题目描述
You are switching from computer science to agriculture and your new job involves growing sunflowers in an underground greenhouse. The greenhouse contains n sunflower plants arranged in a straight line and numbered with integers 1 through n, from left to right. Two lamps provide the light and heat the sunflowers need to grow: the lamp A is positioned at the left end, while the lamp B is positioned at the right end of the line.
Every day exactly one of the lamps is on, causing all of the sunflowers to turn towards the light and some of them to grow. The sunflower will grow if and only if the sunflower directly in front of it (towards the light) is higher. The growth is continuous with a uniform rate of exactly 1 centimeter per day. Notice that, when a sunflower starts to grow, it may cause the sunflower directly behind it to start to grow instantaneously.
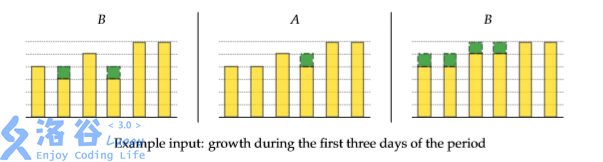
You are given initial heights of the sunflowers and the lamp schedule for the following m day period, find the final heights of all the sunflowers.
输入格式
The first line contains two integers n and m (1≤n, m≤300000) – the number of sunflowers and the number of days in the period. The following line contains n integers h1,h2,...,hn (1≤ hk ≤10^9109) – the initial heights (in centimeters) of the sunflowers, from left to right.
The following line contains a string consisting of exactly m characters A or B – the lamp schedule starting from the first day of the period.
输出格式
Output a single line containing n integers – the final heights of the sunflowers, from left to right.
题意翻译
有两盏灯在最左边和最右边。有 nn 盏向日葵在中间。
每一天都一定会有一个灯开着。向日葵仅仅当它前面的(朝向灯的方向)向日葵比它高时它才会成长,成长速度为 11。注意,当一个向日葵开始成长时,它还可能使得在它后面的向日葵瞬间成长。
给你每株向日葵的高度,还有每天开灯的时间表,求出最后所有的向日葵的高度。
n,m≤3×10 5次方,h≤109。
输入输出样例
输入 #1复制
6 5 4 3 5 3 6 6 BABAA
输出 #1复制
5 5 6 6 6 6
说明/提示
Central Europe Regional Contest 2015 Problem G
题解
提供一个 O(n\log n)O(nlogn) 的做法。
可以发现向日葵的长高一定是一段一段的,这启示我们使用差分。
考虑把原数组 aa 差分成数组 cc,即 c_x=c_x-c_{x-1}cx=cx−cx−1 且 cc 下标的范围是 2\sim n2∼n。显然差分数组为 00 的地方可以合并,因为前后相等的时候,生长都是同时的。所以下面讨论的是 cc 数组中没有 00 的情况。
对于操作 A,所有 cc 数组中当前位置小于 00 的地方 aa 数组都会加一(即一个数小于前面的数,aa 数组就会加一),考虑这对差分数组 cc 的影响。如果 c_x>0cx>0,那么 a_xax 不会改变,而如果 c_{x-1}<0cx−1<0,那么 a_{x-1}ax−1 会加一,所以 c_xcx 要减一。如果 c_x<0cx<0,那么 a_xax 会加一,而如果 c_{x-1}>0cx−1>0,那么 a_{x-1}ax−1 不会改变,所以 c_xcx 要加一。
对于操作 B,所以 cc 数组中后一个位置大于 00 的地方 aa 数组都会加一(即一个数小于后面的数,aa 数组就会加一),同样的,考虑其对差分数组 cc 的影响。如果 c_{x+1}>0cx+1>0,那么 a_{x}ax 会加一,而如果 c_{x+2}<0cx+2<0,那么 a_{x+1}ax+1 不会变,所以 c_{x+1}cx+1 会减一。如果 c_{x+1} <0cx+1<0,那么 a_{x+1}ax+1 不会变,而如果 c_{x+2}>0cx+2>0,那么 a_{x+1}ax+1 会加一,所以 c_{x+1}cx+1 会加一。
从上面的推导可以发现,所有 cc 会发生改变的地方都是前面或者后面的 cc 的正负性和当前不同,所以考虑把所有极长的符号相同的 cc 看成一段。
那么对于操作 A,就是把所有正数段的最左边的数减一,所有负数段的最左边的数加一,特别的,如果第一段是正数段,那么它不需要减一。
