long refs;
bool updated;
void Start();
inline void Release() { duplicator.Release(); }
gs_duplicator(gs_device_t *device, int monitor_idx);
~gs_duplicator();
};
gs_duplicator_update_frame 中:
hr = res->QueryInterface(__uuidof(ID3D11Texture2D),
(void **)tex.Assign());
这一步调用dx查询接口,将屏幕帧写入tex
copy_texture(d, tex)
//copy材质到d->duplicator->texture因为obs用的都是directX或openGL 的texture来存储data数据,这样做的好处是copy和渲染都直接在显存操作,避免了内存和显存交换数据进行的效率损耗
对应的获取可以用这个接口,从显存map地址可供cpu访问
bool gs_texture_map(gs_texture_t *tex, uint8_t **ptr, uint32_t *linesize)
{
HRESULT hr;
if (tex->type != GS_TEXTURE_2D)
return false;
gs_texture_2d *tex2d = static_cast<gs_texture_2d *>(tex);
D3D11_MAPPED_SUBRESOURCE map;
hr = tex2d->device->context->Map(tex2d->texture, 0,
D3D11_MAP_WRITE_DISCARD, 0, &map);
if (FAILED(hr))
return false;
*ptr = (uint8_t *)map.pData;
*linesize = map.RowPitch;
return true;
}output_frames

中调用

即 static void duplicator_capture_render(void *data, gs_effect_t *unused) 数据传送到 opengl 或者d3d中进行处理,显示
当需要推流或录制时:会调用到
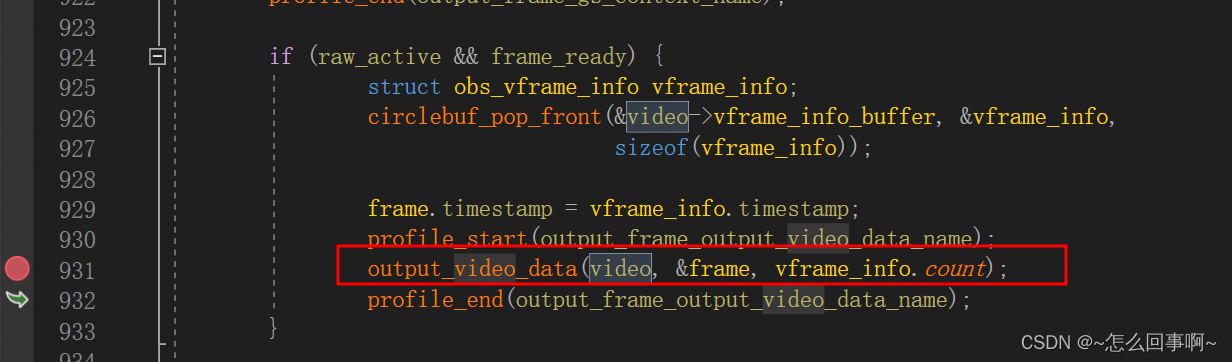
output_video_data 中:
os_sem_post通知video_thread线程进行编码
output_video_data告知video_thread新数据到来。
video_thread线程中的流程:
Step1: 等到数据到来,最终调用receive_video函数进行编码;
Step2: receive_video中调用do_encode对数据进行编码;
Step3: 然后在do_encode中还调用send_packet对数据执行发送
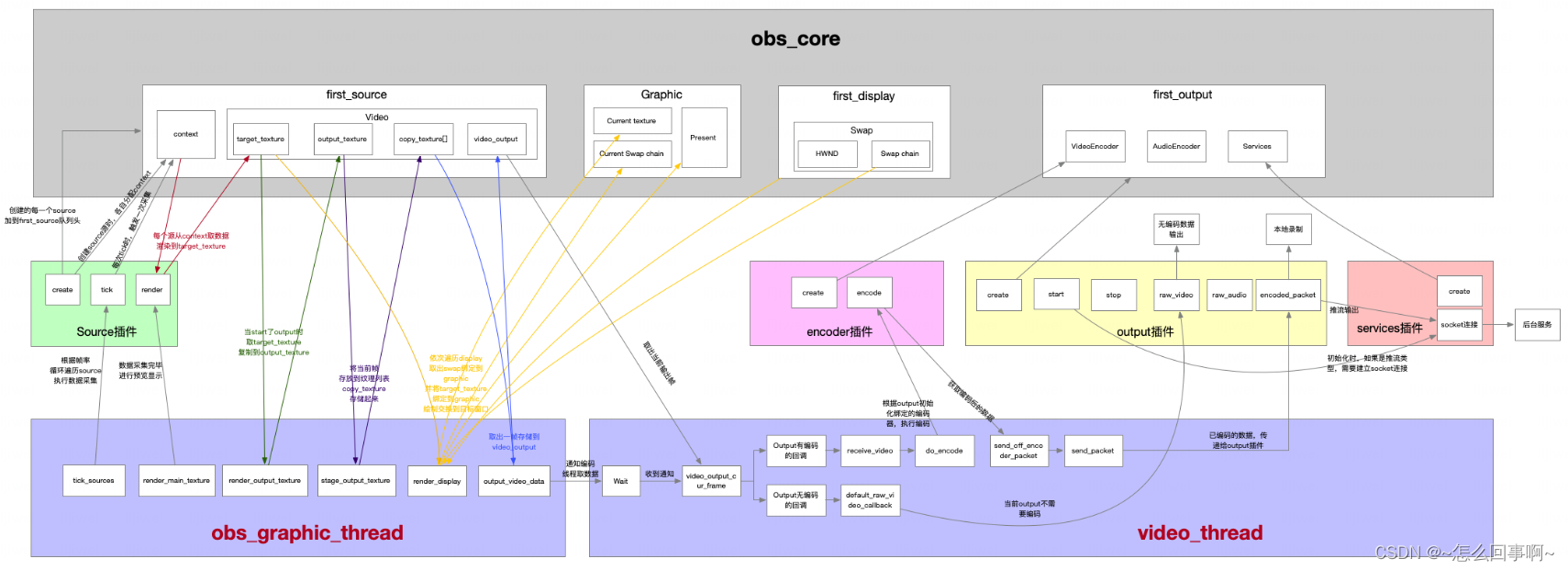
视频显示和视频编码后输出流程图



























 2379
2379

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