同样的,对于操作 B,就是把所有正数段的最右边的数减一,所有负数段的最右边的数加一,特别的,如果最后一段是负数段,那么它不需要加一。
如果某个 c_xcx 变成了 00,那么就把它从这个段里面删掉,如果这个段此时被删空了,那么它就会造成其前后的段合并,这时候直接合并即可。
直接用可删堆分别维护大小大于等于 22 和大小等于 11 的段,对于每次操作,直接打一个全局标记,然后如果有 c_x=0cx=0 的 xx 就进行删除处理即可。
一个位置的 cc 只可能等于 00 一次,所以它只会进堆一次,出堆一次,造成前后合并一次,故总复杂度 O(n\log n)O(nlogn)。
得到最后的差分数组 cc 后,考虑还原数组 aa。不难发现最大值是不会超过原序列的最大值的,找到原序列的最大值及其位置之后就可以直接还原了。
代码如下:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define debug(...) fprintf(stderr, __VA_ARGS__)
#define RI register int
typedef long long LL;
#define FILEIO(name) freopen(name".in", "r", stdin), freopen(name".out", "w", stdout);
using namespace std;
int const MAXN = 3e5 + 5;
int a[MAXN], b[MAXN];
int cf[MAXN];
int nxt[MAXN], pre[MAXN];
struct Node {
int val, id;
bool operator < (const Node &A) const { return val ^ A.val ? val > A.val : id > A.id; }
bool operator == (const Node &A) const { return val == A.val && id == A.id; }
};
struct DeleteHeap {
priority_queue <Node> I, O;
inline void Flush() {
while (!O.empty() && I.top() == O.top())
I.pop(), O.pop(); }
inline void insert(Node x) { /*cout << this << " insert " << x.id << " " << x.val << endl;*/ I.push(x); }
inline void erase (Node x) { /*cout << this << " erase " << x.id << " " << x.val << endl;*/ O.push(x); }
inline bool empty() { Flush(); return I.empty(); }
inline Node top() { Flush(); return I.top(); }
} Head, Tail, HT; // 前两个维护大小大于等于 2 的段,最后一个维护大小为 1 的段。
int tagh, tagt, taght; // 全局标记
int size[MAXN], L[MAXN], R[MAXN]; // 段大小,左右端点
int ans[MAXN];
// 找每个段的左右端点
int FindL(int x) { return x == L[x] ? x : L[x] = FindL(L[x]); }
int FindR(int x) { return x == R[x] ? x : R[x] = FindR(R[x]); }
void Init(int n) { // 求得差分数组,以及初始化。
for (RI i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
cf[i] = a[i] - a[i - 1], b[i] = (cf[i] > 0 ? 1 : -1);
for (RI i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
nxt[i] = i + 1, pre[i + 1] = i;
for (RI i = 2; i <= n; ++i)
if (cf[i] == 0) {
nxt[pre[i]] = nxt[i];
pre[nxt[i]] = pre[i];
}
int las = nxt[1], cnt = 0;
for (RI i = nxt[1]; i != n + 1; i = nxt[i], ++cnt)
if (b[i] != b[las]) {
for (RI j = las; j != i; j = nxt[j])
L[j] = las, R[j] = pre[i];
size[las] = cnt;
if (size[las] >= 2) {
Head.insert((Node){b[las] * cf[las], las});
Tail.insert((Node){b[pre[i]] * cf[pre[i]], pre[i]});
}
else
HT.insert((Node){b[las] * cf[las], las});
las = i, cnt = 0;
}
for (RI j = las; j; j = nxt[j])
L[j] = las, R[j] = pre[n + 1];
size[las] = cnt;
if (size[las] >= 2) {
Head.insert((Node){b[las] * cf[las], las});
Tail.insert((Node){b[pre[n + 1]] * cf[pre[n + 1]], pre[n + 1]});
}
else
HT.insert((Node){b[las] * cf[las], las});
}
inline void Del(int x) { // 删除一个段
int sz = size[FindL(x)];
if (sz >= 2) {
int l = FindL(x), r = FindR(x);
Head.erase((Node){b[l] * cf[l], l});
Tail.erase((Node){b[r] * cf[r], r});
cf[l] -= b[l] * tagh;
cf[r] -= b[r] * tagt;
}
else {
int l = FindL(x);
HT.erase((Node){b[l] * cf[l], l});
cf[l] -= b[l] * taght;
}
}
inline void Ins(int x) { // 加入一个段
int sz = size[FindL(x)];
if (sz >= 2) {
int l = FindL(x), r = FindR(x);
cf[l] += b[l] * tagh;
cf[r] += b[r] * tagt;
Head.insert((Node){b[l] * cf[l], l});
Tail.insert((Node){b[r] * cf[r], r});
}
else {
int l = FindL(x);
cf[l] += b[l] * taght;
HT.insert((Node){b[l] * cf[l], l});
}
}
void Merge(int lc, int rc) { // 合并两个段
int szr = size[FindL(rc)];
int r = FindR(lc);
int l = FindL(rc);
R[r] = FindR(rc);
L[l] = FindL(lc);
size[FindL(lc)] += szr;
Ins(lc);
}
int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
FILEIO("a");
#endif
int n, m; scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (RI i = 1; i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d", a + i);
Init(n);
while (m--) {
char ch = getchar();
while (ch != 'A' && ch != 'B') ch = getchar();
if (ch == 'A') {
++tagh, ++taght;
if (b[nxt[1]] == 1) { // 上文说的特判
Del(nxt[1]);
cf[FindL(nxt[1])] += b[FindL(nxt[1])];
Ins(nxt[1]);
}
}
else {
++tagt, ++taght;
if (b[pre[n + 1]] == -1) { // 上文说的特判
Del(pre[n + 1]);
cf[FindR(pre[n + 1])] += b[FindR(pre[n + 1])];
Ins(pre[n + 1]);
}
}
while (666) { // 删除 c[x]=0 的位置
int flag = 1;
while (!HT.empty() && HT.top().val <= taght) {
flag = 0;
Node t = HT.top();
Del(t.id);
int P = pre[t.id], N = nxt[t.id];
nxt[P] = N, pre[N] = P;
if (P != 1 && N != n + 1) {
Del(P), Del(N);
Merge(P, N);
}
}
while (!Head.empty() && Head.top().val <= tagh) {
flag = 0;
Node t = Head.top();// Head.erase(t);
Del(t.id);
int l = FindL(t.id);
L[l] = L[nxt[l]] = nxt[l];
size[nxt[l]] = size[l] - 1;
nxt[pre[l]] = nxt[l];
pre[nxt[l]] = pre[l];
Ins(t.id);
}
while (!Tail.empty() && Tail.top().val <= tagt) {
flag = 0;
Node t = Tail.top();// Tail.erase(t);
Del(t.id);
int l = FindL(t.id), r = FindR(t.id);
R[r] = R[pre[r]] = pre[r];
size[l] = size[l] - 1;
nxt[pre[r]] = nxt[r];
pre[nxt[r]] = pre[r];
Ins(t.id);
}
if (flag) break;
}
}
while (!Head.empty()) Del(Head.top().id);
while (!Tail.empty()) Del(Tail.top().id);
while (!HT.empty()) Del(HT.top().id);
int mx = -1, pos = -1;
for (RI i = 1; i <= n; ++i) // 还原 a 数组
if (a[i] > mx)
mx = a[i], pos = i;
ans[pos] = a[pos];
for (RI i = pos + 1; i <= n; ++i)
ans[i] = ans[i - 1] + cf[i];
for (RI i = pos - 1; i >= 1; --i)
ans[i] = ans[i + 1] - cf[i + 1];
for (RI i = 1; i <= n; ++i)
printf("%d ", ans[i]);
cerr << (double)(clock()) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << " s " << endl;
return 0;
}
// created by Daniel yuan
/*
________
/ \
/ / \ \
/ / \ \
\ /
\ ______ /
\________/
*/




















 249
249

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








